14 Creatures That Can Regenerate Entire Nervous Systems

The ability to regenerate entire nervous systems is a fascinating feature exhibited by certain creatures in the animal kingdom.
This extraordinary capacity allows them to recover from severe injuries that would be devastating to others. In this article, we explore 14 amazing creatures that possess this remarkable regeneration ability.
1. Axolotl
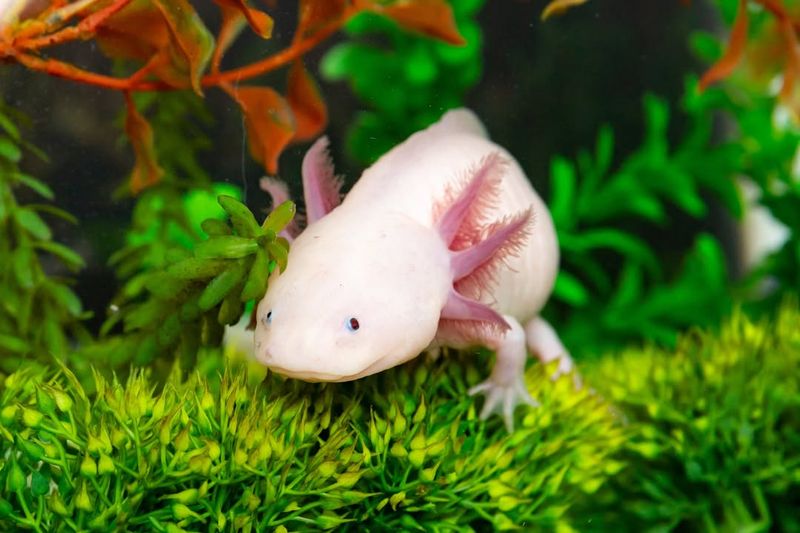

The axolotl is renowned for its exceptional regenerative abilities. Unlike most vertebrates, these aquatic salamanders can completely regrow not only limbs but also parts of their spinal cords and brains. This capability allows them to recover from injuries that would be devastating to other species.
In their natural habitat in Mexico’s freshwater lakes, axolotls thrive in an environment rich in nutrients and oxygen. This unique feature of axolotls has made them a subject of fascination and study in scientific research.
Scientists are keen to understand the molecular mechanisms behind such regeneration. Translating these findings could lead to breakthroughs in human medicine, especially in nerve repair.
Axolotls’ regenerative prowess is attributed to their stem cells, which are capable of transforming into various cell types. This quality makes them an important model organism in the field of regenerative biology and a marvel of nature’s ingenuity.
2. Planarian
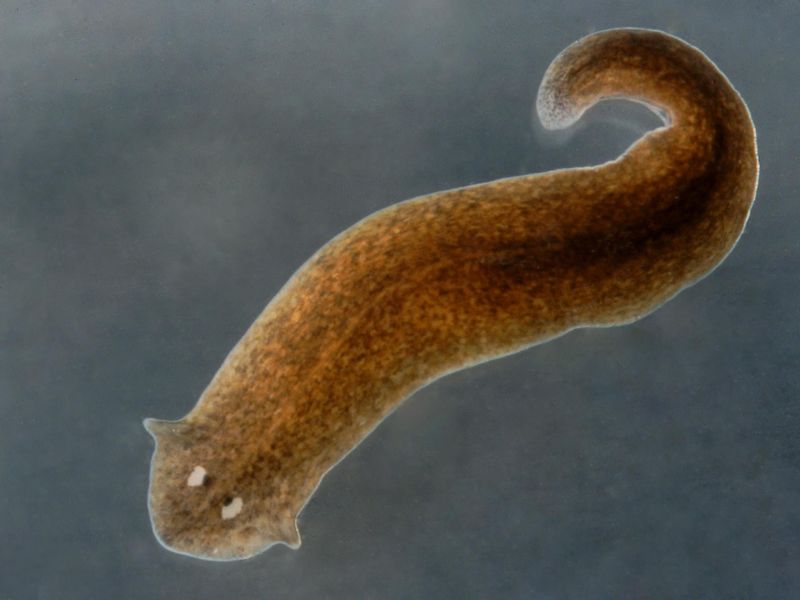
Planarians are flatworms celebrated for their incredible regenerative abilities. When a planarian is cut into pieces, each piece can regenerate into a complete organism. This feat is made possible by a special type of stem cell called neoblasts, which are abundant throughout their bodies.
