Scientists Uncover Silent Frog Species In Tanzania That Can’t Vocalize
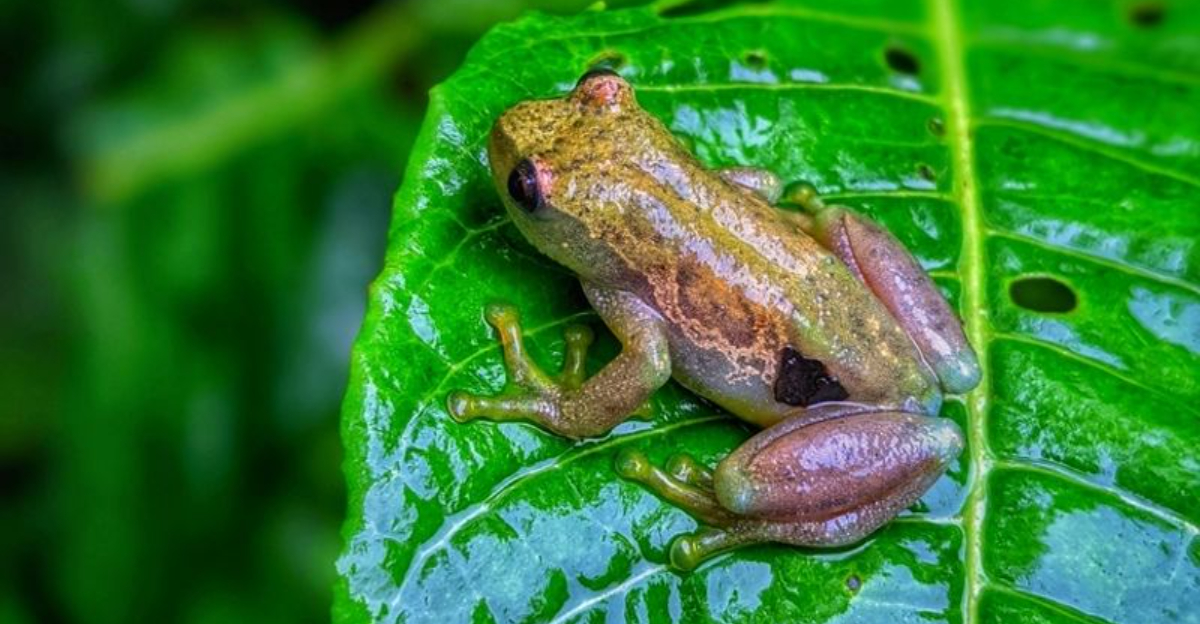

Scientists have made an extraordinary discovery in the remote Ukaguru Mountains of Tanzania – a frog species that can’t make sounds!
Named Hyperolius ukaguruensis, this amphibian challenges everything we know about frogs. While most frogs croak to attract mates and defend territory, this unique species has evolved different ways to communicate, making it a fascinating subject for researchers worldwide.
1. Newly Discovered Species
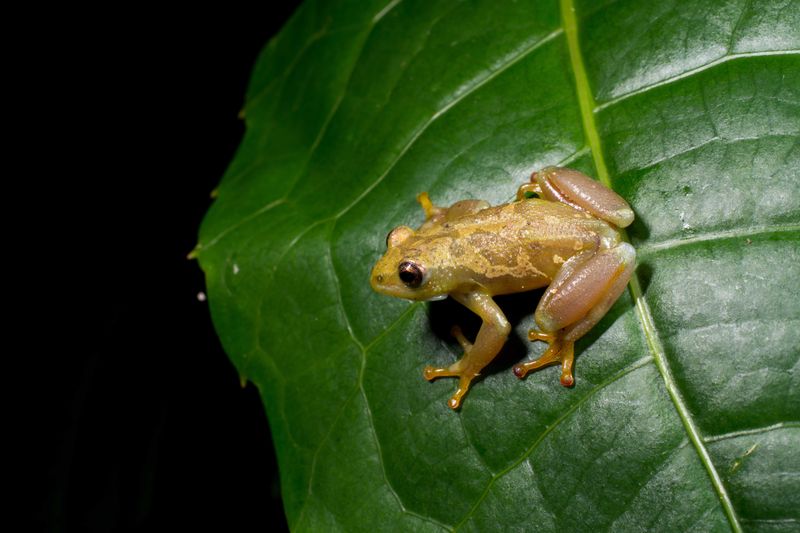

