17 Weird And Incredible Frog Facts

Frogs are fascinating creatures that come in more shapes, sizes, and colors than you’d think! From their unique habitats to their extraordinary abilities, these amphibians have captivated the minds of scientists and animal lovers alike.
Join us as we explore some of the most unusual and astonishing facts about frogs, spanning their surprising diets to their remarkable survival tactics.
Whether you’re a seasoned frog enthusiast or just curious about these quirky critters, you’ll find plenty of intriguing tidbits in this list of weird and incredible frog facts.
1. Glass Frog Transparency
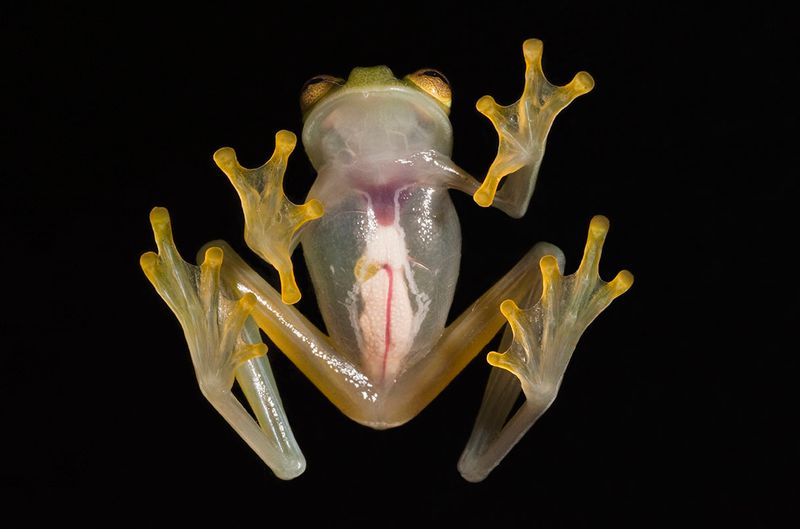
The glass frog is an anomaly in the animal kingdom with its strikingly transparent skin. This fascinating creature, mostly found in Central and South America, has skin so translucent that its internal organs are visible.
Such transparency provides an excellent camouflage against predators, as it blends seamlessly with the leaves of tropical rainforests. This unique feature not only serves as a defense mechanism but also offers scientists a rare opportunity to study its physiology without dissection.
The heart, liver, and digestive tract are easily observable, and researchers can monitor these organs’ functions in a living animal. Glass frogs are a testament to nature’s ingenuity, highlighting how evolution can lead to extraordinary adaptations.
Their transparent skin acts as both a shield and a window into their world, making them a subject of endless fascination. With their unique biology, these amphibians remind us of the incredible diversity found in the animal kingdom.
2. Tungara Frog Mating Calls
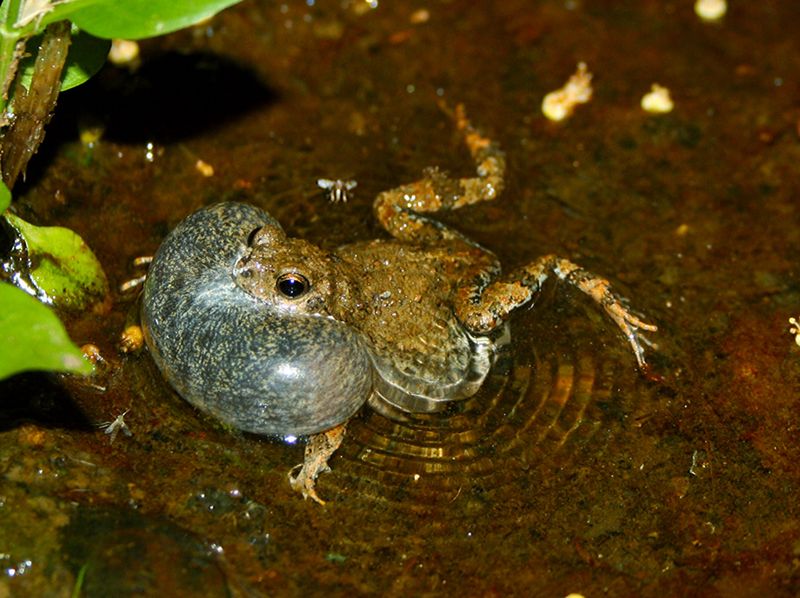

