Shell Shocked: 17 Things You Never Knew About Tortoise Shells
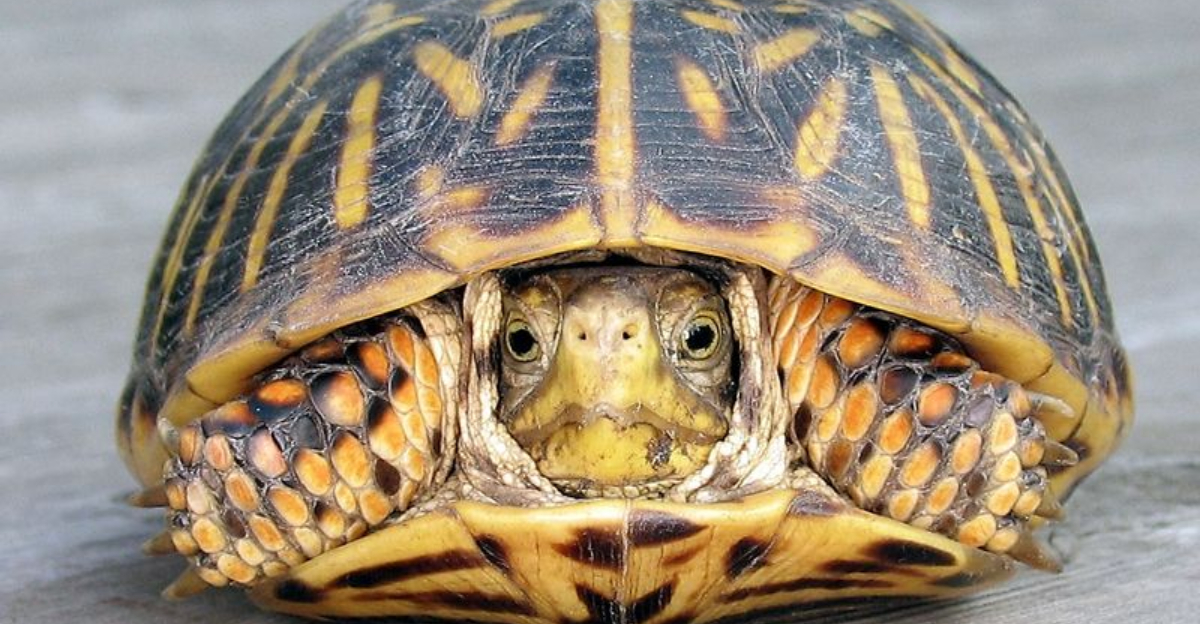

Tortoises might move slow, but their shells are packed with fast facts that’ll blow your mind! These natural suits of armor are more than just tough—they’re full of surprises.
Get ready to crack open the secrets behind one of nature’s coolest built-in accessories.
1. The Role Of Shells In Predator Defense
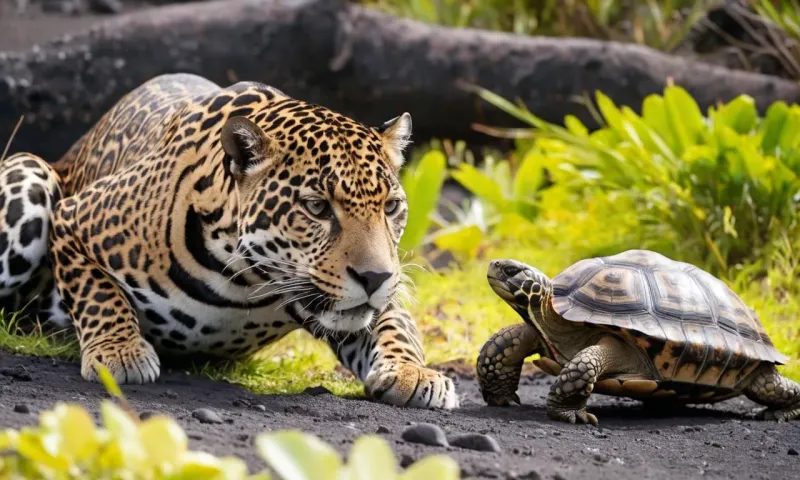