In 2022, biologists stumbled upon Hyperolius ukaguruensis while conducting biodiversity surveys in Tanzania. The tiny amphibian immediately stood out because it didn’t respond to recorded frog calls.
Further examination confirmed it belonged to the rare category of voiceless frogs, making it a remarkable scientific discovery that expands our understanding of amphibian evolution.
2. Habitat In The Ukaguru Mountains
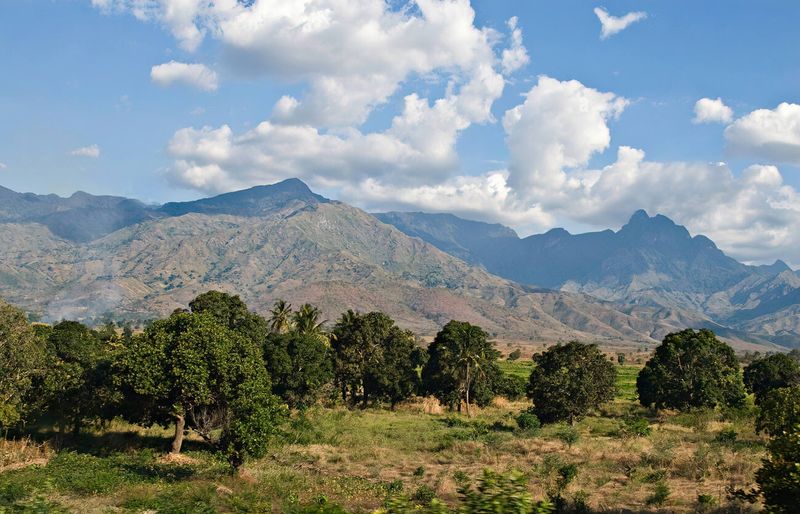

Nestled in east-central Tanzania, the Ukaguru Mountains rise dramatically from surrounding plains, creating isolated ecosystems perfect for unique species development. Mist frequently shrouds these peaks, maintaining constant humidity.
This remote mountain range harbors countless undiscovered species, with the silent frog being just one extraordinary example of its biological treasures.
3. Lack Of Vocalization
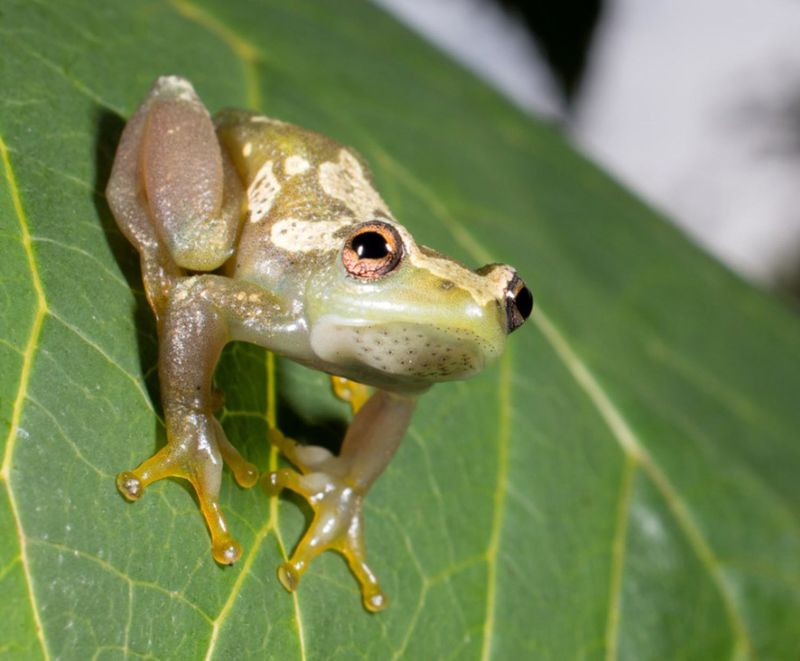

