13 Signs Of Aging In Dogs And What To Do

As our furry friends grow older, they show a variety of signs that indicate they are aging. Understanding these signs can help pet owners provide their canine companions with a comfortable and fulfilling life.
Here’s a guide to recognizing 13 common signs of aging in dogs and what you can do to support them through these changes.
Always remember that each dog is unique, and consulting with a vet is essential for personalized care.
1. Gray Muzzle
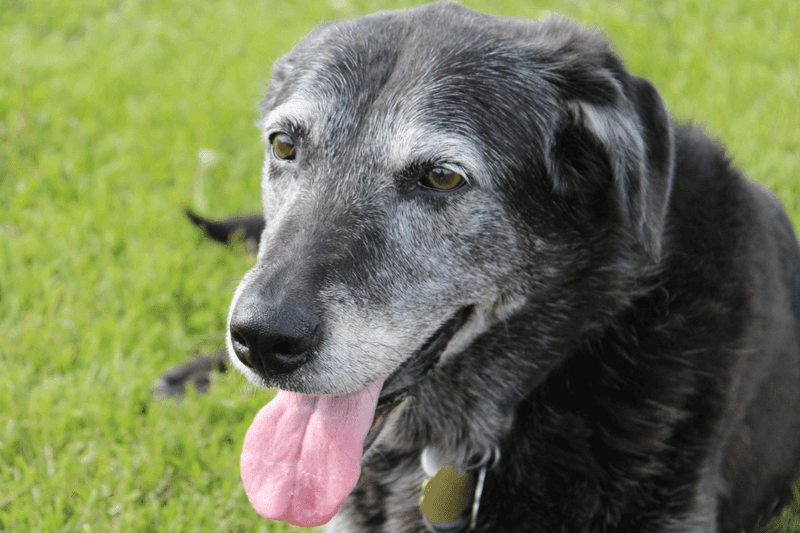

A beloved sign of aging in dogs is the charming gray that appears around their muzzle. This change is usually one of the first visible signs and often begins in middle age.
While the salt-and-pepper look can be adorable, it’s also a reminder of your dog’s advancing years.
To keep them comfortable, ensure their diet supports healthy aging. Foods rich in antioxidants can be beneficial.
Regular vet check-ups will help monitor their overall health. Additionally, maintaining a low-stress environment contributes to their well-being.
2. Joint Stiffness
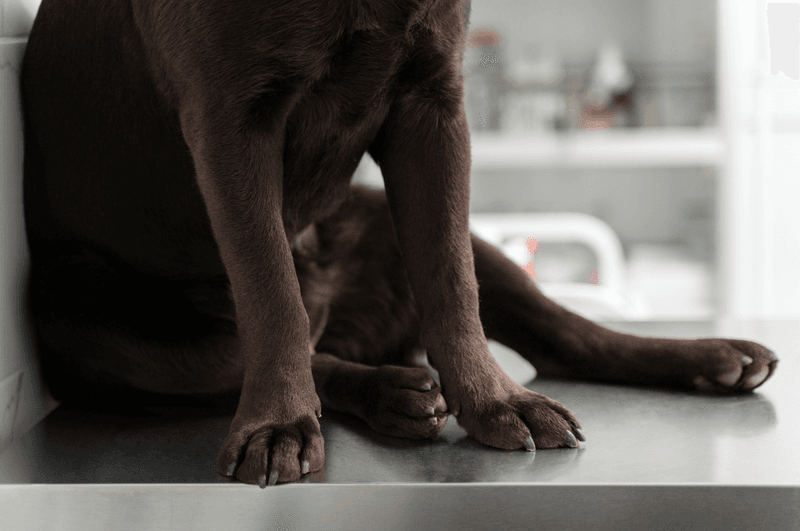