A tortoise’s shell might look bulky, but it’s a carefully crafted blend of protection and movement.
While it adds weight and limits speed, tortoises still manage to move with surprising agility.
Some even have shell shapes tailored for climbing rocky terrain or burrowing into the ground.
Every curve and contour is a response to the challenges of their habitat.
It’s a delicate evolutionary dance—trading speed for safety without missing a step.
2. Impact of Environment on Shell Development
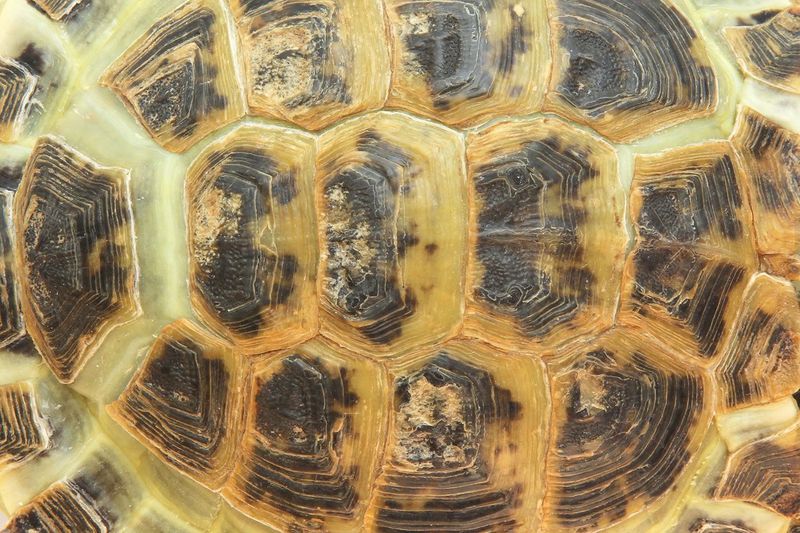

The environment plays a crucial role in shaping a tortoise’s shell. Factors such as humidity, temperature, and available nutrients can influence shell development.
Tortoises in arid regions may develop more robust shells as a defense against predators and harsh conditions. Conversely, those in lush, humid areas might have lighter, more flexible shells.
Studying these variations helps conservationists understand how tortoises adapt to their habitats, shedding light on evolutionary processes.
3. Tortoise Shells And Sensitivity
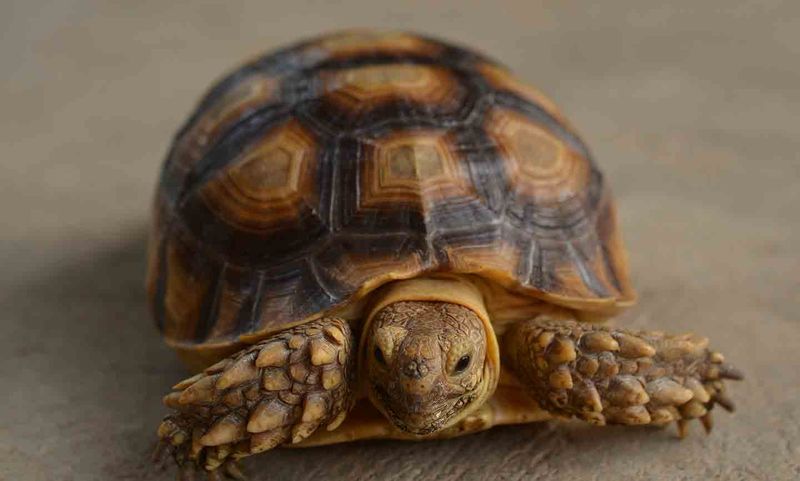

