Mysterious Sea Creature Spotted By Scuba Divers In Bermuda’s Hidden Tidal Cave
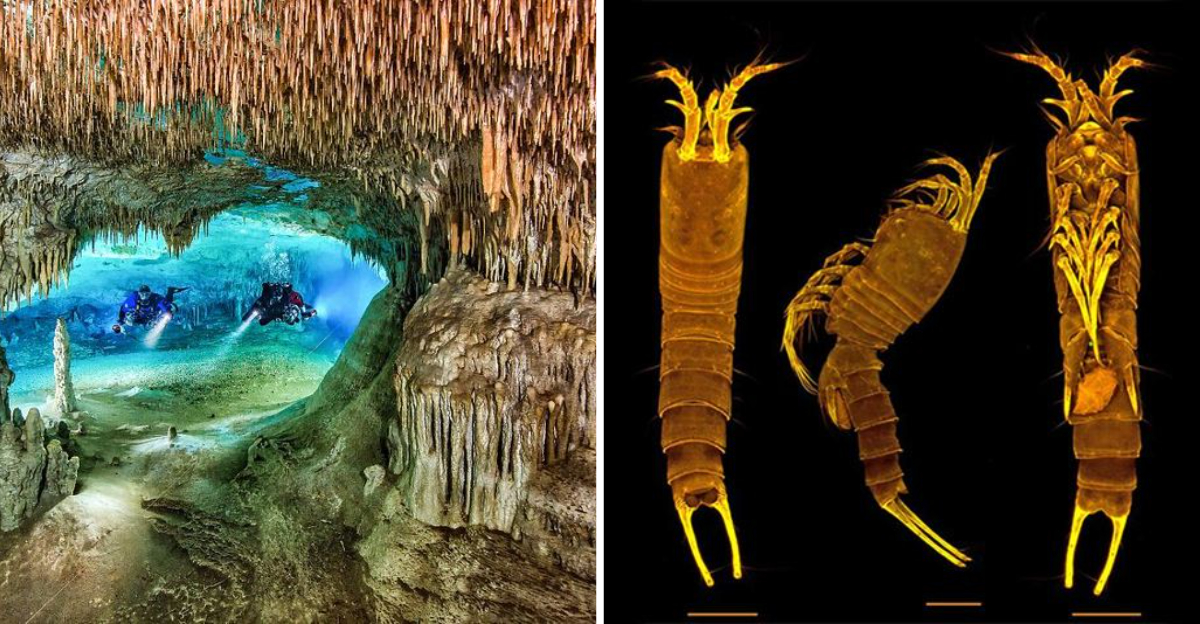

Imagine swimming through crystal-clear waters and suddenly coming face-to-face with an unknown species! That’s exactly what happened to a group of scuba divers exploring a hidden tidal cave in Bermuda.
The divers discovered what scientists have now identified as Tetragoniceps bermudensis, a previously undocumented crustacean species.
This remarkable finding has marine biologists worldwide buzzing with excitement and raises fascinating questions about what other secrets might be hiding in Bermuda’s underwater cave systems.
1. Bermuda’s Hidden Tidal Caves: A Unique Habitat For Rare Sea Creatures
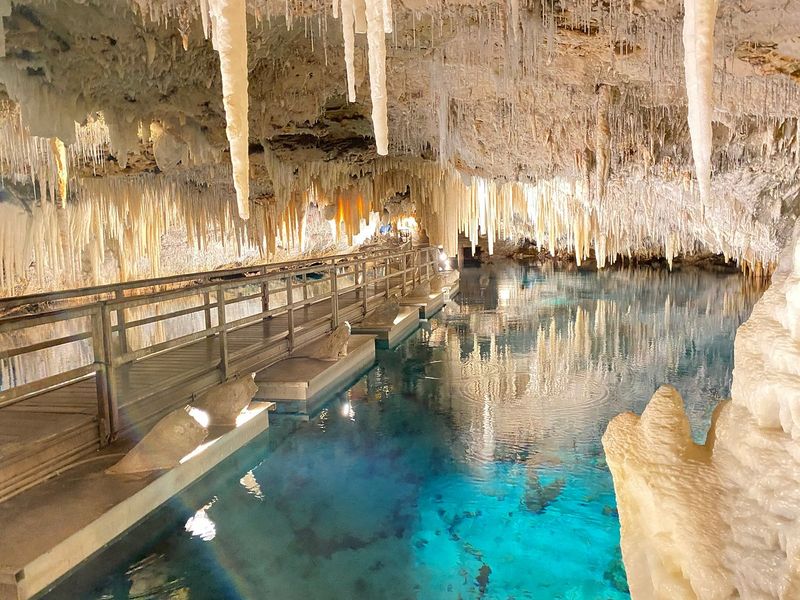