Neoblasts can differentiate into any cell type, allowing the flatworm to heal from almost any damage. Resident in freshwater habitats, planarians are essential study subjects in biological research.
Scientists are particularly interested in understanding how their regenerative capabilities can be applied to human medicine. Their simplicity and regenerative power make them ideal for laboratory studies.
The genetic and cellular processes that govern planarian regeneration offer insights into healing and regeneration in more complex organisms. These worms are not only important to biological research but also demonstrate the astounding diversity of life forms capable of regeneration.
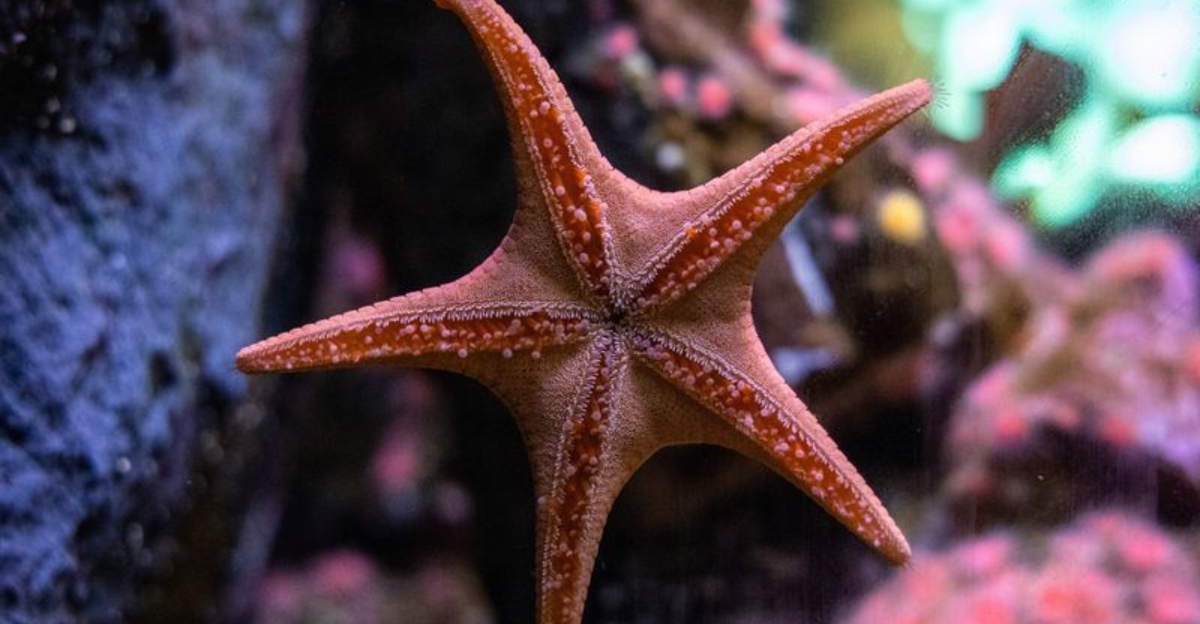
3. Sea Star
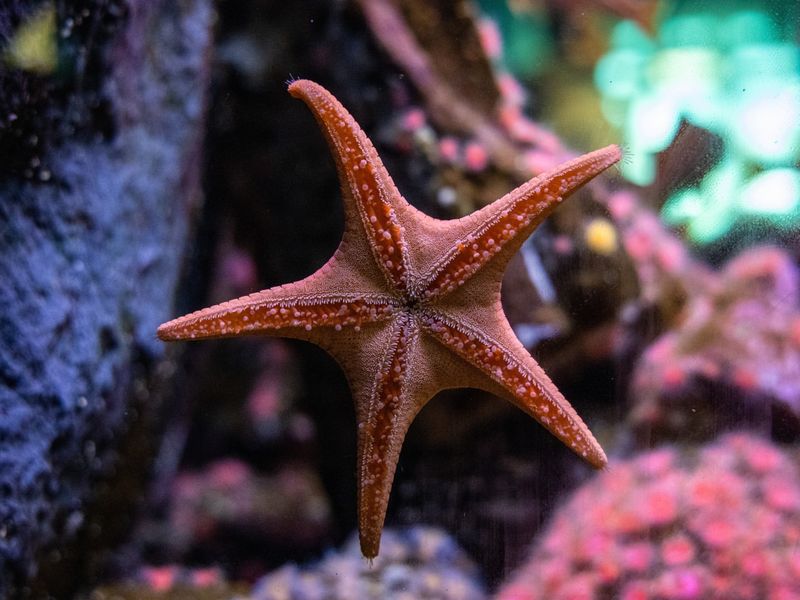

Sea stars, commonly known as starfish, possess the remarkable ability to regenerate entire limbs and, in some species, their entire nervous systems. This regeneration is crucial for survival, as losing limbs to predators is a common occurrence.