Tungara frogs possess one of nature’s most captivating mating rituals. Native to Central and South America, these frogs are known for their distinctive calls, which males use to attract females.
The calls are complex, consisting of a series of whines followed by chucks. Interestingly, while the elaborate calls may attract more female attention, they also increase the risk of attracting predators, such as bats.
The frogs must strike a delicate balance, making the calls intricate enough to entice a mate but not so conspicuous as to draw unwanted attention. This fascinating behavior demonstrates the intricate dynamics of natural selection, where reproductive success may come with increased risks.
The tungara frog’s calls are a symphony of survival and reproduction, illustrating the complex interplay between attraction and danger in the animal kingdom. These calls provide a glimpse into the evolutionary strategies that have shaped these amphibians’ natural history.
3. African Bullfrog Parental Care
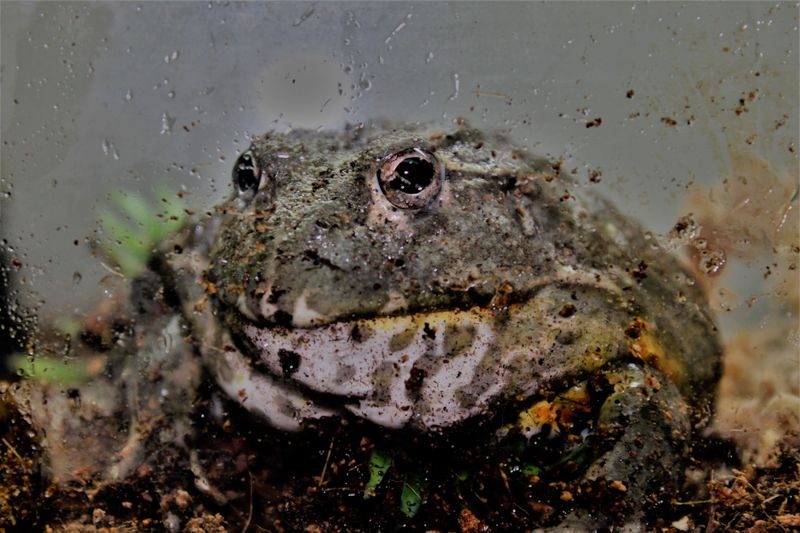

Among frogs, the African bullfrog stands out for its remarkable parental care. Unlike most amphibians, male African bullfrogs are dedicated fathers, going to great lengths to ensure the survival of their offspring.
These large, robust frogs can be found across sub-Saharan Africa, inhabiting savannas and grasslands. During the breeding season, the male guards the eggs laid by the female in shallow water bodies. Once the eggs hatch into tadpoles, the father’s duties intensify.
He actively protects them from predators and even digs channels to connect drying ponds to larger water bodies, ensuring the tadpoles’ survival. This level of parental investment is uncommon in the amphibian world and highlights the diversity of reproductive strategies among frogs.
The African bullfrog’s dedication to its young showcases the lengths nature’s creatures will go to ensure the continuity of their lineage, providing a fascinating example of animal behavior.
4. Surinam Toad Reproduction
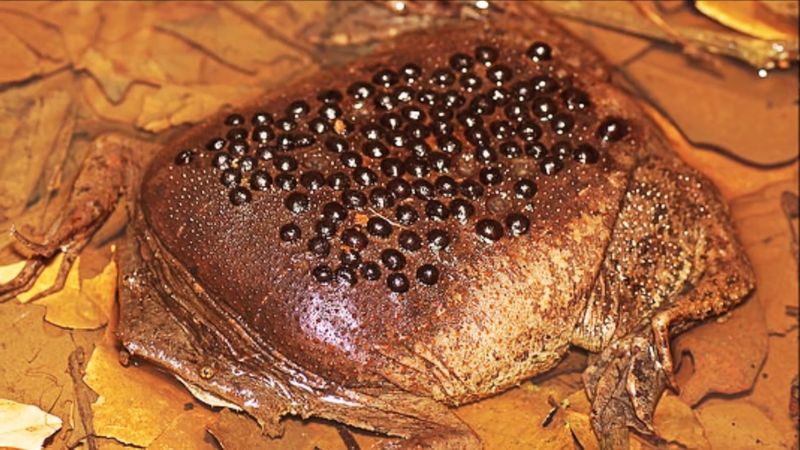