Tortoise shells aren’t just tough shields—they’re full of feeling!
These bony coverings are wired into the tortoise’s nervous system, making them sensitive to touch, pressure, and even pain.
That sensitivity helps tortoises sense danger, respond to their surroundings, and pick up on important environmental cues.
It also comes into play during social interactions—gentle shell nudges can be their way of saying hello.
Because of this, it’s super important to handle them with care; rough touches can actually hurt.
Their shell isn’t just protection—it’s a living, feeling part of them that deserves kindness and respect.
4. Conservation Efforts For Tortoise Shell Protection
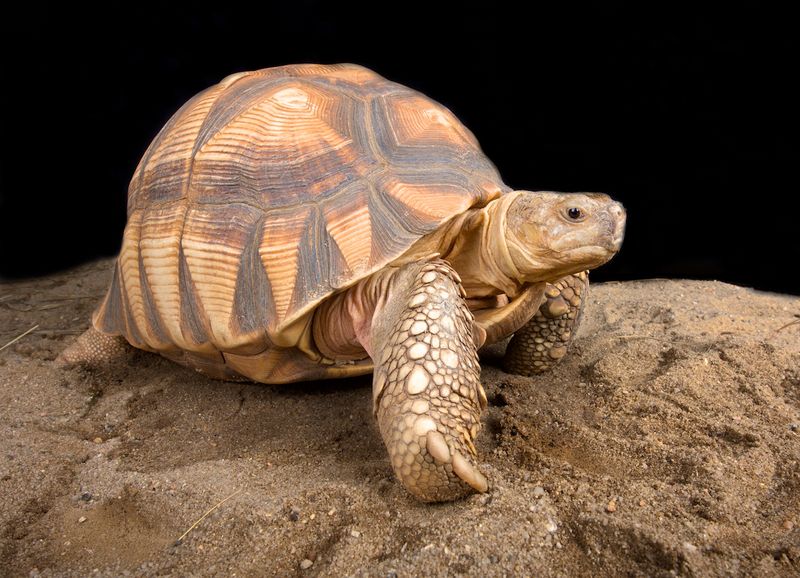

Tortoises and their iconic shells face serious threats—from habitat loss to illegal trade. Human activity has pushed many species toward decline, making conservation more important than ever.
Protected areas, anti-trafficking laws, and public education all play a part in the fight to save them.
Breeding programs and habitat restoration offer hope for long-term survival.
By protecting tortoises, we’re also preserving biodiversity and the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
5. Shell Regeneration And Healing
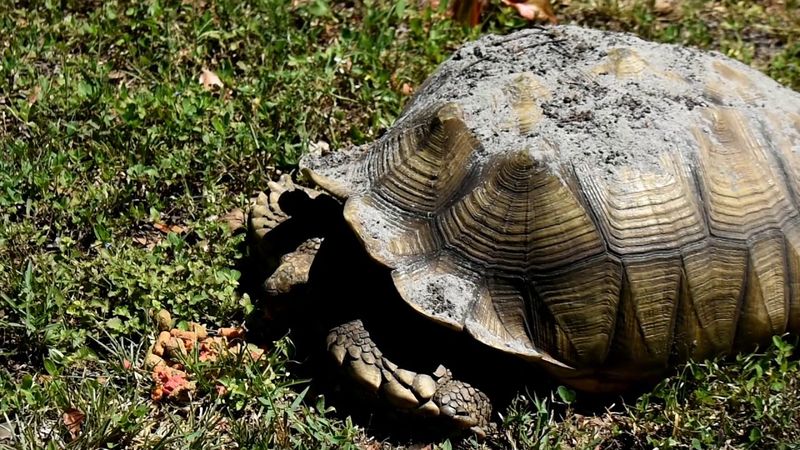

Tortoises have a surprising superpower—the ability to heal their own shells! Small cracks and chips can gradually mend as the shell’s bony layers regenerate over time.
This built-in repair system is a lifesaver in the wild, where bumps, bites, or falls are part of the journey.
But when injuries are severe, they need a helping hand from a vet, sometimes with fiberglass patches or other clever fixes.
It’s just one more reason tortoises are living testaments to resilience and survival.
6. The Role of Shells In Thermoregulation
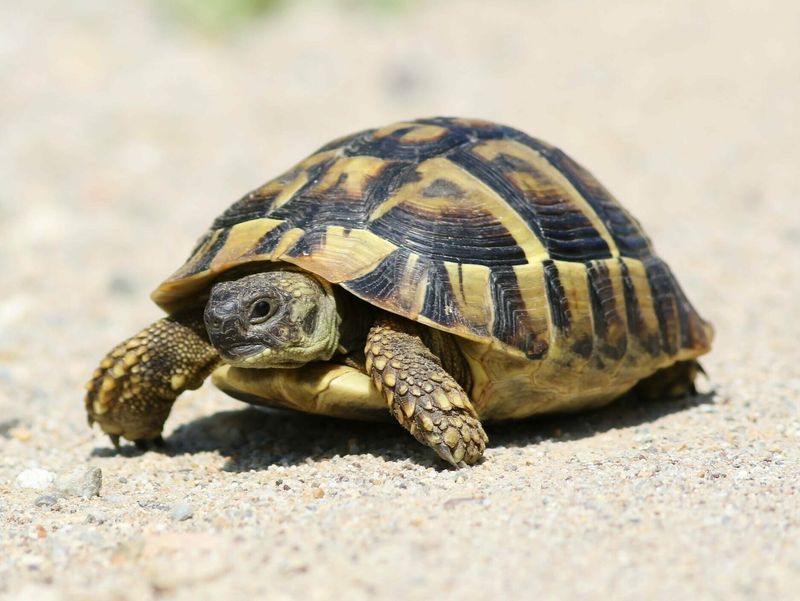