Imagine a frog without its iconic ribbit! While researchers initially thought their recording equipment was malfunctioning, they soon realized this species physically cannot produce sounds.
Anatomical studies revealed the frog lacks the specialized vocal cords and resonating throat sacs that other frogs use. This silence represents a dramatic evolutionary departure from typical amphibian communication.
4. Unique Adaptation
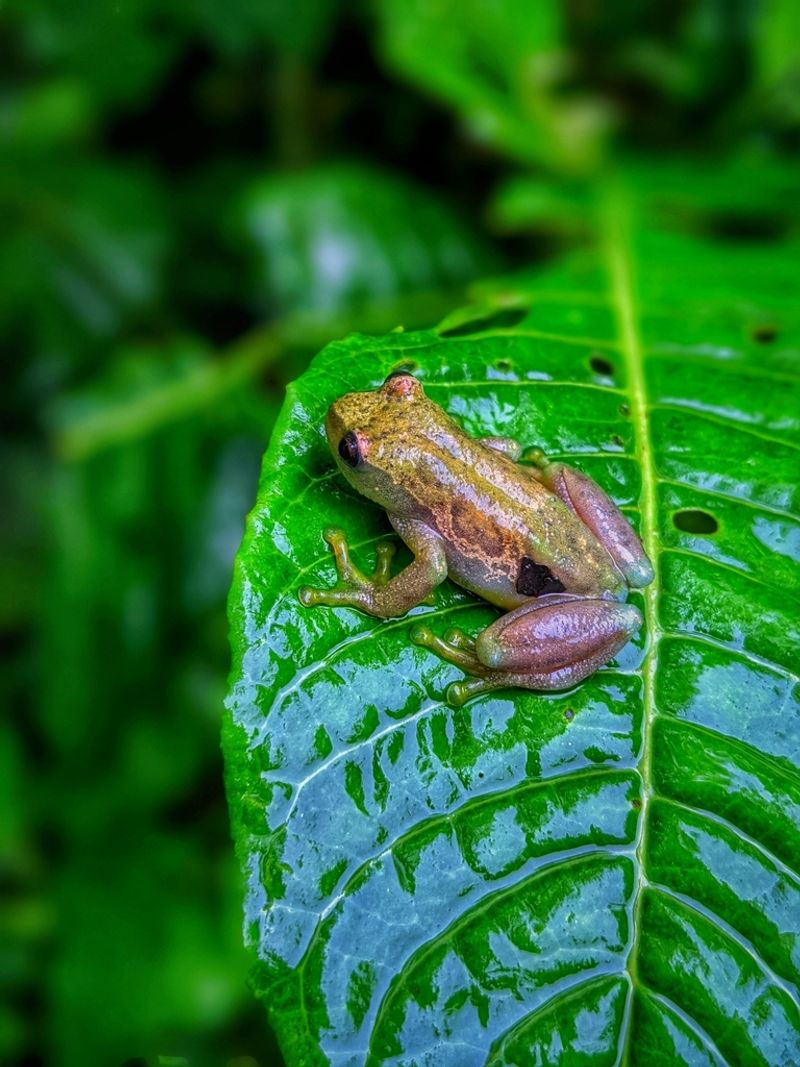