The Surinam toad exhibits one of the most bizarre reproductive methods in the animal kingdom. Native to the waterways of South America, this toad’s breeding process involves the female carrying fertilized eggs embedded in her back.
After mating, the male helps the female deposit the eggs onto her skin, where they become embedded. Over time, the skin grows over the eggs, creating a protective matrix in which they develop. This bizarre method provides a safer environment for the eggs, protecting them from aquatic predators.
Once fully developed, the young toads emerge from the mother’s back, having undergone their embryonic development in a unique setting.
The Surinam toad’s reproductive strategy is a testament to the diversity and adaptability of amphibians, illustrating the myriad ways life has evolved to ensure survival in different environments.
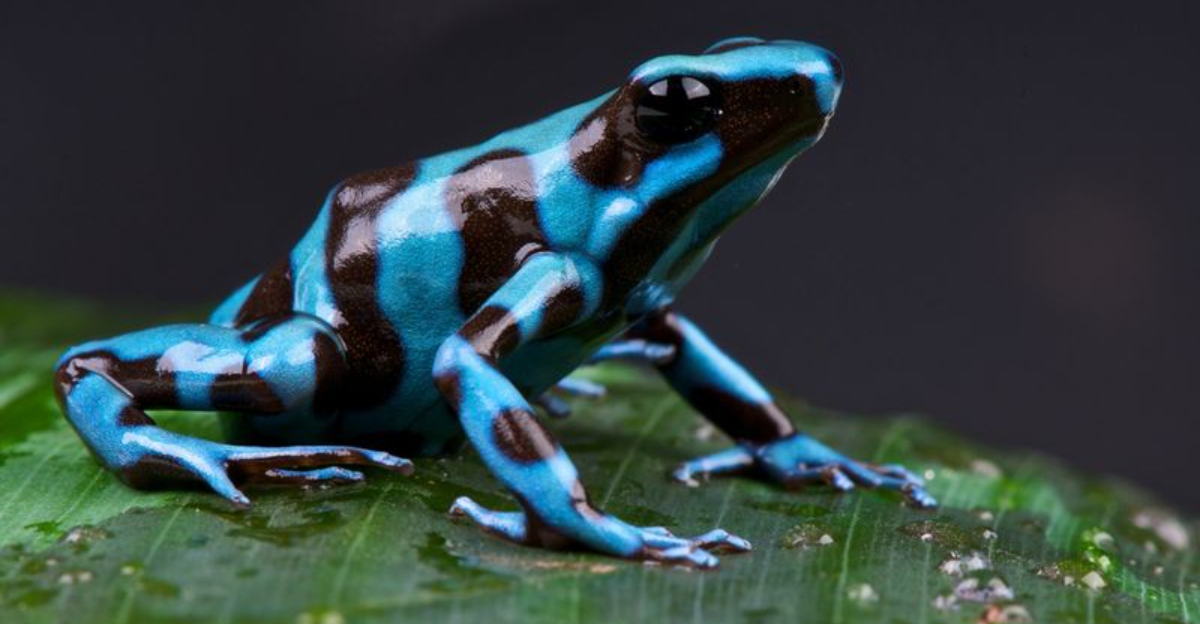
5. Poison Dart Frog Colors And Toxicity
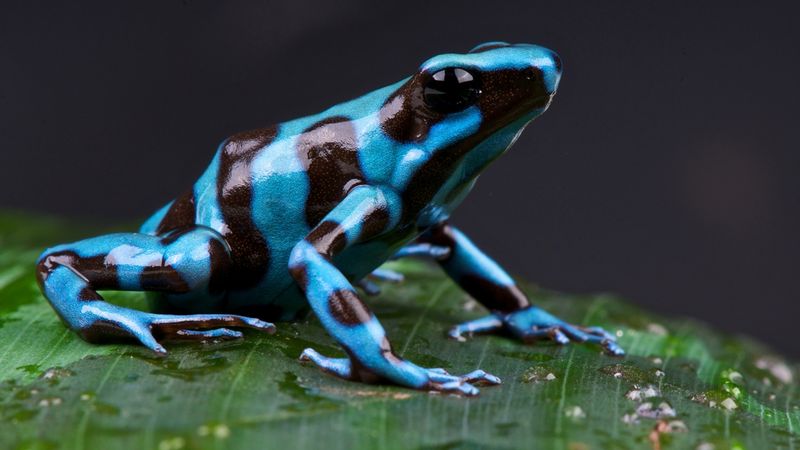

