Experts Warn – California’s Monarch Butterflies In Crisis

California’s Monarch butterflies, once a symbol of the vibrant ecosystem, are now facing severe challenges threatening their very existence.
These beautiful creatures have seen a dramatic decline in numbers, sparking concern among environmentalists and scientists alike.
Join us as we uncover the critical challenges facing California’s Monarch butterflies, and explore ways we can all contribute to their survival.
1. Habitat Loss

Habitat loss stands as a monumental threat to the Monarch butterflies in California. Urban expansion and agricultural development have resulted in the destruction of vast areas of natural habitat, particularly milkweed plants, which are essential for Monarch larvae. The disappearance of these crucial plants means fewer breeding grounds for the butterflies. Monarchs are highly dependent on specific environments, and when these are destroyed, their delicate life cycle is severely disrupted.
Furthermore, the increasing use of herbicides has drastically reduced the availability of milkweed. Many farmers and landowners unknowingly contribute to this issue by prioritizing crop yield over biodiversity. This trend has severe implications for Monarch populations, leading to a dwindling number of butterflies returning each year.
Addressing habitat loss requires a concerted effort to educate communities about the importance of preserving natural landscapes and implementing butterfly-friendly practices. Creating butterfly gardens and supporting conservation efforts can be vital steps in restoring Monarch populations. As awareness grows, individuals and communities can unite to safeguard these magnificent creatures and ensure a brighter future for them.
2. Climate Change

Climate change is undeniably impacting the Monarch butterflies in California. These insects are particularly sensitive to weather patterns, and sudden changes can have devastating effects on their migration and breeding cycles. Unpredictable weather, such as late frosts or intense storms, can result in the destruction of eggs and larvae.
Additionally, rising temperatures pose another threat, altering the delicate balance of ecosystems that Monarchs rely upon. As temperatures increase, the availability of food sources such as nectar from flowers may be diminished, creating further challenges for the butterflies.
Adapting to these changes requires a multifaceted approach. Encouraging the planting of native plants that can withstand climate shifts and supporting initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions can help. Public awareness campaigns can educate individuals about the effects of climate change on wildlife. By taking action, we can help create an environment that supports Monarchs and other vulnerable species, emphasizing the need for collective responsibility in combating climate change.
3. Pesticide Use

The widespread use of pesticides is contributing significantly to the decline of Monarch butterflies in California. These chemicals, designed to kill pests, often have harmful effects on non-target species, including the Monarchs. Pesticides can contaminate milkweed and other plants, leading to poisoning of larvae and adult butterflies.
Pesticides disrupt the balance of ecosystems, affecting the availability of food sources for the butterflies. This disruption can lead to malnutrition and decreased survival rates among the population. As pesticides become more prevalent in agricultural practices, the risks to Monarchs continue to grow, highlighting an urgent need for alternative solutions.
Promoting organic farming and integrated pest management practices can reduce the dependency on harmful chemicals. Encouraging farmers to adopt eco-friendly techniques and educating the public about the detrimental effects of pesticides can pave the way for a more sustainable environment. By making conscientious choices, we can protect the Monarch butterflies and ensure their presence for future generations.
4. Deforestation

Deforestation is another critical issue impacting Monarch butterflies in California. The removal of trees and vegetation for development or agriculture removes essential habitats for these butterflies. Monarchs are highly dependent on specific trees for roosting during their migration, and losing these areas can disrupt their journey.
The loss of forests also affects the microclimate that Monarchs rely on. Without the protective cover of trees, they become more vulnerable to extreme weather conditions. This exposure can lead to increased mortality rates, especially during migration and breeding seasons.
Reforestation and conservation projects are vital in counteracting deforestation’s impact. Planting native trees and creating protected areas can provide Monarchs with the necessary habitats to thrive. Supporting organizations focused on forest conservation and participating in local tree-planting initiatives can make a significant difference. By taking these steps, we can help restore the natural balance and support the survival of Monarch butterflies.
5. Pollution