The process begins with the formation of a small structure called a blastema at the wound site, which facilitates new growth. In their natural marine environments, sea stars contribute significantly to the ecosystem’s balance by preying on mollusks.
Their presence is vital in controlling the population of their prey. The regenerative process in sea stars has drawn interest from scientists aiming to understand the cellular mechanisms involved. These creatures exemplify resilience and adaptability in the animal kingdom.
Their ability to regenerate allows them not only to recover from injuries but also to reproduce asexually by splitting their bodies. This resilience is a testament to the wonders of evolution and adaptation.
4. Zebrafish
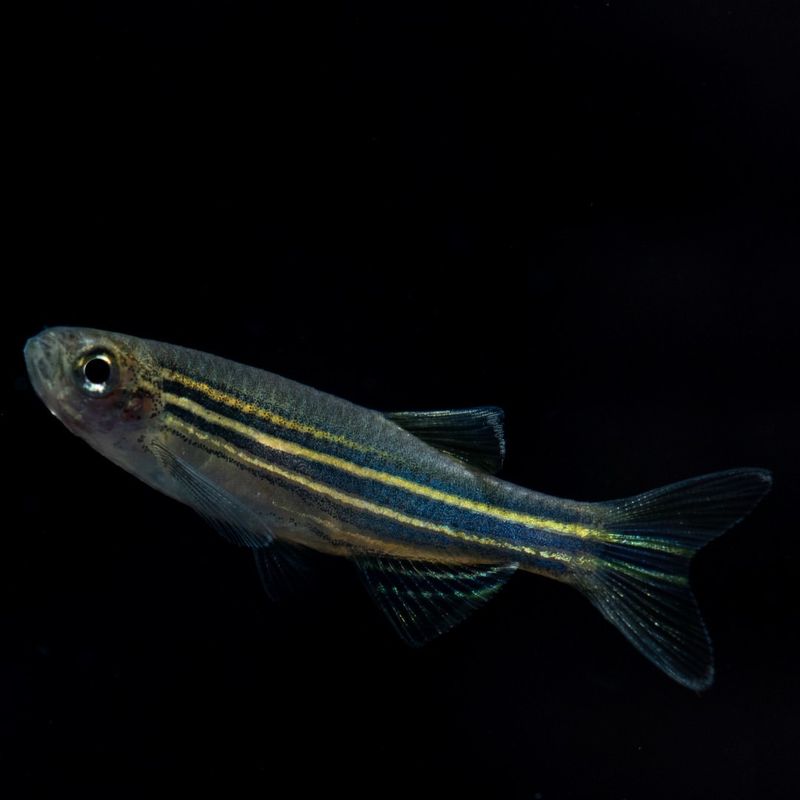

Zebrafish are small freshwater fish renowned for their ability to regenerate various tissues, including parts of their central nervous system. This capability includes the regeneration of their spinal cord, retinas, and even parts of their heart.