Poison dart frogs are as beautiful as they are deadly. Found primarily in Central and South America, these small, vibrantly colored amphibians are known for their toxicity.
Their bright colors, ranging from electric blue to fiery red, serve as a warning to potential predators about their poisonous nature. The toxins are derived from their diet in the wild, which includes ants and other small insects.
These compounds are potent enough that indigenous peoples have used them to coat blow darts for hunting, giving the frogs their common name.
Interestingly, when kept in captivity and deprived of their natural diet, poison dart frogs lose their toxicity, suggesting a direct link between their diet and their poisonous nature.
These frogs serve as a fascinating example of how diet can influence an animal’s biology, providing valuable insights into evolutionary adaptations.
6. Wood Frog’s Freezing Ability
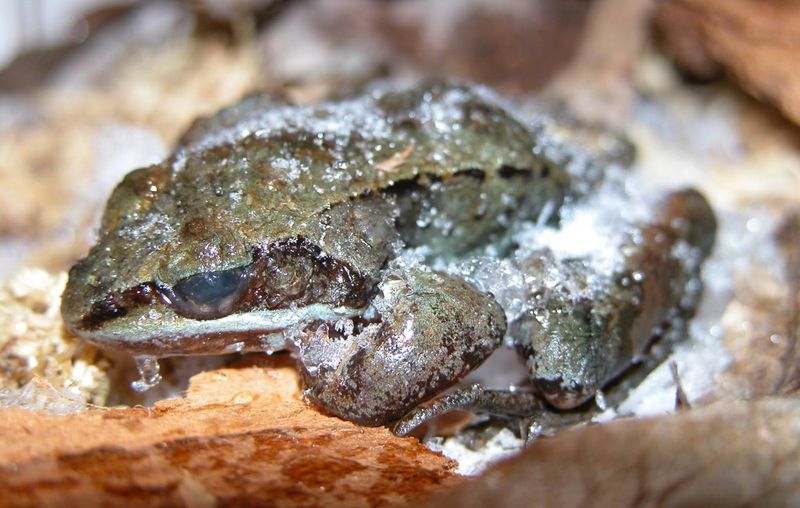

The wood frog is nature’s little ice wizard. Native to North America, it has the astonishing ability to survive freezing temperatures that would be lethal to most other animals.
During the cold winter months, wood frogs enter a state of suspended animation. Their bodies freeze solid, with up to 70% of the water in their bodies turning to ice.
Remarkably, their cells remain intact due to the presence of special cryoprotectants—substances that prevent the formation of ice crystals within the cells. As temperatures rise, the frogs thaw and resume their normal activities, seemingly unaffected by their icy ordeal.
This incredible adaptation allows wood frogs to thrive in environments with harsh winters, showcasing the amazing resilience and adaptability of amphibians.
7. Frog Communication Through Vibrations
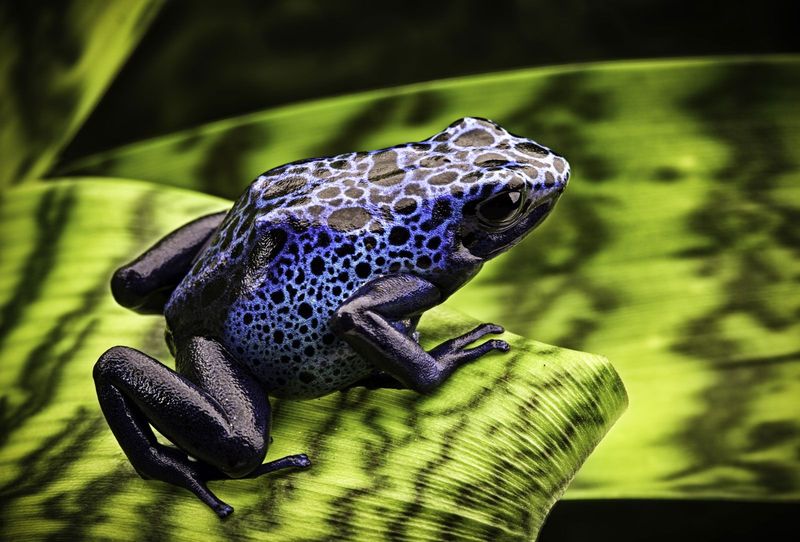

