15 Must-Know Differences Between Male And Female Dogs You Should Consider Before Adopting

Choosing a new furry family member is exciting, but did you know a dog’s gender can influence their personality and care needs? Male and female dogs often show distinct behavioral patterns, health considerations, and training responses.
Understanding these differences before bringing home your new best friend can help ensure you find the perfect match for your lifestyle and home environment.
1. Size Matters

Ever noticed how boys tend to be taller than girls in school photos? The same pattern applies to our canine companions. Male dogs typically grow larger and heavier than females of the same breed.
This size difference can affect everything from food costs to the space needed in your home and car. For apartment dwellers or those with limited space, a female might be more practical.
2. Marking Territory
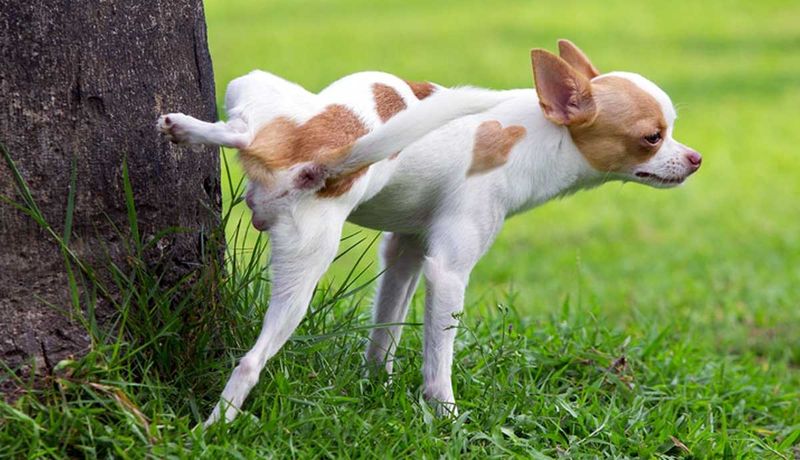

Male dogs have earned quite the reputation as enthusiastic territory markers. They’re programmed to leave their scent everywhere, making walks an exercise in patience as they stop at every lamppost and tree.
Females typically squat and finish business in one spot. This difference might seem small, but imagine dozens of stops during every single walk! Training can help, but those male instincts run deep.
3. Energy Levels

Picture this: your male puppy bouncing off walls while his sister naps in the corner. Many dog owners report male dogs maintain puppy-like playfulness longer into adulthood.
Females often mature faster mentally, showing more focus during training sessions. This energy difference isn’t universal across all breeds, but it’s something to consider if you’re looking for a jogging partner versus a cuddle buddy.
4. Affection Styles

Boys wear their hearts on their paws! Male dogs often show affection more openly and consistently, frequently seeking cuddles and attention from their humans.
Females tend toward independence, choosing when they want affection rather than constantly demanding it. Neither style is better – just different. Consider which matches your own need for doggy affection when choosing your furry companion.
5. Training Responsiveness

Training sessions reveal fascinating gender differences. Female dogs typically focus better during training, picking up commands faster and showing more consistent responses.
Males can learn just as well but are more easily distracted by interesting smells or potential playmates. Their “what’s in it for me?” attitude means they might need more motivation through treats or play rewards to stay engaged.
6. Health Costs
Your wallet feels the gender difference too! Spaying (females) typically costs more than neutering (males) because it’s a more complex surgery requiring longer anesthesia and recovery time.
Beyond the initial surgery, females face potential mammary tumors and uterine infections if not spayed. Males have their own concerns with prostate issues and testicular cancer. Budget-conscious adopters should factor these differences into their planning.
7. Mood Swings

Unspayed females experience heat cycles twice yearly, bringing hormone-driven mood changes and unwanted attention from male dogs. During these periods, they might become clingy, restless, or irritable.
Males tend to have more consistent personalities year-round if neutered. However, intact males can become frustrated and difficult to manage when they detect a female in heat, even from impressive distances!
8. Social Dynamics