Pollution poses a significant threat to the Monarch butterflies in California. Contaminated water sources and air pollution can lead to health issues for both larvae and adult butterflies. Toxic substances in the environment may interfere with their ability to feed, breed, and thrive.
Air pollution can also affect the availability of nectar-producing plants, essential for the butterflies’ survival. Polluted environments often result in reduced plant growth, limiting the food sources for Monarchs. This scarcity can lead to weakened butterflies, unable to complete their migration or reproduction cycles.
Addressing pollution requires a collective effort from individuals, communities, and policymakers. Supporting clean energy initiatives, reducing waste, and advocating for stricter regulations on pollutants can help create a healthier environment for the butterflies. By raising awareness and taking action, we can reduce the harmful effects of pollution and contribute to the recovery of Monarch populations.
6. Urbanization

Urbanization represents a growing challenge for Monarch butterflies in California. As cities expand, natural habitats are increasingly being transformed into urban landscapes. This shift leads to the fragmentation of ecosystems, making it difficult for Monarchs to find suitable breeding and feeding areas.
The encroachment of urban areas also results in increased light pollution, which can interfere with the butterflies’ natural behaviors, including navigation and reproduction. Light pollution disrupts their internal clocks, leading to disorientation and increased mortality rates.
Promoting urban planning that considers wildlife preservation can help mitigate these effects. Incorporating green spaces, such as butterfly gardens and parks, into urban designs can provide Monarchs with essential habitats.
Educating urban dwellers about the importance of biodiversity and encouraging community involvement in conservation efforts can foster a more harmonious coexistence between humans and nature. By prioritizing sustainable urban development, we can support the survival of Monarch butterflies in our cities.
7. Disease
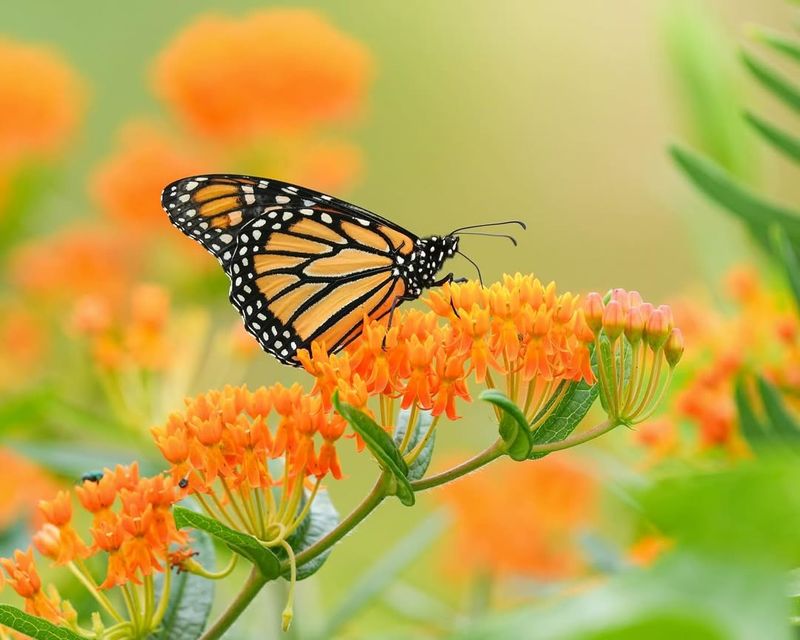