Communication in frogs isn’t limited to just croaks and calls. Some species have developed a sophisticated method of ‘talking’ through vibrations. These vibrations are often used to communicate territorial boundaries or attract mates without making a sound.
This silent mode of communication is particularly advantageous in noisy environments, like dense rainforests, where traditional vocal calls might get lost amidst the cacophony. By transmitting vibrations through the ground or surrounding vegetation, frogs can send clear signals even in the noisiest habitats.
This fascinating adaptation highlights the diversity of communication strategies in the animal kingdom. By ‘speaking’ through vibrations, these frogs demonstrate an innovative way to overcome environmental challenges and ensure their messages are heard.
8. Darwin’s Frog Mouth-Brooding
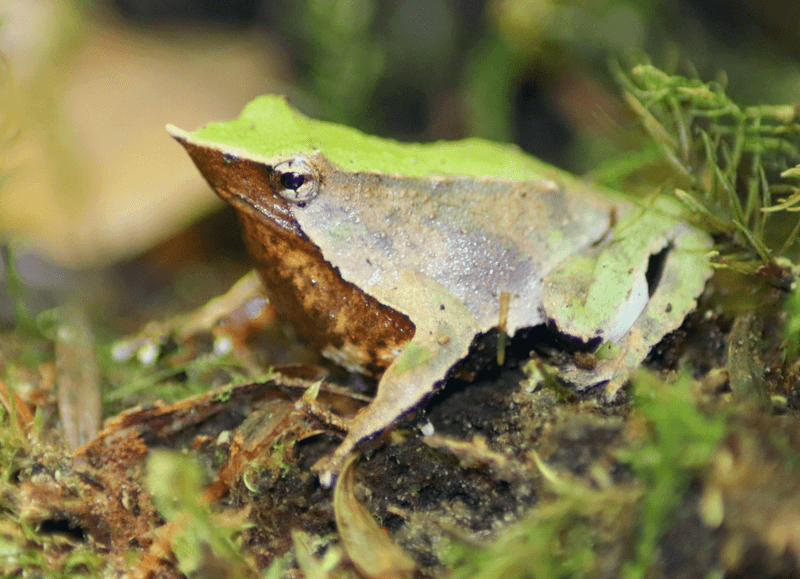

Darwin’s frog is a master of unusual parenting. Found in the forests of Chile and Argentina, this small frog is known for its extraordinary method of caring for its young. The male Darwin’s frog takes on the responsibility of brooding the young within his vocal sac.
After the female lays eggs, the male guards them vigilantly. Once they hatch, he swallows the tadpoles, keeping them safe in his vocal sac until they metamorphose into miniature frogs. This process can take several weeks, during which time the male continues his normal activities.
This unique form of parental care is rare among amphibians and underscores the lengths to which some species will go to protect their offspring. Darwin’s frog provides a remarkable example of adaptation and the varied strategies life employs to ensure survival.
9. Flying Frogs And Their Gliding Skills
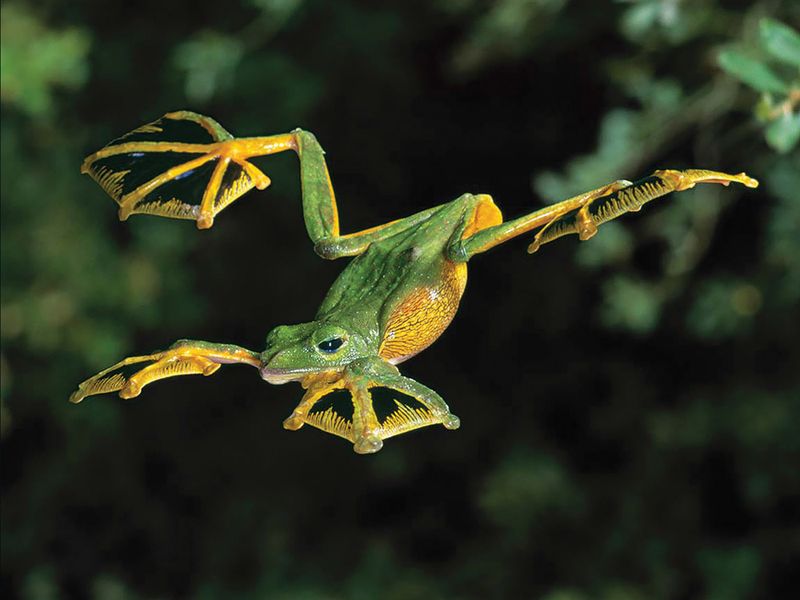