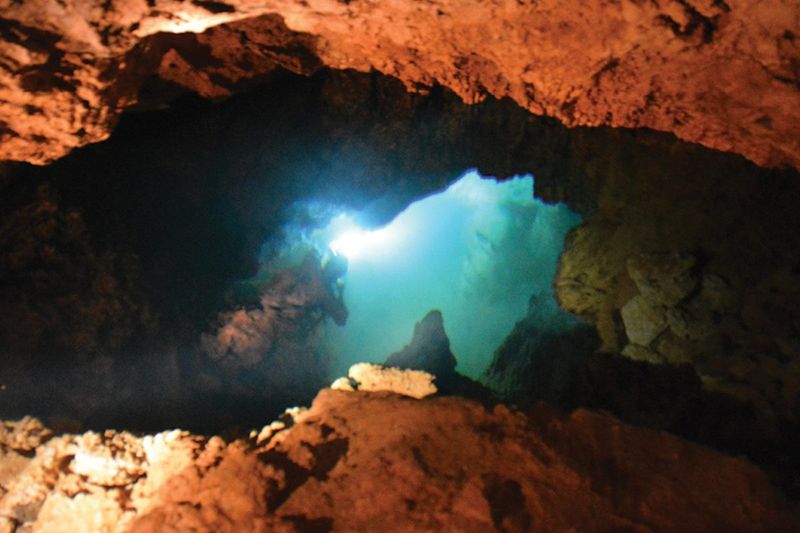
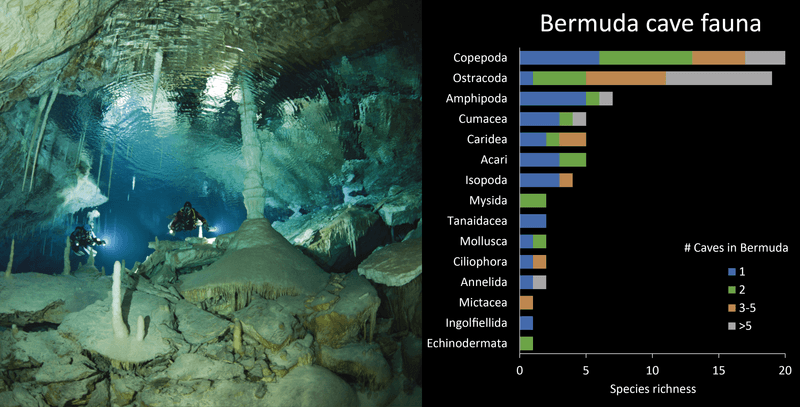
Bermuda’s limestone tidal caves, like the Roadside Cave in the Walsingham District, are unique, hidden ecosystems with challenging conditions.
These caves feature dark, oxygen-poor waters where freshwater and seawater mix, creating a dynamic environment that supports rare and specialized species. The stratified layers and limited light offer a habitat for organisms adapted to survive in nutrient-scarce environments.
Carved from ancient carbonate rock, the caves’ narrow passages and pools remain largely undisturbed, making them biodiversity hotspots.
However, their fragile nature calls for strong conservation efforts to protect the life thriving within.
2. Tetragoniceps Bermudensis: A Newly Discovered Creature
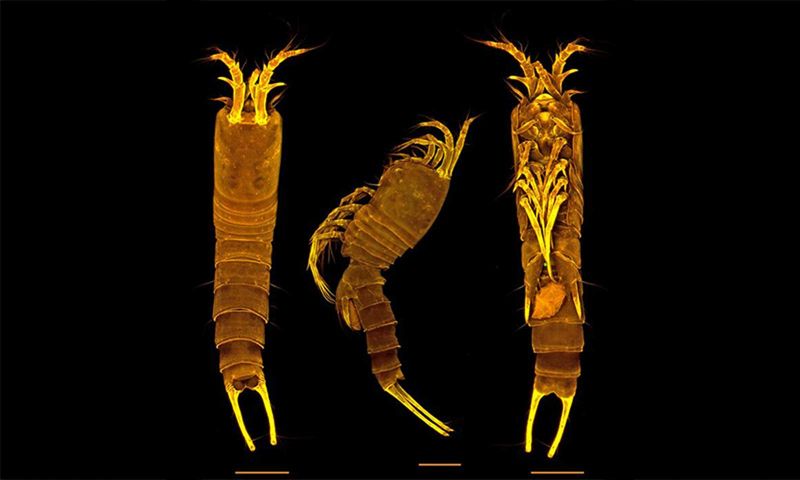