Tortoise shells do more than protect—they help control body temperature too! By basking in the sun, the shell soaks up heat and passes it to the tortoise’s body.
If things get too toasty, the tortoise cools off in the shade, using the shell to release that extra warmth.
Because tortoises rely on their surroundings for heat, this system is key to their survival.
Even the shell’s color plays a part—darker shells heat up faster than lighter ones.
It’s a clever natural thermostat that lets tortoises thrive from hot deserts to lush forests.
7. Shells As Indicators Of Age And Health
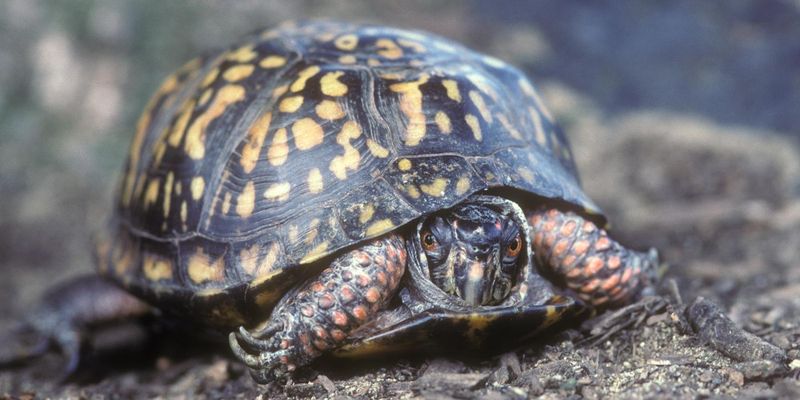

A tortoise’s shell isn’t just armor—it’s a window into its life story. Like tree rings, growth lines on the shell can hint at age, though reading them takes a trained eye.
Environmental factors affect how fast those rings form, so it’s more of an estimate than a sure thing.
The shell’s condition also reveals health clues—cracks, odd colors, or lumps can signal trouble.
Keeping an eye on shell changes is key to keeping tortoises healthy and thriving for years to come.
8. Tortoise Shell Colors
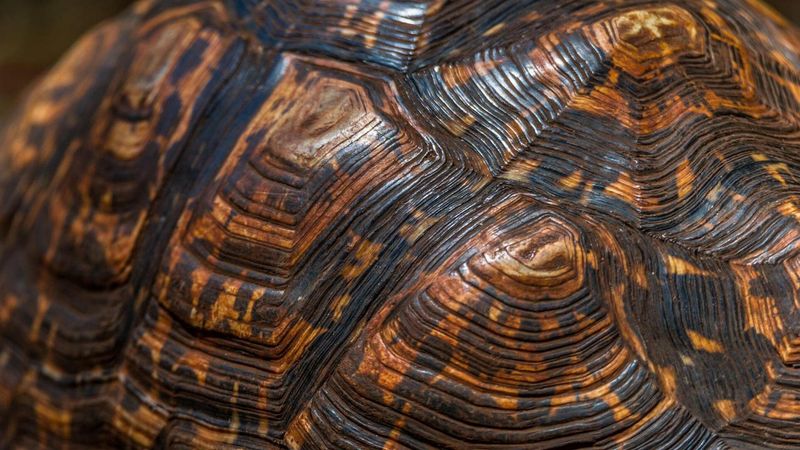