Flying frogs are gravity-defying wonders of the amphibian world. Found in Southeast Asia, these frogs have evolved specialized adaptations that allow them to glide gracefully through the air.
They possess webbed feet and loose skin flaps that act like parachutes, enabling them to leap from tree to tree. This mode of locomotion is not only a thrilling spectacle but also a practical adaptation to avoid ground-dwelling predators and to travel efficiently between feeding and breeding sites.
Gliding allows these frogs to access resources and habitats that would otherwise be unreachable. Flying frogs showcase the inventive ways in which animals adapt to their environments. Their ability to glide seamlessly through the forest canopy is a testament to the power of evolution and the surprises it holds in the natural world.
10. Frogs’ Role In Ecosystem Balance
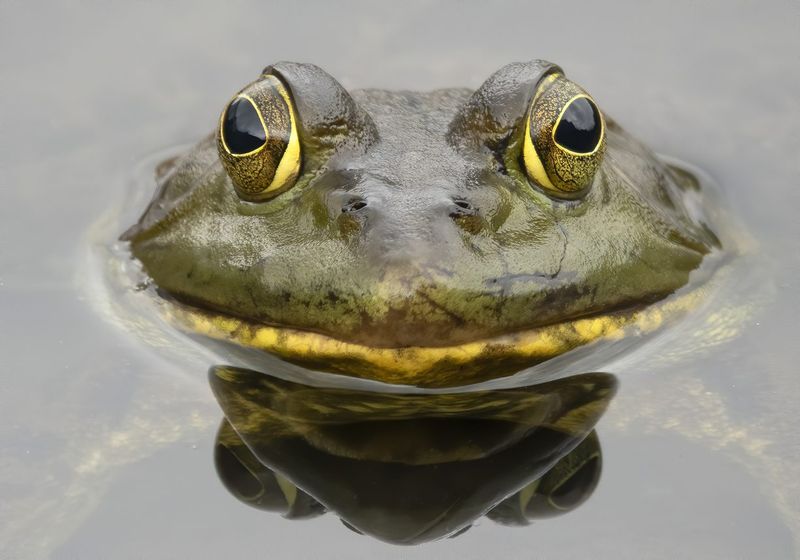

Frogs play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. As both predator and prey, they are integral to many food webs, controlling insect populations and providing food for birds, mammals, and reptiles. Their presence in an ecosystem often indicates a healthy environment.
Amphibians are particularly sensitive to changes in their surroundings, making them excellent bioindicators. A decline in frog populations can signal environmental issues such as pollution, habitat loss, or climate change.
Efforts to conserve frog habitats not only benefit these amphibians but also help preserve entire ecosystems. By ensuring the survival of frogs, we support biodiversity and the delicate balance of nature.
Their role as ecological linchpins underscores the interconnectedness of life on Earth, highlighting the importance of protecting these remarkable creatures.
11. Frog’s Incredible Jumping Ability
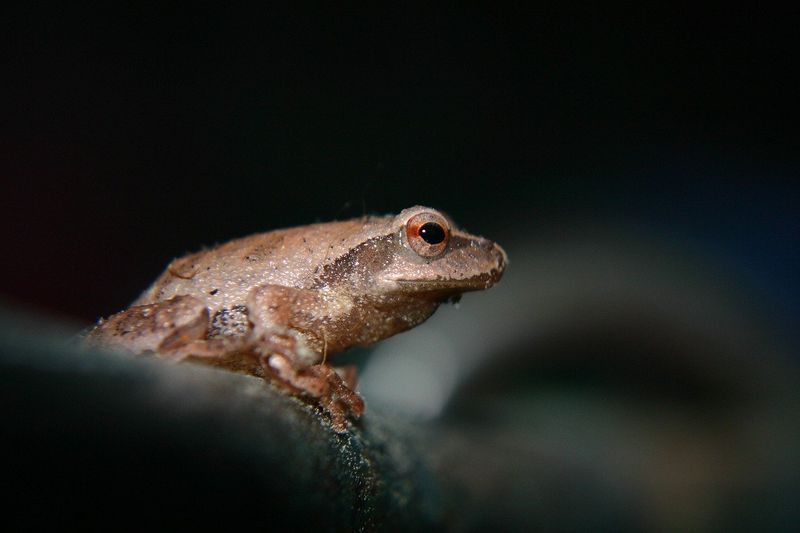

Frogs are renowned for their extraordinary jumping abilities. Their powerful hind legs and specialized muscles allow them to leap great distances, far exceeding their body length. This remarkable skill is crucial for escaping predators and catching prey.
Some species, like the South African sharp-nosed frog, can jump over 40 times their body length in a single bound. This impressive feat is facilitated by unique leg structures and muscle compositions that store and release energy with incredible efficiency.
Jumping is not just a means of locomotion or escape; it is also a display of strength and agility that can deter potential predators. Frogs’ jumping prowess demonstrates the incredible adaptations that have evolved in response to environmental challenges, showcasing nature’s ingenuity.
12. Frogs’ Unique Skin Secretions