Tetragoniceps bermudensis, a tiny copepod crustacean, has been spotted in Bermuda’s limestone tidal caves, adding to the region’s already rich biodiversity.
This unique creature features a translucent body, adapted to the low-light conditions of the cave, with strikingly delicate features that make it appear almost ghostly.
With its four pairs of legs and a segmented body, it closely resembles other cave-dwelling species, but its distinctive features set it apart.
Tetragoniceps bermudensis thrives in the dynamic environment where fresh and saltwater mix, demonstrating remarkable adaptations to survive in nutrient-poor waters.
Its discovery highlights the mysterious and often overlooked species that inhabit Bermuda’s tidal caves, emphasizing the importance of conserving these delicate ecosystems.
3. Unusual Feeding Behavior

Marine biologists were stunned to witness this crustacean’s bizarre feeding technique. Rather than actively hunting, it creates tiny vortexes with specialized limbs to pull microscopic food particles toward its mouth – a method never before documented in similar species.
The creature can process food items up to 200 times smaller than itself. This remarkable ability allows it to thrive in an environment where larger food sources are scarce.
Even more fascinating, the crustacean appears to sort particles by size and type before consumption, showing an unexpected level of selectivity for such a small organism.
4. Ancient Evolutionary Origins

DNA analysis reveals this mysterious creature might be a living fossil! Preliminary genetic studies suggest Tetragoniceps bermudensis separated from its closest relatives over 100 million years ago, making it a biological time capsule from the Cretaceous period.
The creature shares genetic markers with specimens found in amber deposits, suggesting its ancestors once lived in shallow coastal waters worldwide. Bermuda’s isolated cave systems created the perfect evolutionary sanctuary for this ancient lineage to survive unchanged.
Scientists are particularly excited about studying these genetic time travelers to better understand how marine life evolved through major extinction events.
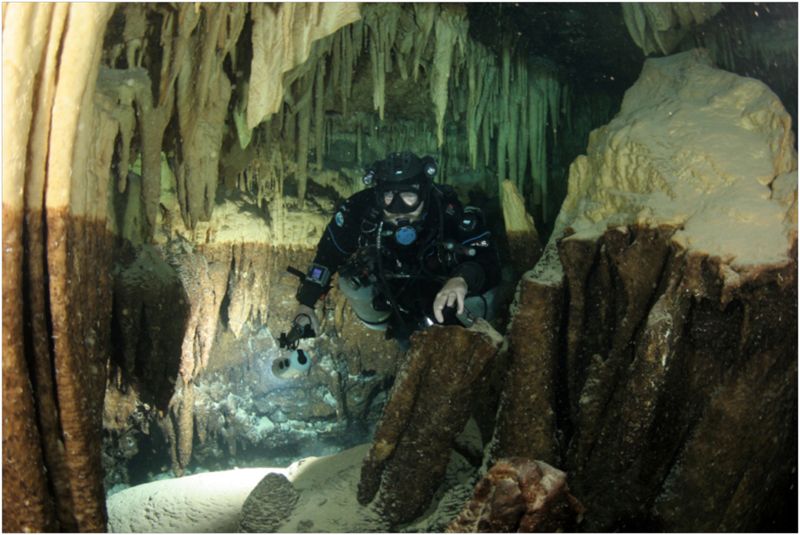
5. Unexpected Symbiotic Relationships
These mysterious creatures don’t live alone! Each specimen hosts tiny bioluminescent bacteria in specialized pouches along their bodies. The bacteria receive protection and nutrients while providing the crustacean with light – a perfect partnership in the dark cave environment.
Even more surprising, the creatures appear to “farm” certain types of cave fungi, deliberately spreading spores to new areas of the cave system. Researchers believe they later feed on the mature fungi, showing remarkable ecological sophistication.
This complex web of relationships helps explain how these creatures thrive in an environment that would be challenging for most other species.
6. A Glimpse Into Evolutionary Adaptation