Tortoise shells come in a surprising variety of colors.
These colors, ranging from rich browns and bright yellows to muted greens, are not just for show. The pigmentation helps tortoises blend into their environments, offering camouflage.
Each shell’s unique color pattern can also signal different species or genetic lineages. This natural artistry is not just a visual treat but a crucial survival tool.
The colors can change subtly as the tortoise ages, providing insights into its growth and health.
Understanding these color variations offers a glimpse into the evolutionary adaptations that have helped tortoises thrive in diverse habitats.
9. Historical Uses Of Tortoise Shells
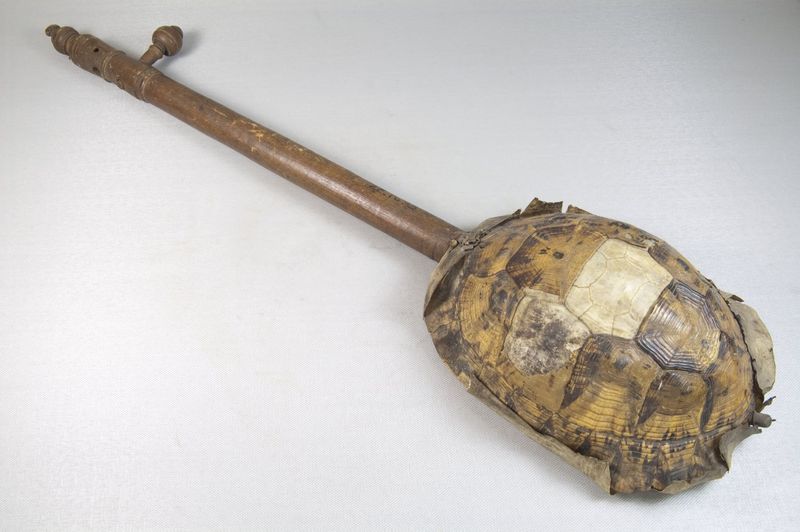

Throughout history, tortoise shells were prized for both their strength and beauty. Ancient artisans turned them into combs, jewelry, tools, and even musical instruments.
The demand, especially for hawksbill shells, surged over time—taking a serious toll on tortoise populations.
Some cultures, like traditional Chinese medicine, believed the shells had healing powers, further fueling the trade.
Thankfully, awareness and regulation have stepped in to protect these incredible animals.
Now, preserving tortoises means leaving their stunning shells right where they belong—on their backs.
10. Tortoise Shells In Mythology And Culture
Tortoises have strutted their way into myths and legends across the globe.
In Hindu mythology, a giant tortoise carries the weight of the world, while African tales often cast tortoises as clever and wise.
Their sturdy shells symbolize protection and long life, making them powerful icons in storytelling.
Native American traditions see the tortoise as a symbol of Mother Earth—steady, enduring, and life-giving.
Across cultures, these ancient reptiles have come to represent stability and resilience, earning them a lasting place in our collective imagination.
11. The Impact Of Diet On Shell Health

What a tortoise eats has a big impact on its shell—think of food as the fuel behind that tough exterior.
Calcium and vitamins are especially important to keep the shell strong and growing properly.
In the wild, tortoises munch on a variety of plants packed with the nutrients they need.
Pet tortoises, however, rely on their humans to provide a well-rounded diet—and sometimes supplements—to avoid shell problems.
Good nutrition isn’t just about feeding—it’s about building a healthy, happy tortoise from the shell up!
12. Shell Shapes And Their Significance

Tortoise shells come in all shapes—and each one tells a survival story. Dome-shaped shells are perfect for forest dwellers, making it harder for predators to get a grip.
Flatter shells are more common in desert tortoises, helping them burrow and stay cool in scorching heat.
These shape differences aren’t random—they’re the result of millions of years of evolution.
From movement to behavior, a tortoise’s shell is custom-built for the life it leads.
13. The Cultural Significance of Tortoise Shells