Disease outbreaks are becoming an increasingly concerning threat to Monarch butterflies in California. Pathogens and parasites can spread rapidly within butterfly populations, leading to weakened individuals and increased mortality rates. The overcrowding of habitats, often due to habitat loss, exacerbates this issue, making it easier for diseases to spread.
Parasites such as the Ophryocystis elektroscirrha (OE) have been known to affect Monarchs, causing deformities and reducing their ability to migrate successfully. The increased stress from environmental changes can also make butterflies more susceptible to infections.
Efforts to combat these diseases require monitoring and research to understand the spread and impact better. Encouraging the planting of milkweed and other native plants can help reduce overcrowding and provide healthier environments for Monarchs. Supporting research initiatives focused on disease prevention and treatment can further aid in protecting these vulnerable creatures. By taking proactive measures, we can help ensure the resilience of Monarch butterflies against disease threats.
8. Genetic Diversity Loss
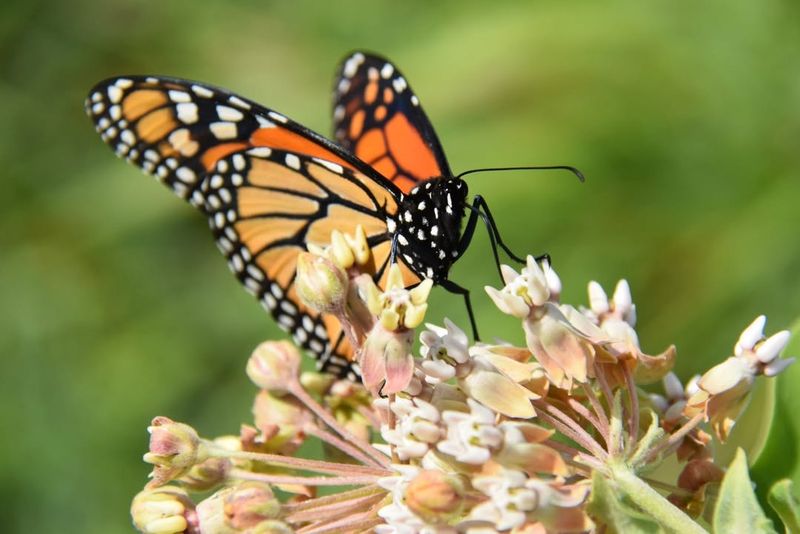

Genetic diversity is crucial for the survival and adaptability of Monarch butterflies in California. A lack of genetic variation can make populations more susceptible to diseases, environmental changes, and other threats. The decline in Monarch numbers has led to reduced genetic diversity, posing a significant risk to their long-term survival.
Inbreeding within small populations can result in weakened individuals and decreased reproductive success. This issue is exacerbated by habitat fragmentation, which isolates groups of Monarchs and limits opportunities for genetic exchange.
Conservation efforts aimed at promoting genetic diversity are vital in addressing this challenge. Initiating breeding programs and facilitating the movement of butterflies between isolated habitats can help increase genetic variation. Supporting initiatives that focus on restoring and connecting habitats can create corridors for migration and genetic exchange. By fostering a diverse and resilient population, we can contribute to the Monarchs’ ability to adapt and thrive in a changing environment.
9. Lack Of Public Awareness
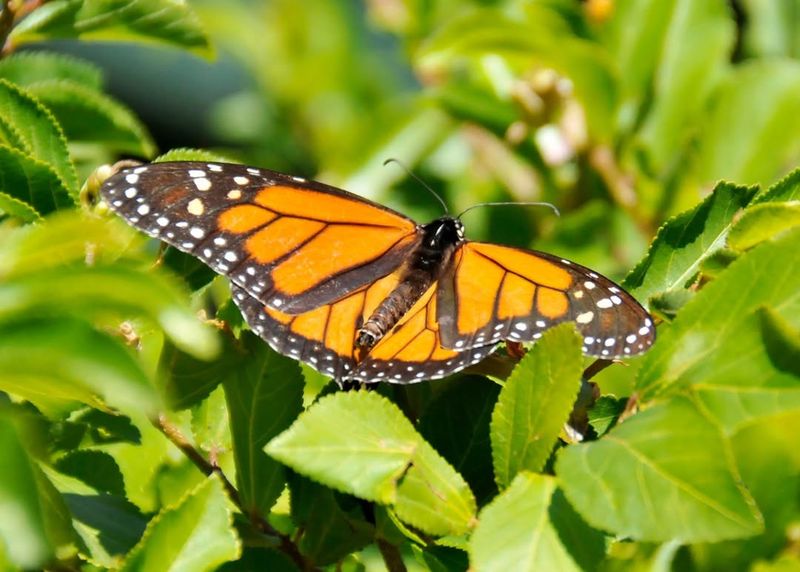

