The Ongoing Fight To Protect Endangered Zebra Species

Striped wonders of the African plains are in trouble. Several zebra species face serious threats from habitat loss, poaching, and climate change.
Understanding these magnificent animals and the challenges they face is the first step toward ensuring future generations can marvel at their distinctive black-and-white patterns in the wild.
1. Stripes As unique As fingerprints

Just like your fingerprints, no two zebras have identical stripe patterns. These natural barcodes help researchers track individual animals in the wild without disturbing them.
Scientists use special software to identify specific zebras from photographs, similar to facial recognition technology. This non-invasive monitoring is crucial for understanding population health and movement patterns.
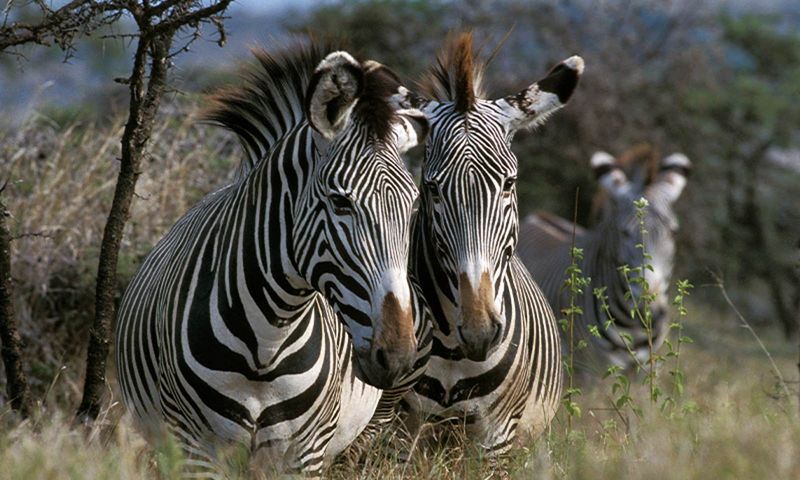
2. Grevy’s Zebra – The Endangered Giant
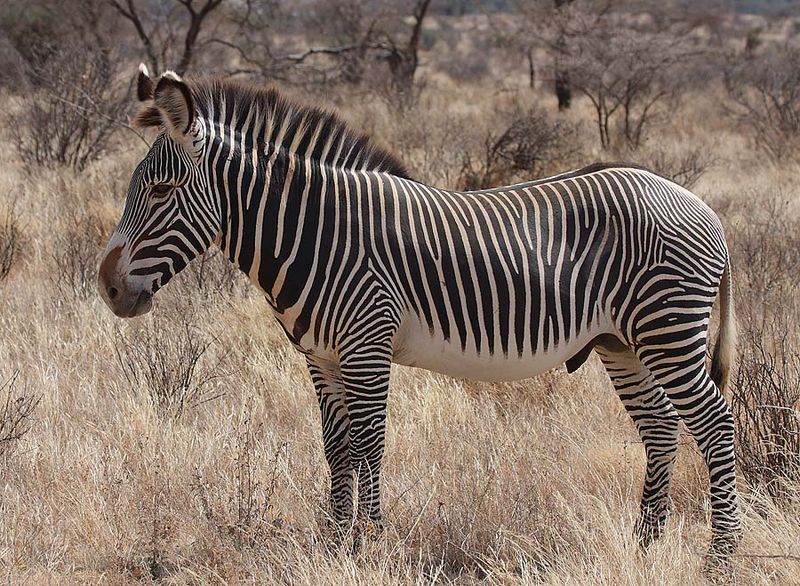