Tortoise shells have long sparked human creativity, inspiring everything from ancient tools to modern art.
Their patterns and strength have made them symbols of beauty, protection, and endurance.
Across cultures, the shell’s influence shows up in architecture, fashion, and decorative design.
Today’s artists and designers still draw on its natural elegance—often in sustainable ways that honor the animal.
It’s a powerful reminder that tortoises have shaped not just ecosystems, but our imaginations too.
14. Shell Patterns And Identification
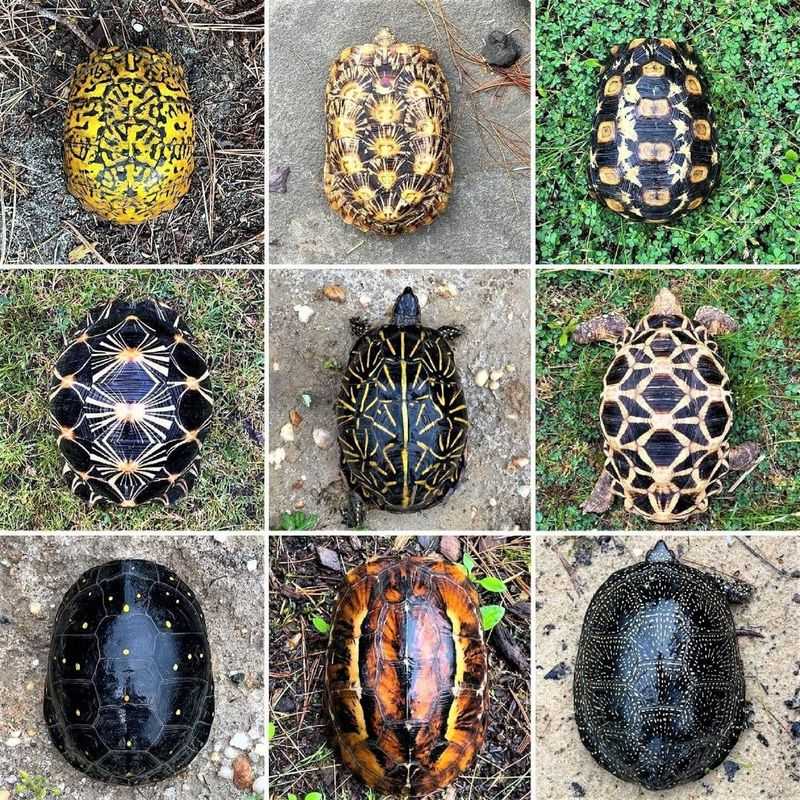

No two tortoise shells are exactly alike—each one has its own set of colors and patterns, like a fingerprint in armor.
These markings develop over time due to genetics, environment, and age.
Scutes, the hard plates on the shell, form unique designs that help researchers tell tortoises apart in the wild.
This stress-free ID method is a game-changer for conservation efforts and long-term studies.
In some species, those patterns even double as camouflage, proving once again how tortoises are masters of survival and style.
15. Shells And Environmental Adaptation
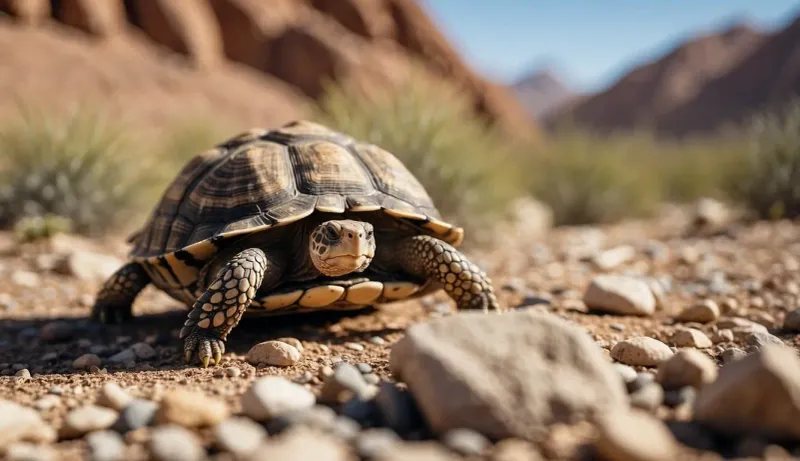