Joint stiffness in older dogs can slow them down, making activities like climbing stairs or jumping onto furniture more challenging.
You might notice them hesitating or showing signs of discomfort during these activities.
To help, consider providing orthopedic beds designed to relieve pressure on joints. Gentle, regular exercise, such as short walks, keeps them moving without overexertion.
Supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin may also help ease stiffness and improve joint health.
3. Decreased Energy
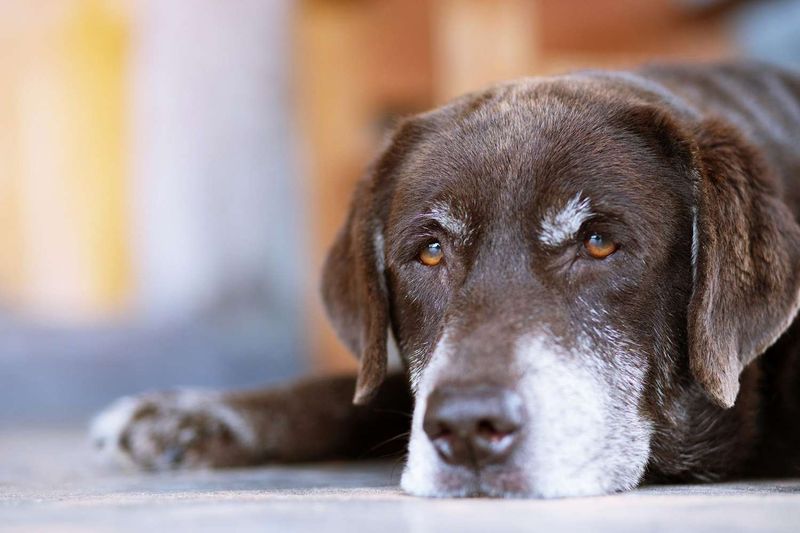

As dogs age, a noticeable decline in their energy levels might occur. Your once playful pup may now prefer lounging over fetching their favorite ball. This decrease in energy is a natural part of the aging process.
Encourage them to stay active with age-appropriate playtime. Interactive toys that stimulate their mind can be both fun and beneficial.
Also, ensure their diet meets their changing needs, providing energy without causing weight gain.
4. Changes In Appetite
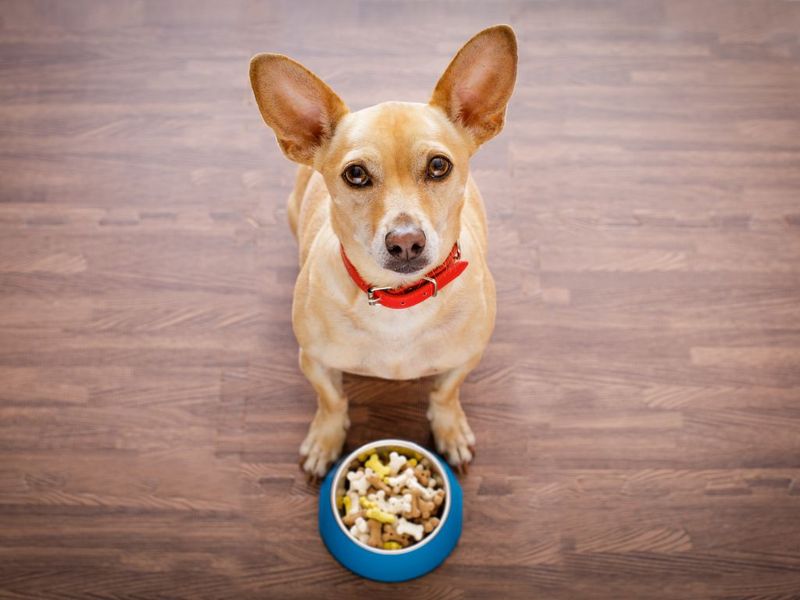