The discovery of T. bermudensis offers insight into how species adapt in isolated environments. Living in Bermuda’s remote tidal caves, this species has evolved unique traits, like translucent skin, due to its seclusion from predators and competitors.
T. bermudensis is a prime example of how isolation fosters distinct evolutionary paths. Studying such species helps scientists understand how life thrives in extreme conditions and provides valuable knowledge for evolutionary biology and conservation.
7. The Ecological Significance Of T. bermudensis
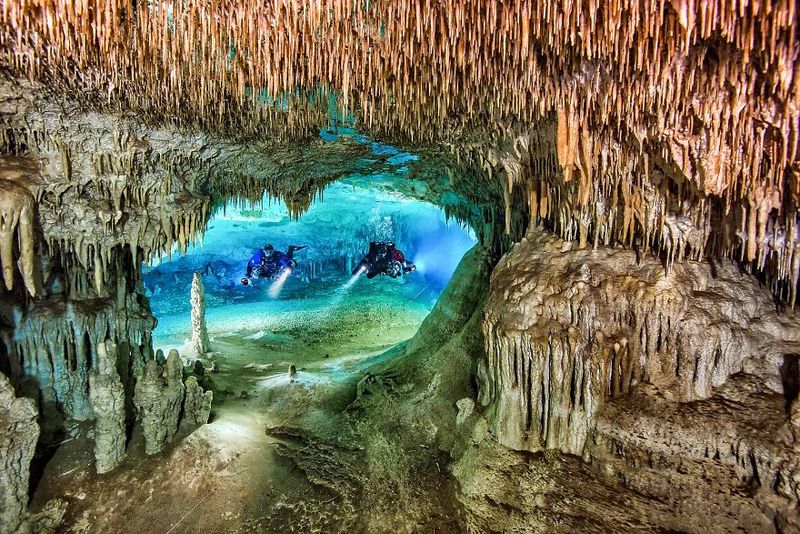

Copepods like T. bermudensis play a vital role in Bermuda’s subterranean ecosystems, acting as primary consumers that channel energy from microscopic algae to larger predators.
In these isolated cave environments, they help maintain the balance of nutrient cycling and energy flow, supporting unique food webs adapted to extreme conditions.
The discovery of T. bermudensis highlights the importance of anchialine caves, where endemic species thrive in fragile ecosystems that are vulnerable to disturbances.
Protecting these habitats is crucial for preserving specialized organisms and the overall health of Bermuda’s hidden biodiversity.
8. The Path From Discovery To Recognition
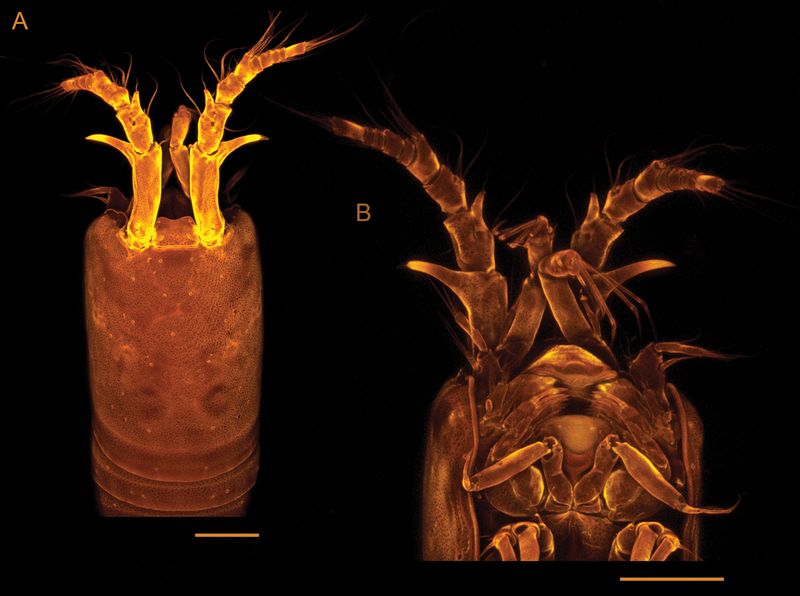
The identification of Tetragoniceps bermudensis took nearly a decade. The first specimen, a female carrying eggs, was found in 2016 during an exploration of Roadside Cave.
Over the years, researchers performed detailed genetic analyses to confirm it as a new species. The formal description was published in 2025 in the journal ZooKeys.
This lengthy process highlights the challenges of studying hidden cave species, relying on advanced techniques and global collaboration.
The discovery demonstrates how careful scientific work uncovers hidden biodiversity in even the most studied regions.
9. Threats To Bermuda’s Cave Ecosystems
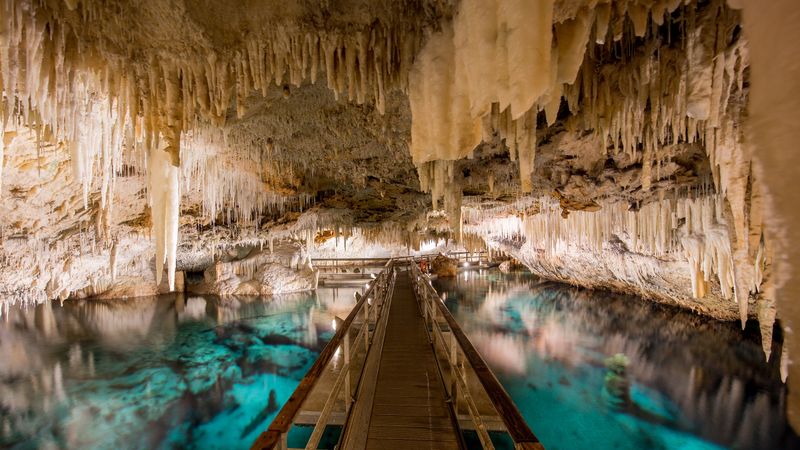