Watch dogs at the park and you’ll notice gender-based social patterns. Males typically establish hierarchy through physical posturing and occasional scuffles, but quickly move on once order is established.
Females often form more complex social relationships and can hold grudges longer after conflicts. Many trainers note that two females are more likely to have serious fights than male-male or male-female combinations in multi-dog households.
9. Territorial Behavior

Surprise! Female dogs often guard home territory more fiercely than males. They tend to be more suspicious of strangers entering their domain and may bark more persistently at perceived threats.
Males typically show more interest in expanding territory during walks. This difference makes females excellent watchdogs, while males might welcome burglars with wagging tails if properly socialized (though individual personality always plays a role).
10. Maturation Timeline

Female puppies typically hit the teenage rebellion phase earlier but also mature faster mentally. By one year, many females display adult behavior patterns while males still embrace puppy chaos.
This earlier maturation means females often finish house training faster. For first-time dog owners with limited patience, this head start can be a blessing during those challenging early months of establishing routines.
11. Bonding Patterns

Male dogs often form strong attachments to all family members equally, spreading their affection generously. They’re the social butterflies of the canine world.
Females frequently bond more intensely with one primary person. This creates a special connection but can appear as aloofness to other family members. Consider family dynamics when choosing – nobody wants to feel left out of doggy love!
12. Problem-Solving Approaches
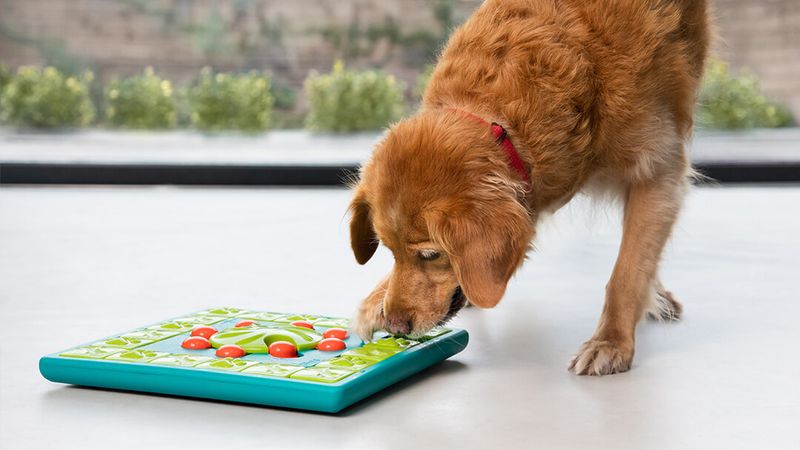

Faced with a puzzle toy, males and females often tackle the challenge differently. Males typically use brute force – pawing, chewing, or tossing the toy until treats emerge.
Females show more patience and methodical problem-solving. This difference extends to training scenarios too. Males might try multiple approaches rapidly, while females observe longer before attempting a solution. Both strategies work – just through different paths!
13. Stubbornness Factors

When a male dog doesn’t want to do something, he’ll make it obvious with dramatic sighs and flopping to the ground. Their resistance is transparent and often comical.
Females excel at passive resistance – appearing to comply while subtly doing exactly what they wanted all along. Many trainers joke that female dogs train their owners better than vice versa! Both genders require consistent boundaries regardless of their negotiation tactics.
14. Protective Instincts

Female dogs show remarkable protective instincts toward children, often treating them like puppies needing supervision. This maternal instinct exists even in females who’ve never had puppies.
Males protect through different means – often positioning themselves between perceived threats and their family. Rather than hovering close like females, they may patrol perimeters. Both approaches stem from the same loyal devotion, just expressed through different behaviors.
15. Long-Term Health Considerations

Beyond reproductive differences, male and female dogs face different health challenges throughout life. Females have higher rates of certain autoimmune diseases and urinary tract infections.
Males more frequently develop certain orthopedic issues and heart problems in some breeds. These differences vary widely by breed, so research your specific breed’s gender-related health tendencies before making your decision. Your vet can provide valuable insight into these patterns.