Frogs have skin like no other animal, secreting substances that serve various purposes. These secretions can include toxins that deter predators, antimicrobial compounds that protect against infections, and mucus that helps retain moisture.
Some species produce potent toxins used by indigenous people for hunting, while others secrete soothing compounds with potential medical applications. These secretions are a testament to the complex chemistry at play in the natural world.
The multifunctional nature of frog skin highlights the intricate adaptations that have evolved to protect and enhance survival. Their skin serves as a living laboratory of chemical interactions, offering insights into potential new medicines and the wonders of evolution.
13. Frog’s Ability To Change Color
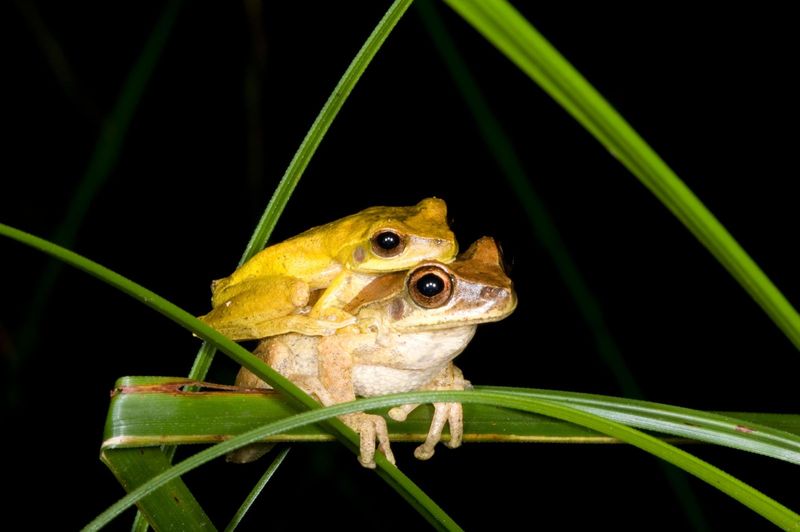

Some frogs possess the remarkable ability to change their skin color. This adaptation serves multiple purposes, from camouflage to communication. By altering their coloration, frogs can blend into their surroundings or signal their mood to other frogs.
Color change is achieved through specialized cells called chromatophores, which expand or contract to alter the skin’s appearance. This dynamic adaptability allows frogs to thrive in diverse environments and avoid predators.
The ability to change color is a powerful tool in the animal kingdom, providing frogs with a versatile means of interaction and survival. It is a vivid demonstration of how evolution equips creatures with the means to navigate a complex world.
14. Frog’s Sensory Adaptations
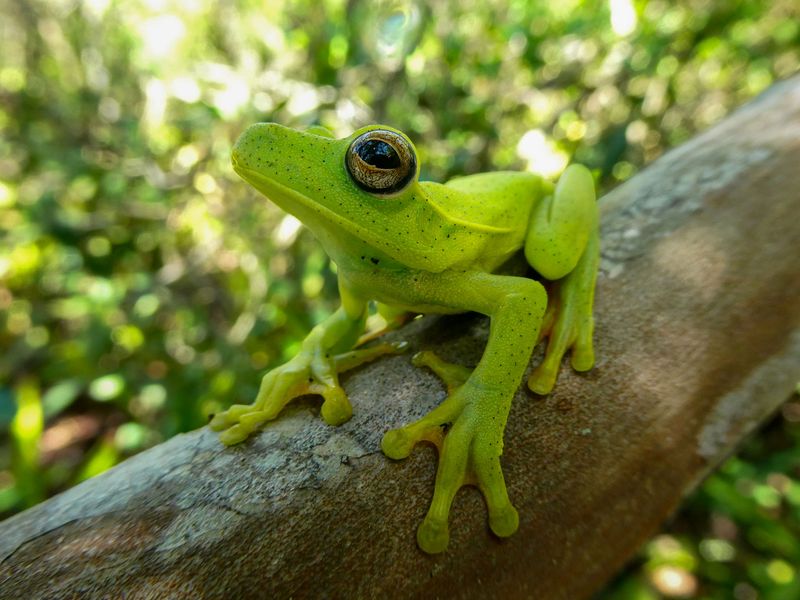