Bermuda’s cave ecosystems are under threat from human activities such as urban development, pollution, and unauthorized access.
These pressures endanger fragile habitats like those of T. bermudensis, where sediment disruption and contamination can upset the delicate balance of anchialine systems, risking the loss of unique species.
Conservationists stress the need for stronger protection of caves like Roadside Cave and better enforcement of existing regulations.
Safeguarding these underground habitats is essential for preserving rare species and maintaining the ecological health of Bermuda’s subterranean biodiversity.
10. The Ongoing Exploration Of Hidden Ecosystems

The discovery of Tetragoniceps bermudensis enhances our understanding of Bermuda’s subterranean biodiversity, highlighting the importance of exploring hidden ecosystems.
It underscores the need for continued research and conservation to uncover and protect life forms in these isolated habitats.
As scientists continue to explore caves around the world, each new species provides valuable insights into evolution, ecology, and the resilience of life.
Protecting these unique environments ensures future generations can study and appreciate the remarkable biodiversity hidden beneath the surface, fostering greater awareness of our planet’s unseen natural wonders.
11. Conservation Concerns
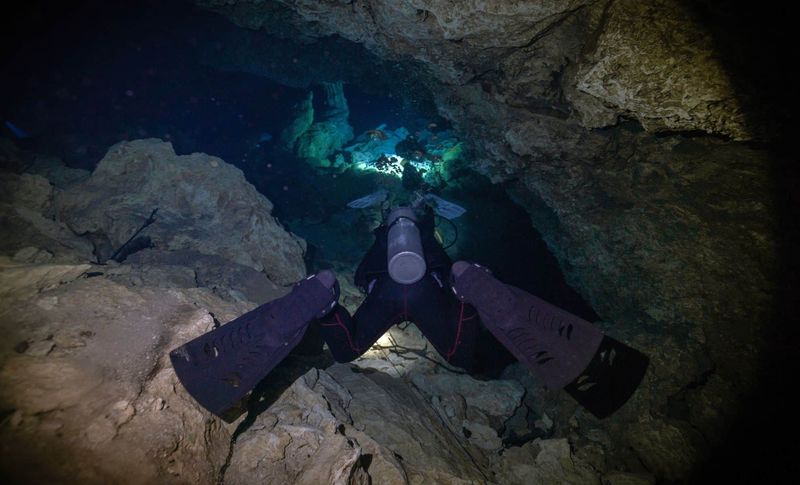

The discovery brings immediate conservation challenges. The cave system hosting these creatures faces potential threats from coastal development and increasing tourism in Bermuda, raising urgent questions about protection.
Scientists worry that even small changes to water quality or cave access could devastate this population. With an estimated total population of fewer than 10,000 individuals confined to just three connected cave systems, the species is inherently vulnerable.
Local conservation authorities have already begun developing a management plan that balances scientific research opportunities with habitat protection, including restricted access zones and water quality monitoring.