Towering above other zebras, the Grevy’s zebra is the largest wild equid alive today. With fewer than 2,000 individuals remaining, these majestic animals face a serious risk of extinction.
Found primarily in Kenya and Ethiopia, they’ve lost nearly 80% of their range. Their distinctive narrow stripes and white belly make them easy to distinguish from other zebra species.
3. Mountain Zebras Cling To Survival
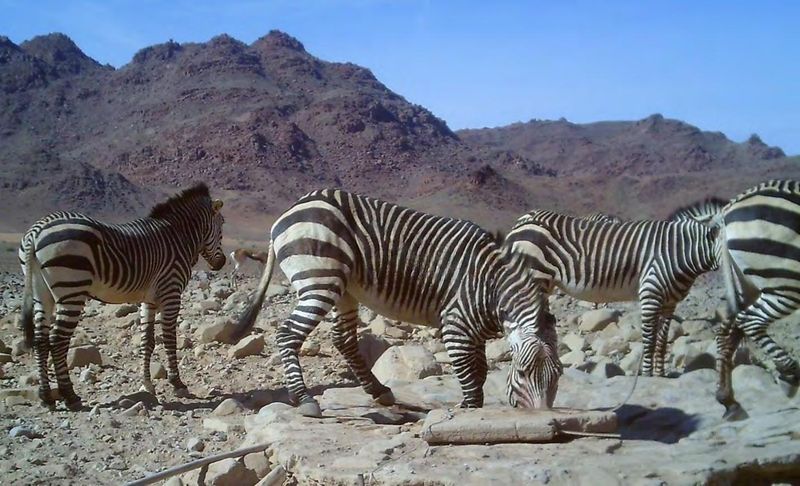

Rocky mountainsides might seem like strange zebra habitat, but mountain zebras have special hooves designed for climbing. These specialized adaptations help them escape predators by scaling steep terrain where lions and hyenas can’t follow.
Split into two subspecies, Hartmann’s and Cape mountain zebras, both face habitat fragmentation challenges as human development encroaches on their territory.
4. Plains Zebras – Not As Safe As You’d Think
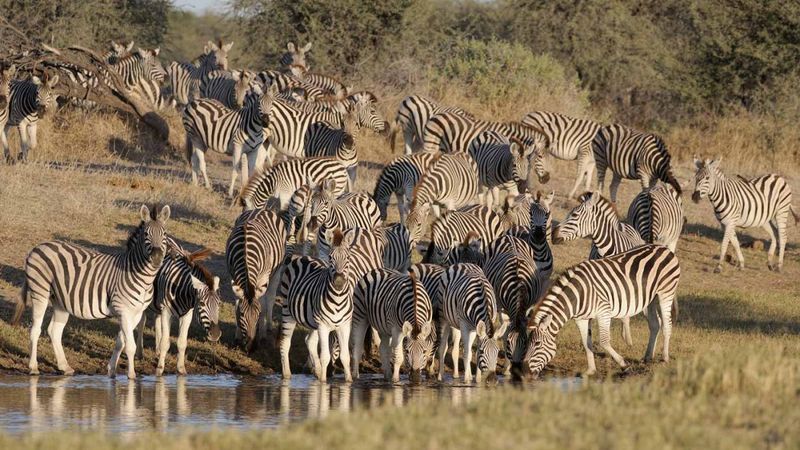

Despite being the most abundant zebra species, plains zebras have declined by 24% over the past decade. You might recognize them from nature documentaries about the Serengeti migration, but their future isn’t guaranteed.
Hunting for meat and hides continues to threaten these iconic animals. Conservation efforts focus on protecting migration corridors and reducing human-wildlife conflict in farming areas.
5. Zebra Stripes As Natural Bug Repellent
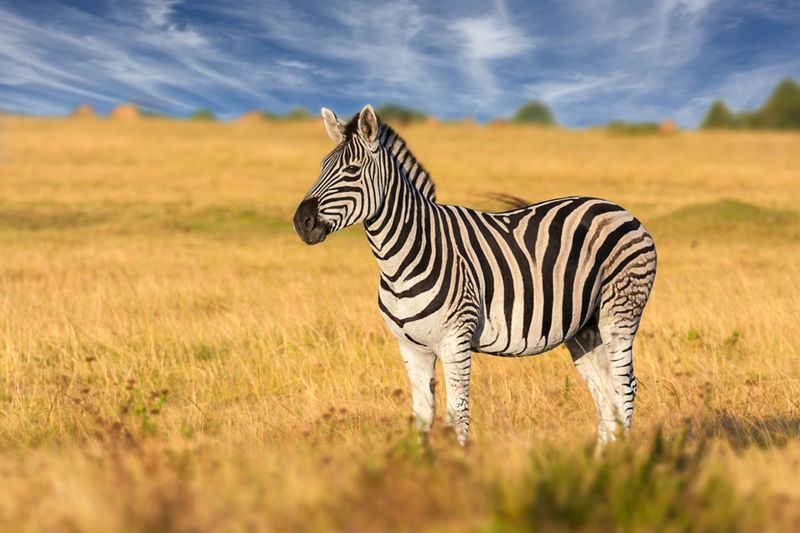