Evolutionary biologists are fascinated by this frog’s silent strategy. In the noisy rainforest where predators might locate prey by sound, staying quiet offers surprising advantages.
The species likely developed alternative communication methods over thousands of years. This adaptation demonstrates nature’s remarkable ability to find diverse solutions to survival challenges, even within well-established animal groups.
5. Physical Description
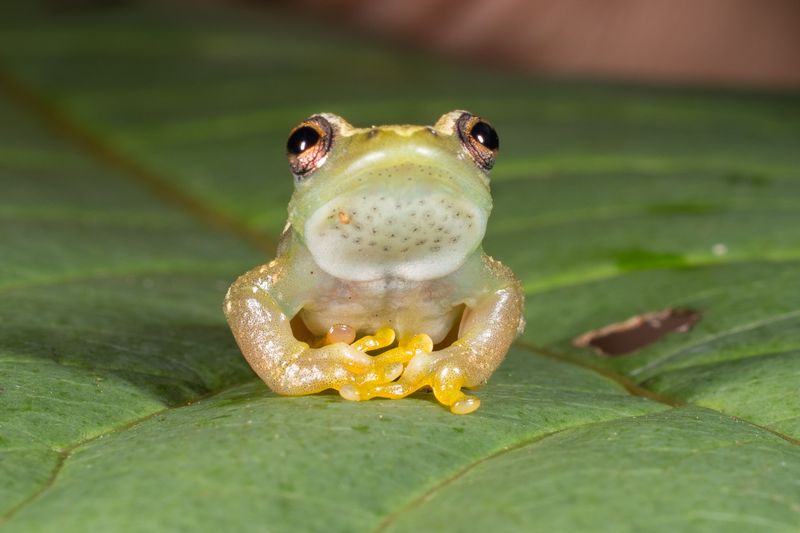

No larger than your thumbnail, these jewel-like amphibians sport vibrant lime-green bodies adorned with distinctive yellow patterns that vary between individuals. Their skin has a slightly glossy appearance that catches forest light.
Large, expressive eyes dominate their small faces, while their slender limbs end in specialized adhesive toe pads perfect for climbing vegetation in their mountainous home.
6. No Croaks Or Ribbits
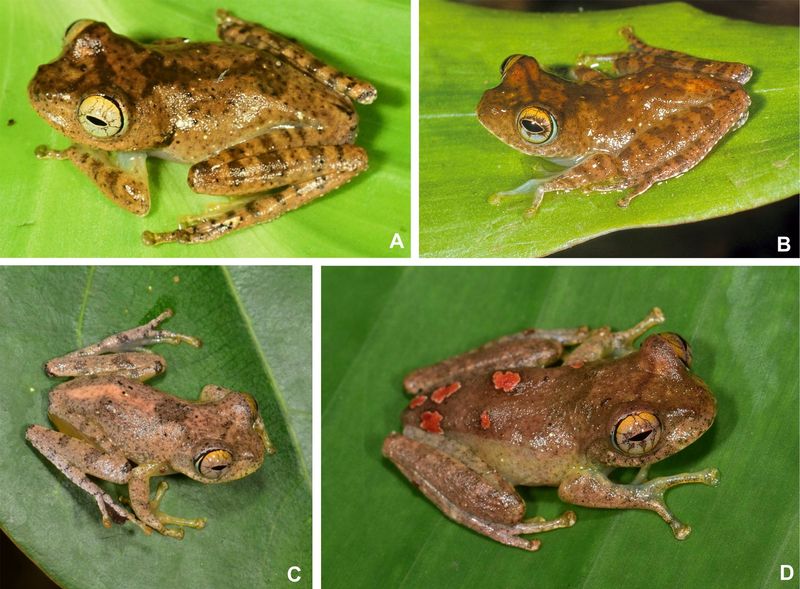