Older dogs can experience changes in appetite. Some may eat less as their metabolism slows, while others might eat more due to medical conditions. Either scenario can affect their weight and overall health.
Monitor their eating habits and consult your vet if you notice significant changes. A balanced diet, tailored to their age and health needs, is crucial.
Sometimes, warming their food or offering smaller, frequent meals can stimulate their appetite.
5. Vision Problems
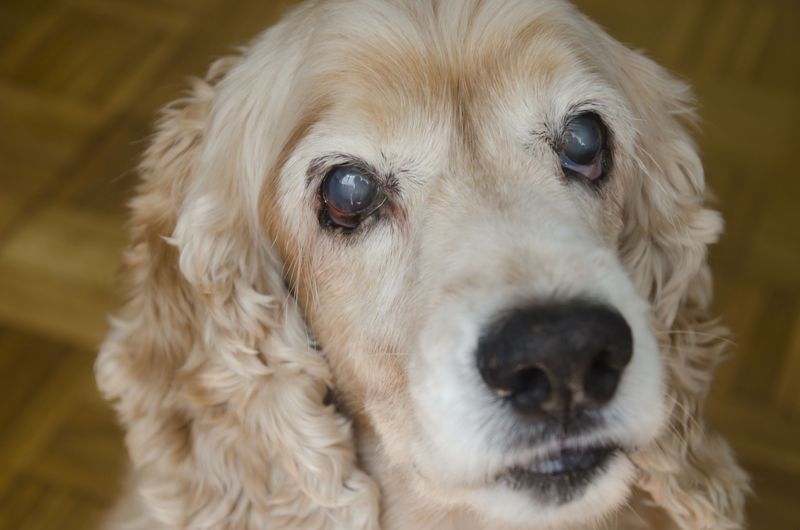

Vision problems, like cloudiness or cataracts, are common in aging dogs.
These changes can cause them to bump into furniture or appear hesitant in new environments. It’s crucial to maintain a safe and familiar space for them.
Keep pathways clear, and consider using non-slip mats to help them navigate. Regular eye check-ups can detect issues early, and in some cases, surgery might be an option to improve their vision.
Helping them adapt to their changing sight ensures comfort.
6. Hearing Loss

Hearing loss in aging dogs can affect their response to sounds, commands, or even their name. They might seem more startled by sudden movements if they don’t hear you approaching.
Communicate using visual signals or touch. Consistency in your gestures will help them understand. Keeping their environment familiar and minimizing loud noises can make them feel secure.
Patience and understanding are key to supporting them through this change.
7. Dental Issues
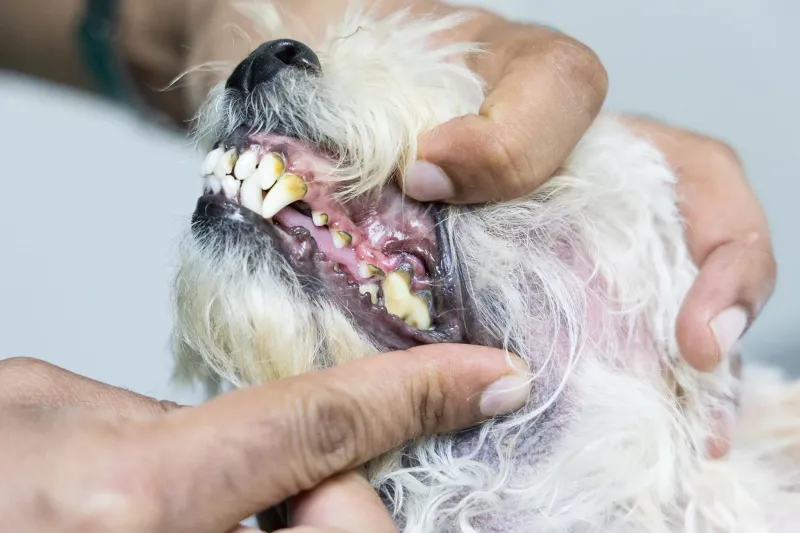
Dental health often deteriorates with age, leading to problems like tartar buildup, gum disease, or tooth loss. Signs include bad breath, difficulty eating, or excessive drooling.
Regular dental check-ups are vital. Brushing their teeth and providing dental treats can maintain oral health.
If chewing is painful, offer softer food options. Addressing dental issues promptly prevents them from affecting your dog’s overall well-being.
8. Weight Fluctuations
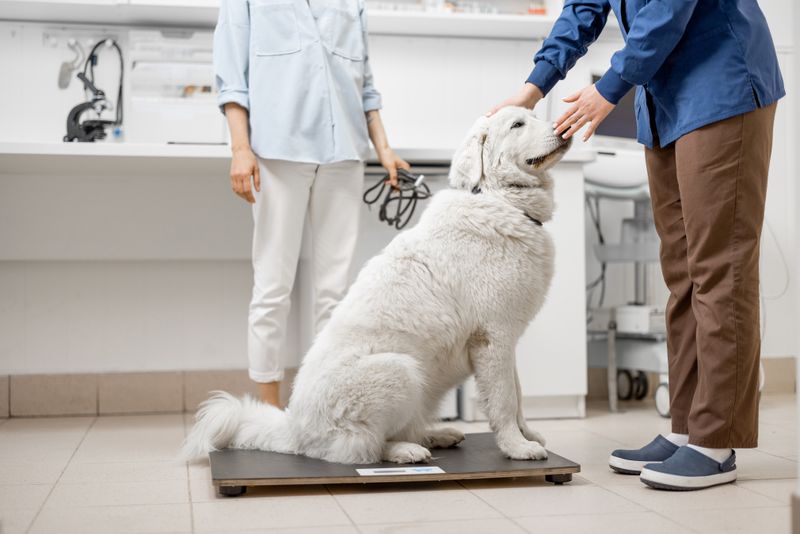