Public awareness plays a pivotal role in the conservation of Monarch butterflies in California. Many people are unaware of the challenges facing these beautiful creatures and the actions they can take to help. Increasing awareness can lead to greater conservation efforts and support for policies that protect Monarch habitats.
Educational programs and community outreach initiatives can inform the public about the importance of Monarch butterflies and the threats they face. Schools, local organizations, and social media platforms can all contribute to spreading knowledge and encouraging individual action.
Engaging the public in conservation activities, such as planting milkweed gardens and participating in butterfly counts, can foster a sense of responsibility and connection to the natural world. By raising awareness and inspiring action, we can create a community of informed advocates dedicated to preserving the Monarch butterfly population. Together, we can ensure these iconic insects continue to grace California’s landscapes.
10. Invasive Species
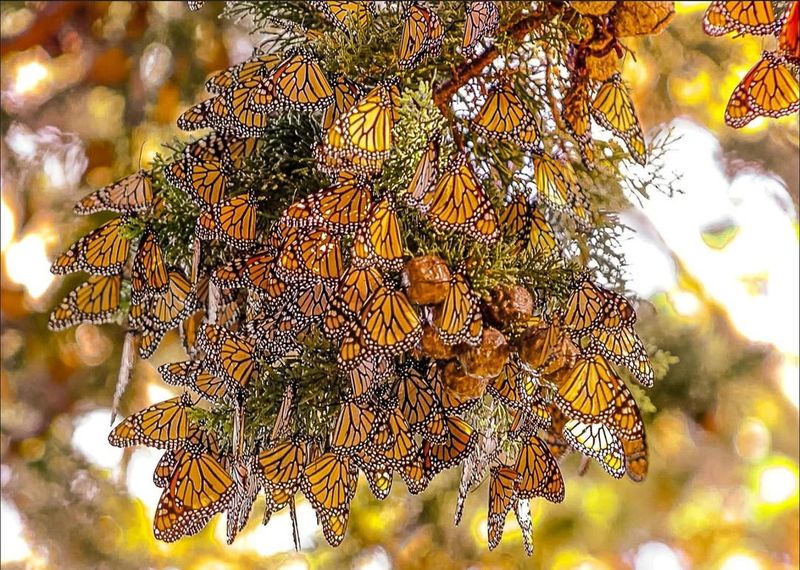

Invasive species present a growing threat to the Monarch butterflies in California. Non-native plants and animals can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, outcompeting native species that Monarchs rely on for survival. This competition can lead to the decline of essential food sources and breeding grounds.
Invasive plants, for example, may overtake milkweed and other native flora, reducing the availability of resources needed for Monarch larvae development. The presence of invasive predators can also lead to increased mortality rates among butterflies.
Preventing the spread of invasive species requires concerted efforts from individuals and communities. Supporting local conservation projects that focus on removing invasive species and restoring native habitats is crucial. Educating the public about the dangers of invasive species and promoting the use of native plants in landscaping can further help protect Monarch habitats. By actively managing and restoring ecosystems, we can support the resilience of Monarch butterflies against these threats.
11. Overwintering Site Destruction
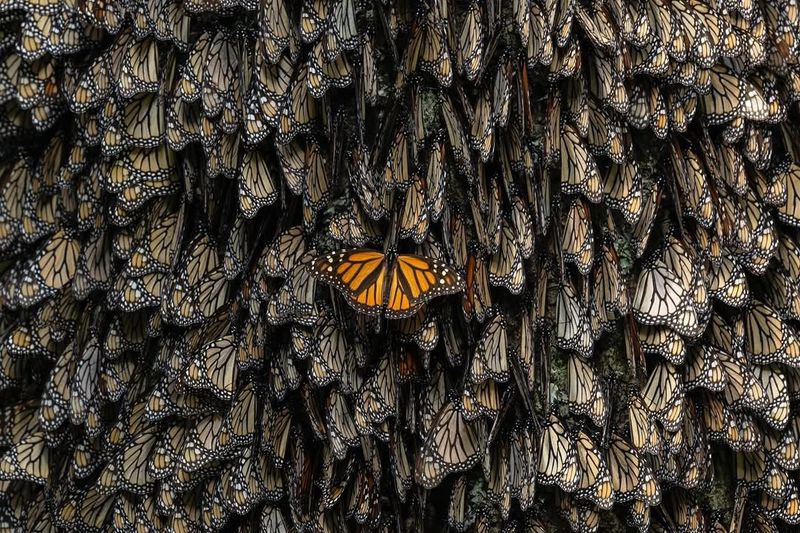