In scientific research, zebrafish serve as a model organism due to their genetic similarity to humans. The regenerative abilities of zebrafish have made them a valuable resource for studying human diseases.
By understanding the processes behind their regeneration, researchers aim to translate these mechanisms into potential treatments for spinal cord injuries and degenerative diseases. Their transparent embryos and rapid development make zebrafish particularly useful in laboratory settings.
This transparency allows scientists to observe cellular processes in real-time, providing insights into the complex nature of tissue regeneration. Zebrafish continue to contribute to the field of regenerative medicine, offering hope for future medical advancements.
5. Sea Cucumber
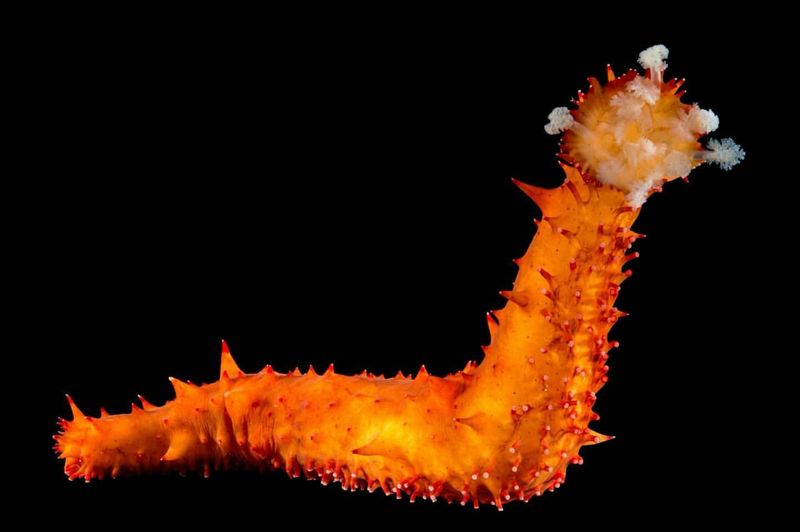

Sea cucumbers are marine animals closely related to sea stars and sea urchins. Known for their unique defense mechanisms, they can expel their internal organs when threatened.
Remarkably, these animals can regenerate the expelled organs, including parts of their nervous system, in a process that can take several weeks. In their ocean environments, sea cucumbers play a vital role in nutrient recycling by breaking down detritus and organic matter.
Their regenerative abilities have intrigued scientists, who are investigating the cellular and molecular basis of this process to apply it to human tissue regeneration. The study of sea cucumbers offers insights into the potential for regenerative medicine and organ replacement therapies.
Their ability to regenerate complex internal structures demonstrates nature’s capability to overcome damage and adapt to environmental challenges, showcasing the resilience inherent in marine life.
6. Lizard
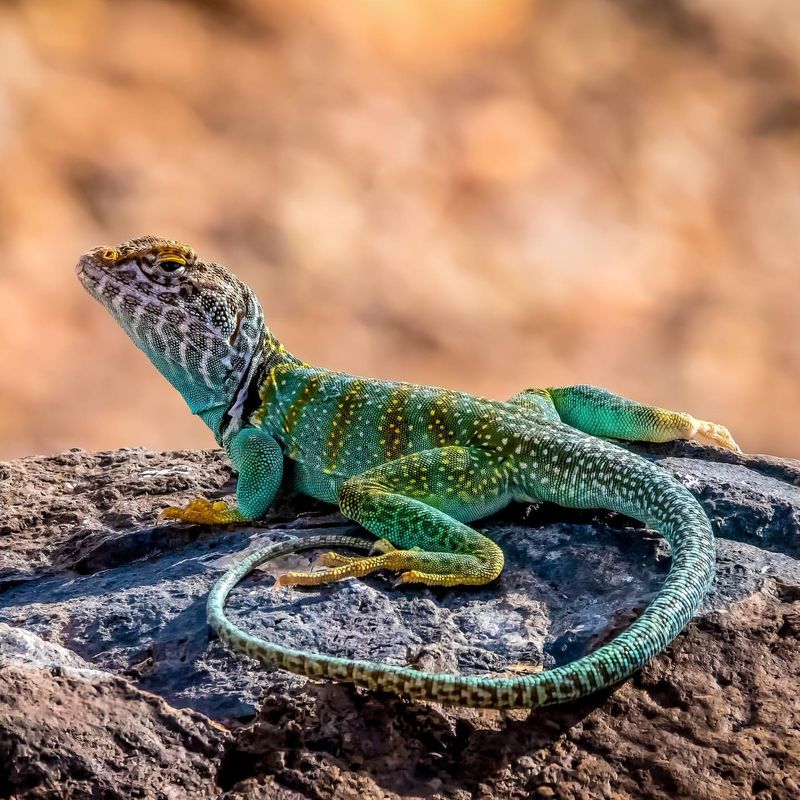

Many lizard species are famous for their ability to regenerate their tails after losing them to predators or other threats. This adaptation provides a survival advantage, allowing them to escape while leaving part of their tail behind.