Tortoise shells aren’t just built tough—they’re built smart. In marshy regions, some shells help tortoises float, while desert species have shells that reflect sunlight to stay cool.
Each design is perfectly matched to the tortoise’s environment, shaping how it moves, survives, and lives day to day.
From wetlands to arid landscapes, their shells are tailored for survival.
It’s evolution at its finest—resilient, resourceful, and remarkably well-adapted.
16. Composition Of Tortoise Shells
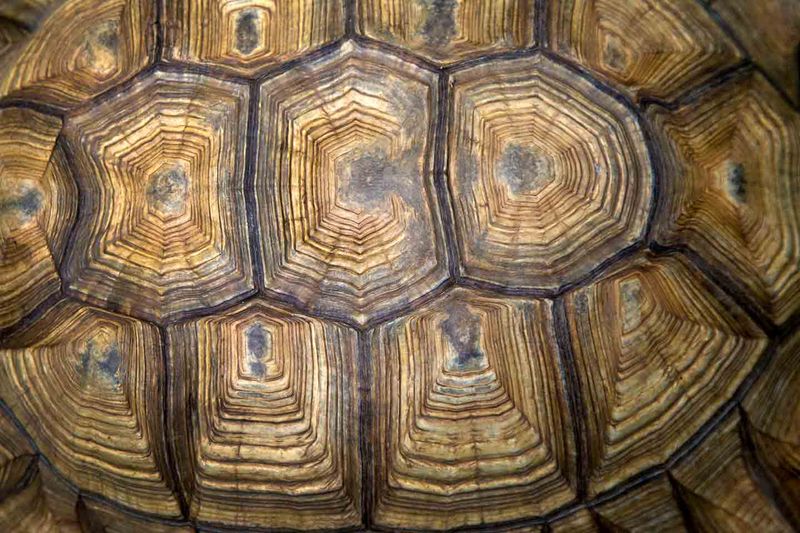

A tortoise shell isn’t just tough—it’s a bone-and-keratin masterpiece!
The top part is the carapace, the bottom is the plastron, and they’re connected by bony “bridges” that hold it all together.
Each scute (those outer plates) is made of keratin—the same stuff in your hair and nails—giving the shell its strength without weighing it down.
As the tortoise grows, its shell grows too, adding layers like rings on a tree. Those layers can even hint at the tortoise’s age!
It’s a brilliant bit of natural engineering that’s been evolving for millions of years—and it’s still doing the job perfectly.
17. The Influence Of Shells On Tortoise Mobility
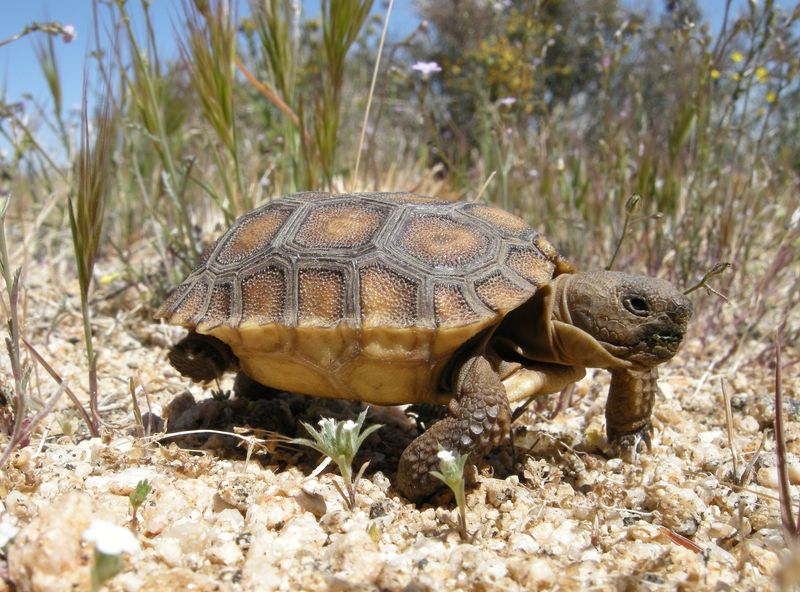

A tortoise’s shell might look bulky, but it’s a carefully crafted blend of protection and movement.
While it adds weight and limits speed, tortoises still manage to move with surprising agility.
Some even have shell shapes tailored for climbing rocky terrain or burrowing into the ground.
Every curve and contour is a response to the challenges of their habitat.
It’s a delicate evolutionary dance—trading speed for safety without missing a step.