Wonder why zebras evolved those eye-catching stripes? Recent research suggests they actually function as a natural insect repellent! The pattern creates an optical illusion that confuses biting flies, making it harder for them to land.
Scientists tested this by dressing horses in zebra-striped coats and observed fewer flies landing on them. This adaptation helps zebras avoid diseases carried by insects in their native habitats.
6. Climate Change Threatens Zebra Migrations
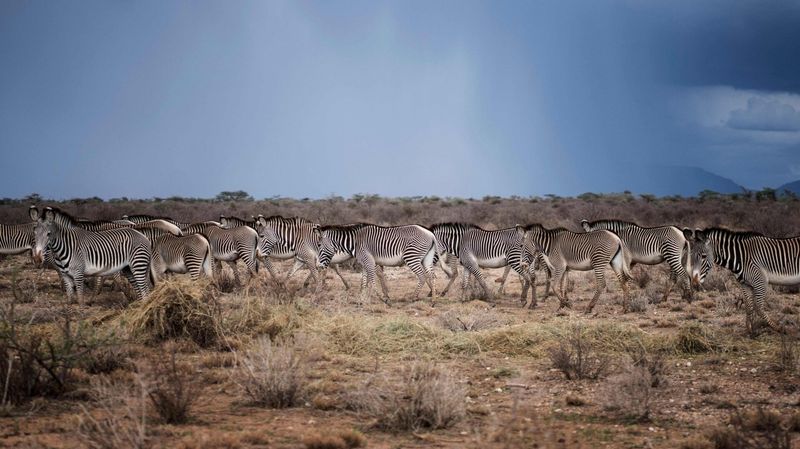

Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns disrupt the ancient rhythm of zebra migrations. These animals rely on predictable seasonal changes to find fresh grass and water sources throughout the year.
When droughts become more frequent or rainy seasons shift, zebras struggle to adapt. Conservation programs now include climate monitoring to help predict and mitigate these impacts on endangered zebra populations.
7. Community Conservation Success Stories

Local communities are becoming zebra champions! In Kenya, the Grevy’s Zebra Trust works with indigenous communities to monitor and protect these endangered animals while supporting sustainable livelihoods.
By employing local scouts and creating economic incentives for conservation, these programs have helped stabilize some zebra populations. This collaborative approach proves that wildlife protection and human prosperity can go hand-in-hand.
8. Zebra Crossings – Protecting Migration Routes
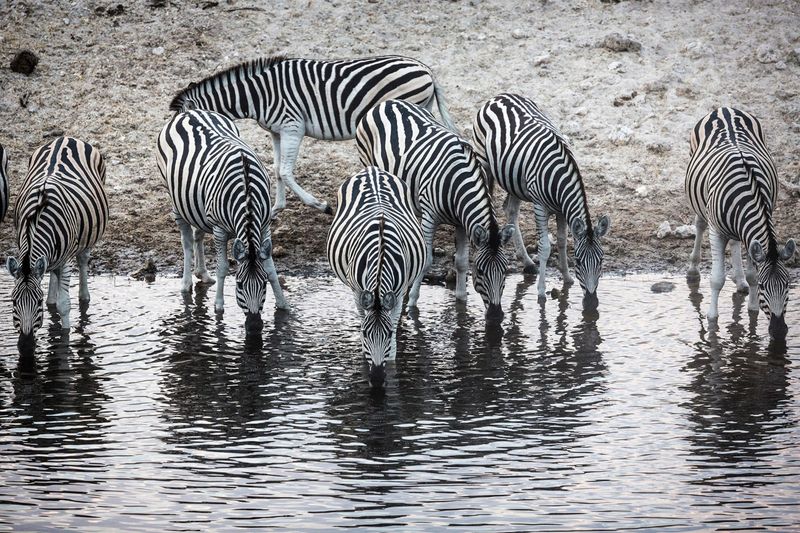