Overwintering sites are essential for the survival of Monarch butterflies, providing a safe haven during colder months. In California, these sites are under threat due to human activities and environmental changes. Destruction of overwintering habitats can lead to increased mortality rates and decreased population numbers.
Human development and land-use changes often encroach on these vital areas, reducing the available space for Monarchs to rest and recover. Climate change exacerbates these challenges, altering the environmental conditions that make these sites suitable for overwintering.
Protecting overwintering sites requires collaboration between conservation organizations, local communities, and policymakers. Establishing protected areas and implementing regulations to limit development in critical habitats can help safeguard these essential sites. By supporting conservation efforts and promoting awareness of the importance of overwintering habitats, we can ensure Monarch butterflies have the refuge they need to thrive year after year.
12. Migration Barriers
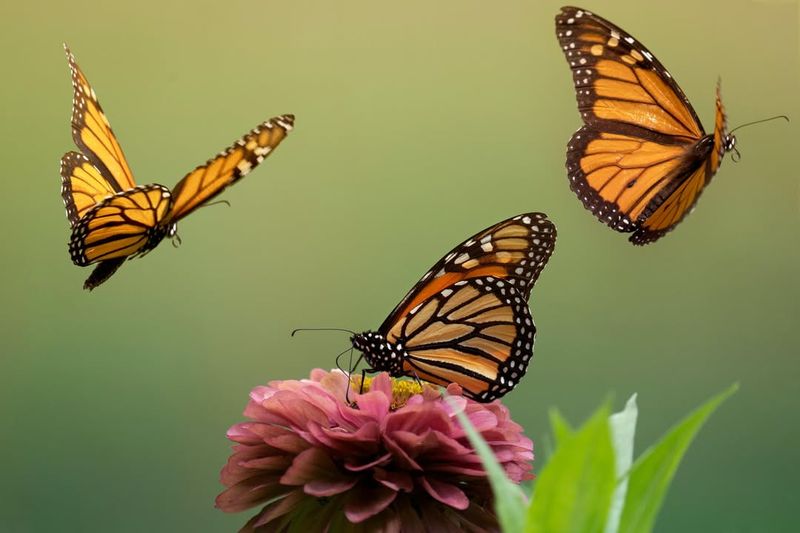

Migration is a critical part of the life cycle of Monarch butterflies, yet human-made barriers increasingly hinder their journey. Urban development, highways, and other structures create obstacles that Monarchs must navigate, leading to increased energy expenditure and mortality rates.
These barriers can fragment habitats, making it challenging for butterflies to find food and breeding sites along their migration routes. Additionally, light pollution from urban areas can disorient Monarchs, further complicating their already perilous journeys.
Addressing migration barriers involves strategic planning and collaboration. Creating Monarch-friendly corridors, reducing light pollution, and implementing wildlife crossings over highways can help facilitate safe migration. Community engagement in conservation efforts can also play a role in identifying and mitigating barriers. By working together, we can support the Monarchs’ incredible migratory journey and ensure their continued survival.
13. Nectar Source Decline

The decline in nectar sources poses a significant threat to Monarch butterflies in California. Flowers that provide essential nectar are dwindling due to environmental changes and human activities. This scarcity can lead to malnutrition, weakened immune systems, and decreased reproductive success among Monarchs.
Climate change and urbanization are key contributors to the decline of flowering plants. Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect the blooming cycles of plants, leading to mismatches between flower availability and butterfly needs.
Promoting the planting of native flowering plants and supporting conservation initiatives can help address this issue. Creating butterfly gardens and encouraging the use of pollinator-friendly plants in landscaping can provide Monarchs with vital nectar sources. By focusing on restoring and maintaining healthy ecosystems, we can support the Monarchs’ nutritional needs and contribute to their survival.
14. Lack Of Scientific Research

Lack of scientific research is a significant barrier to understanding and addressing the challenges faced by Monarch butterflies in California. Comprehensive studies are needed to assess the impact of various threats and inform effective conservation strategies.
Funding limitations and competing priorities often hinder research efforts, leading to gaps in knowledge about Monarch behavior, migration patterns, and population dynamics. Without this information, it becomes difficult to develop targeted conservation measures that can effectively address the butterflies’ needs.
Supporting scientific research through funding and collaboration can help fill these gaps and provide insights into the best practices for Monarch conservation. Engaging academic institutions, government agencies, and non-profit organizations in research initiatives can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of the issues at hand. By prioritizing research, we can develop informed strategies that support the long-term survival of Monarch butterflies.