Weight fluctuations in older dogs can indicate health issues. Some may lose weight due to reduced appetite, while others gain weight due to decreased activity or metabolic changes.
Regularly monitoring their weight helps catch changes early. Adjust their diet as needed, focusing on balanced nutrition.
Encourage light exercise to maintain a healthy weight. Consulting a vet ensures that any underlying issues are addressed promptly.
9. Skin And Coat Changes
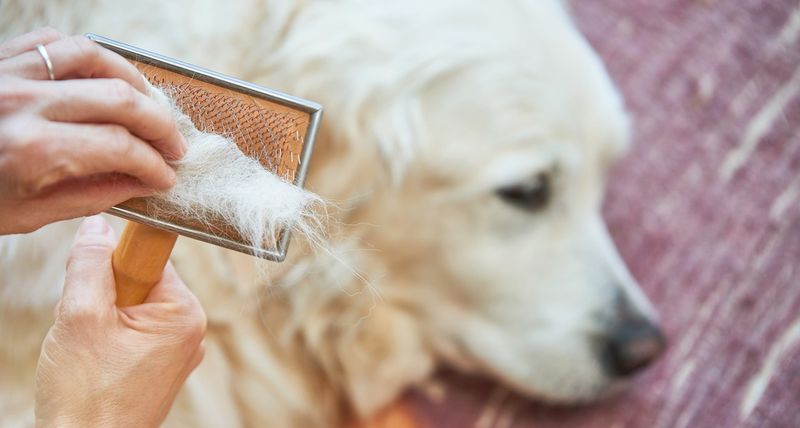

Aging can bring about changes in your dog’s skin and coat. You might notice thinning fur, dryness, or even an increase in lumps and bumps. These changes are natural but require attention.
Regular grooming keeps their coat healthy and allows you to check for new growths. Hydrating shampoos and a balanced diet with omega fatty acids support skin health.
If you discover unusual lumps, consult your vet to rule out serious conditions.
10. Behavioral Changes
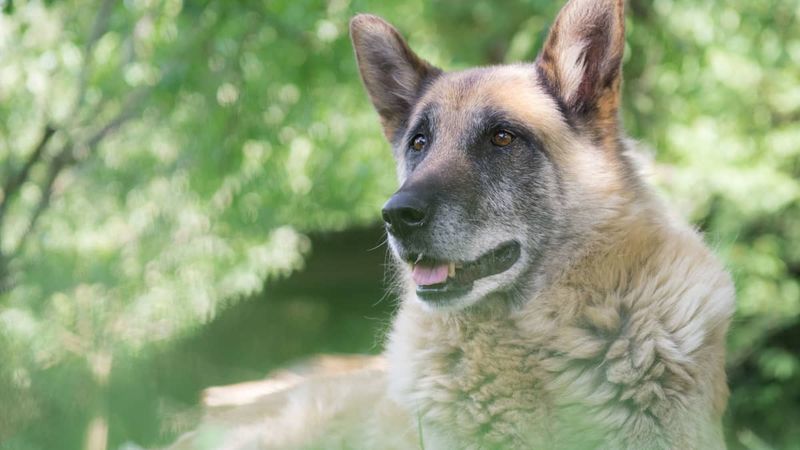