Midnight in the Ukaguru Mountains reveals an eerie silence where these frogs gather. While other amphibian species create a symphony of sounds, these creatures remain mysteriously quiet.
Researchers initially set audio traps expecting typical frog calls, but captured only environmental sounds. This complete absence of vocalization makes traditional frog monitoring methods useless for studying this species.
7. Inhabits Moist Forest Environments
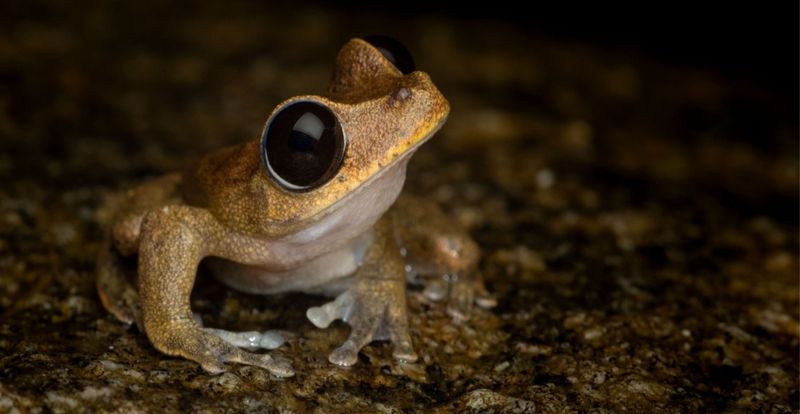

Thriving amidst decaying leaves and moss-covered logs, these silent amphibians prefer the dampest sections of the mountain forests. Morning dew provides essential moisture for their permeable skin.
They’re particularly abundant near small streams and seeps where humidity remains consistently high. Researchers believe their limited range within this specific microhabitat contributed to their isolated evolutionary path.
8. Fossil Record

The discovery fills a puzzling gap in amphibian evolutionary history. Paleontologists have previously found fossilized frogs dating back 200 million years, with most showing evidence of vocal structures.
This modern silent species provides living clues about how and why some frogs might have evolved away from sound-based communication. Ancient climate shifts in East Africa possibly created conditions favoring silent adaptations.
9. Endangered Status
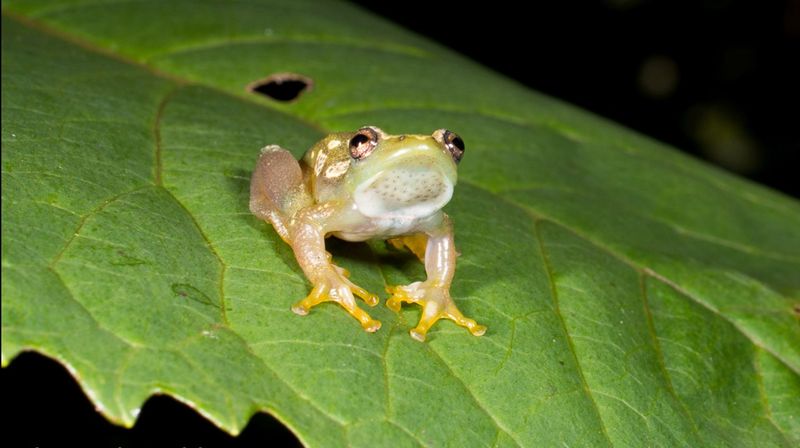

Agricultural expansion creeps steadily up the mountain slopes, threatening these specialized frogs. Their limited range makes them particularly vulnerable to habitat destruction.
Climate change poses another serious threat, as shifting rainfall patterns could dry their moisture-dependent microhabitats. Conservation groups are working to establish protected areas before this remarkable species disappears forever.
10. Behavioral Studies Ongoing
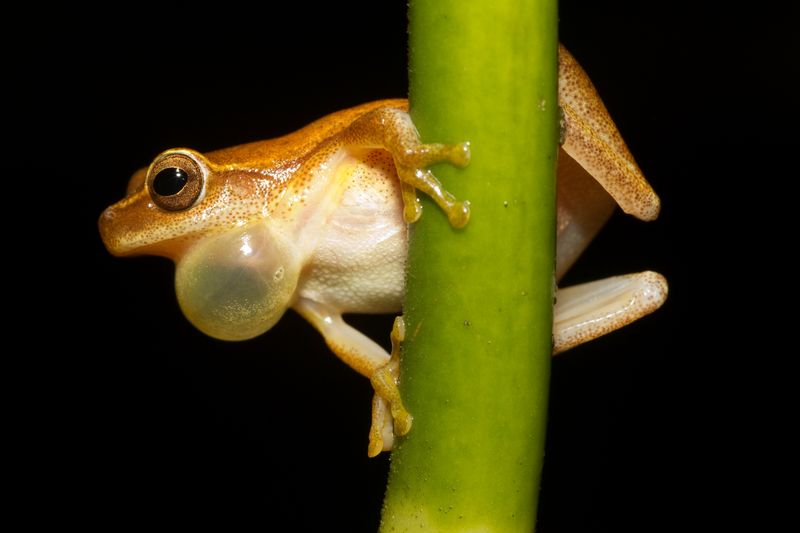