Highways and fences block ancient zebra migration paths, with fatal consequences. Innovative wildlife corridors, sometimes called “zebra crossings,” now help these striped travelers navigate human-dominated landscapes safely.
These protected pathways connect fragmented habitats, allowing zebras to reach seasonal feeding grounds. Some corridors include special underpasses or overpasses designed specifically for wildlife to cross busy roads without risking collisions.
9. Quagga – The Zebra We Lost Forever
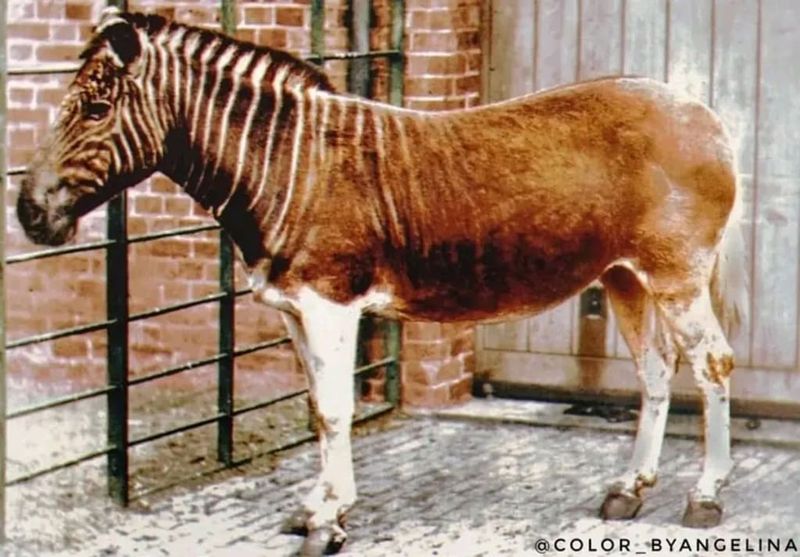
The quagga, a zebra subspecies with stripes only on its front half, was hunted to extinction in the 1880s. This tragic loss serves as a stark warning about how quickly zebra species can disappear without protection.
Scientists have attempted to selectively breed plains zebras to recreate quagga-like animals in the “Quagga Project,” but the original genetic lineage remains extinct. Their disappearance reminds us what’s at stake in current conservation efforts.
10. Technology Tracking Zebra Movements

GPS collars and satellite imagery have revolutionized zebra conservation. Researchers can now track individual animals across vast distances, identifying critical habitats and migration routes that need protection.
Some innovative projects use drones to count zebra populations and monitor for poaching activity. This high-tech approach provides real-time data that helps rangers respond quickly to threats and wildlife managers make better conservation decisions.
11. Zebra Genetic Diversity Under Threat

Small, isolated zebra populations face a hidden danger – genetic bottlenecks. When breeding groups become too small, harmful genetic traits can become concentrated, making animals more vulnerable to disease and environmental changes.
Conservation breeding programs carefully manage genetic diversity by occasionally relocating zebras between protected areas. This genetic rescue helps strengthen endangered populations by introducing new bloodlines and increasing their adaptive potential.
12. How You Can Help Save Zebras

Your choices impact zebra conservation even from thousands of miles away! Supporting organizations like the Grevy’s Zebra Trust or the Wildlife Conservation Network directly funds protection efforts.
Responsible tourism that follows ethical wildlife viewing guidelines helps create economic incentives for conservation. By learning about these magnificent animals and sharing their story, you’re helping build the public awareness needed to ensure zebras continue roaming Africa’s plains.