As dogs age, they may exhibit behavioral changes such as increased anxiety, confusion, or irritability. These changes might be signs of cognitive decline or discomfort.
Maintain a stable routine to provide comfort and familiarity. Enriching their environment with puzzle toys can stimulate their mind.
Consult your vet if their behavior changes significantly, as there might be underlying health issues.
11. Sleeping More Often
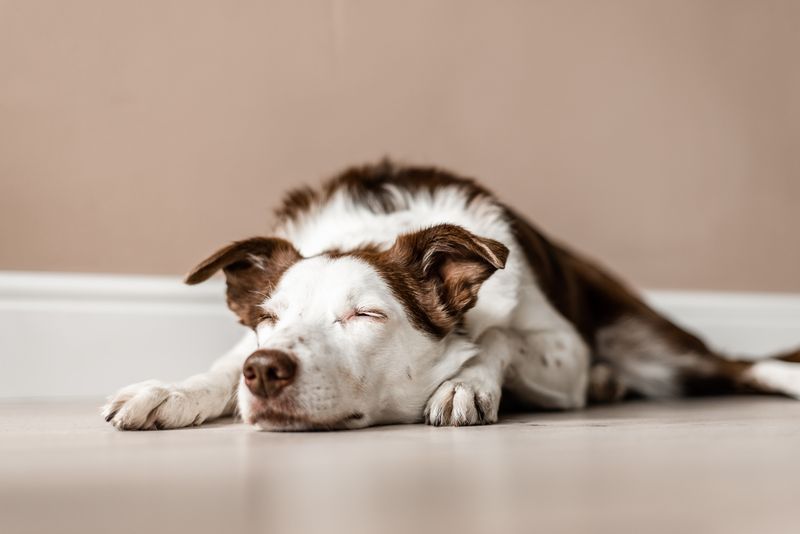

Aging dogs often sleep more, a natural shift as their bodies require more rest. You might find them napping throughout the day, enjoying the warmth of a cozy spot.
Ensure they have comfortable sleeping arrangements. A supportive bed minimizes joint pain and promotes better sleep quality.
While rest is crucial, encourage gentle activities during their awake time to keep them active and engaged.
12. Increased Thirst
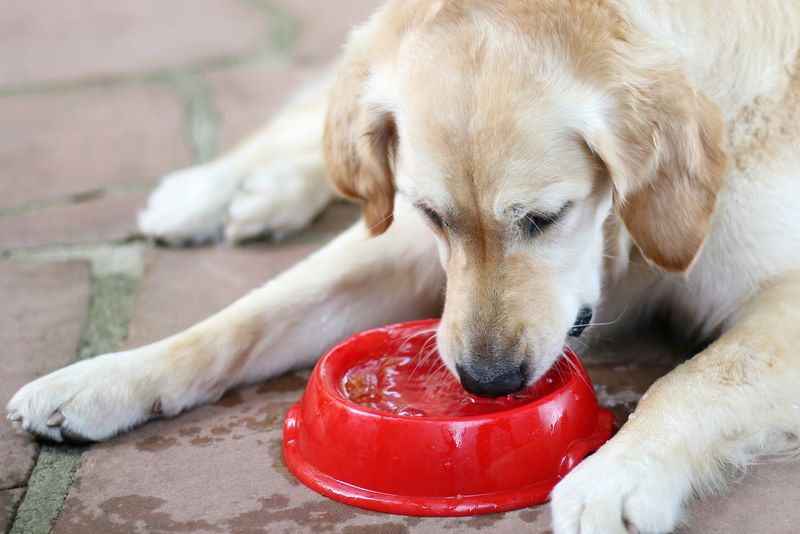

Increased thirst in older dogs can signal underlying health issues such as kidney problems or diabetes. Keeping track of their water intake helps identify changes early.
Provide easy access to fresh water at all times. If excessive thirst is accompanied by other symptoms, consult your vet for a thorough evaluation.
Addressing the root cause is essential for their health and comfort.
13. Digestive Issues

Digestive issues such as vomiting or diarrhea become more frequent as dogs age. These symptoms can result from dietary changes or underlying health conditions.
Monitoring their diet and avoiding abrupt changes helps maintain digestive health. Adding probiotics can support their gut.
If issues persist, consult a vet to rule out serious problems and ensure your dog remains comfortable.