Field researchers use infrared cameras to observe these silent frogs’ nighttime activities. Footage reveals fascinating foot-tapping displays and body postures that appear to replace vocal communication.
Males perform elaborate visual displays, waving their brightly colored limbs to attract females. Scientists suspect they also release chemical signals that other frogs can detect, creating a sophisticated multi-sensory communication system.
11. Part Of The Hyperolius Genus

Genetic analysis places these silent frogs within the colorful Hyperolius genus, commonly known as reed frogs. With over 150 known species, this diverse group showcases remarkable adaptability across African ecosystems.
Most Hyperolius relatives are vocal champions, producing distinctive calls that carry for surprising distances. This silent species represents a dramatic evolutionary experiment within an otherwise chatty family tree.
12. New Insights Into Frog Evolution
Genetic sequencing of these silent frogs has unlocked fascinating evolutionary mysteries. Their DNA reveals they diverged from vocal ancestors approximately 15 million years ago, coinciding with major geological changes in East Africa.
This timeline suggests environmental pressures may have favored silent individuals, gradually leading to complete loss of vocalization. Their story demonstrates how species can abandon seemingly essential traits.
13. Importance For Biodiversity Conservation
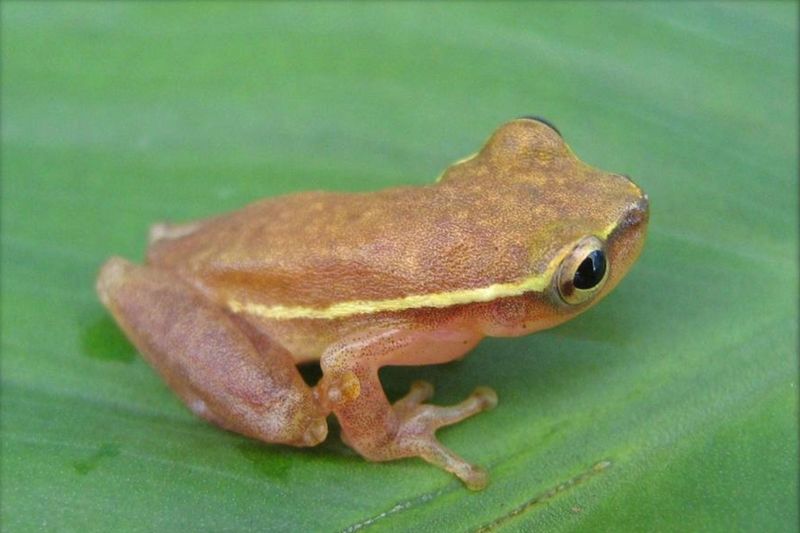

Beyond scientific curiosity, these silent frogs serve as indicator species for ecosystem health. Their specialized needs make them sensitive to environmental changes, providing early warning of habitat degradation.
Local conservation efforts now highlight these frogs as flagship species. Community education programs teach residents about protecting mountain forests, demonstrating how even tiny, silent creatures play crucial roles in maintaining biodiversity balance.