Frogs are equipped with specialized sensory adaptations that help them thrive in their environments. Their large eyes provide a wide field of vision, essential for spotting predators and prey.
Many frogs also have exceptional night vision, enabling them to hunt effectively in low light. Frogs’ eardrums, visible just behind their eyes, are fine-tuned to pick up on the sounds of potential threats or mates.
These sensory adaptations are crucial for survival, allowing frogs to respond quickly to environmental cues. The combination of keen sight and hearing makes frogs formidable hunters and cautious prey.
Their sensory abilities highlight the evolutionary traits that have helped them survive and flourish across diverse habitats.
15. The Gastric-Brooding Frog’s Extinct Mystery
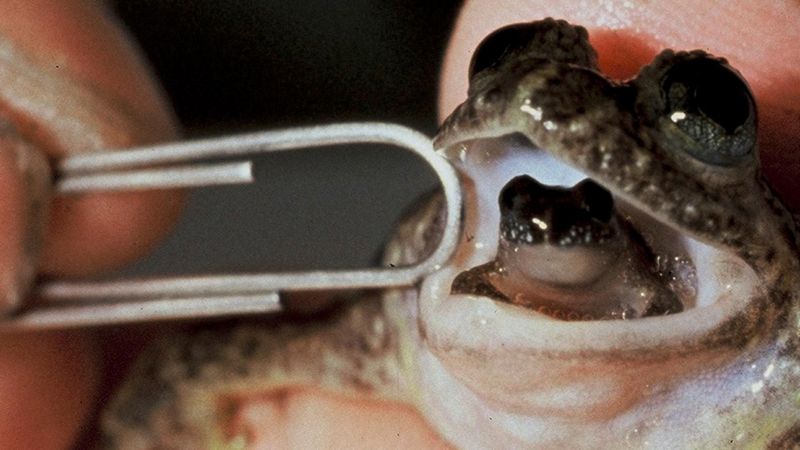
The gastric-brooding frog was an extraordinary species that sadly now exists only in historical records. Native to Australia, this frog had the unique ability to brood its young in its stomach.
Females would swallow fertilized eggs, which developed into tadpoles in their stomachs, eventually emerging as fully-formed frogs. Unfortunately, this remarkable species went extinct in the 1980s, and its ecological role remains a mystery.
The loss of the gastric-brooding frog is a poignant reminder of the fragility of biodiversity and the vital importance of conservation efforts.
The story of the gastric-brooding frog underscores the urgency to protect other unique species that face similar threats today. Its extinction serves as a call to action to preserve the intricate tapestry of life on our planet and prevent the loss of more incredible creatures.
16. Frogs’ Extraordinary Vocal Abilities
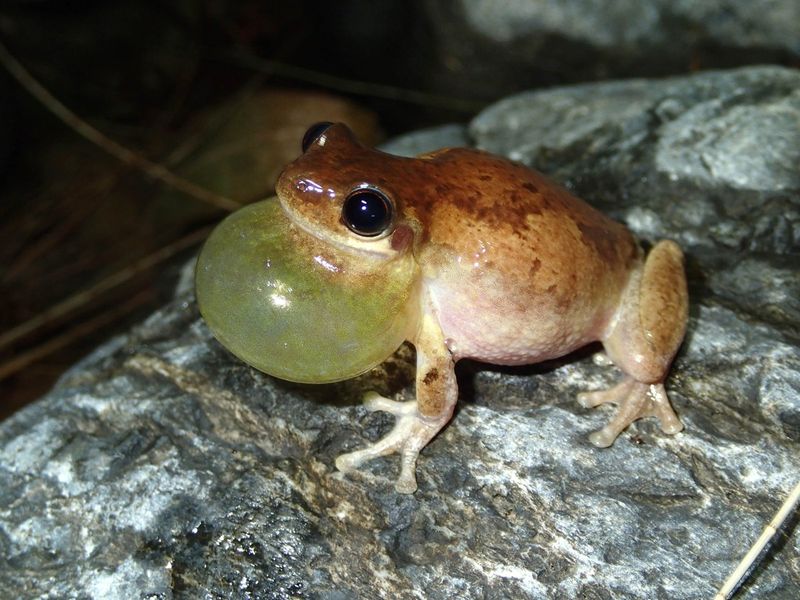

Frogs are known for their vocal prowess, producing a wide range of sounds to communicate with each other. These calls can serve various purposes, from attracting mates to defending territory.
Each species has its own unique call, often distinct enough to be recognized by researchers and enthusiasts. The loudest frog, the male common coquí from Puerto Rico, can produce calls over 90 decibels—equivalent to the sound of a lawn mower.
Such vocalizations can be heard over great distances, ensuring they reach potential mates or rivals. Frogs’ vocal abilities are a testament to the diversity of communication strategies in the animal kingdom. These calls provide a symphony of sounds that enrich natural environments, showcasing the wonders of amphibian communication.
17. Frogs In Mythology And Culture

Frogs hold a special place in cultures and mythologies around the world. In many traditions, frogs are symbols of fertility, transformation, and renewal. The frog’s life cycle, from egg to tadpole to adult, is often seen as a metaphor for transformation and rebirth.
In Egyptian mythology, frogs were associated with the goddess Heqet, a symbol of fertility and childbirth. In Chinese culture, the celestial frog is linked to the moon and represents prosperity and good fortune.
These amphibians’ presence in folklore underscores their significance in human imagination and storytelling. Frogs inspire awe and wonder, bridging the natural and mystical worlds.
Their symbolic roles reflect the deep connections between humans and nature, highlighting the importance of preserving these cultural icons for future generations.