The new tail grows back over several months, although it may not be identical to the original. The regenerative process involves complex cellular activities and is a subject of scientific curiosity.
It could hold keys to understanding how similar processes might be applied to human medicine, particularly in the areas of spinal cord injuries and limb regeneration.
Studying lizards’ regenerative abilities not only enhances our understanding of reptilian biology but also provides inspiration for developing new strategies in regenerative therapies. Their natural resilience and adaptability emphasize the incredible diversity of survival mechanisms in the animal kingdom.
7. Echinoderm
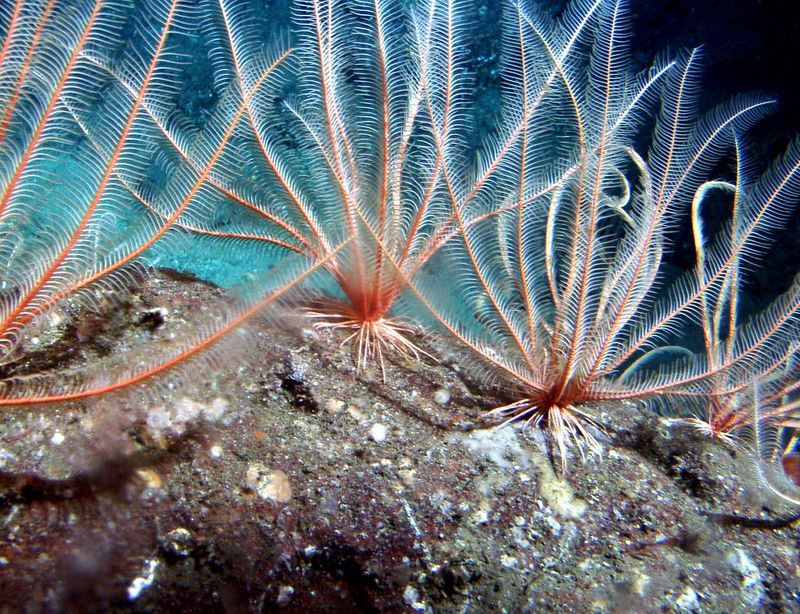

Echinoderms, including brittle stars and feather stars, are known for their impressive ability to regenerate arms and parts of their nervous systems. These marine animals use regeneration as a means of defense, allowing them to survive in predator-rich environments by sacrificing limbs and growing them back.
In their natural habitats, echinoderms contribute to the marine ecosystem by being both prey and predator, maintaining ecological balance. The study of their regenerative mechanisms provides valuable insights into cellular regeneration and differentiation.
Their ability to regenerate complex structures is not only fascinating but also has potential applications in understanding human tissue regeneration.
By examining echinoderms, scientists hope to uncover the molecular pathways that could lead to advancements in regenerative medicine. These creatures epitomize the remarkable regenerative capabilities found in marine life.
8. Hydra
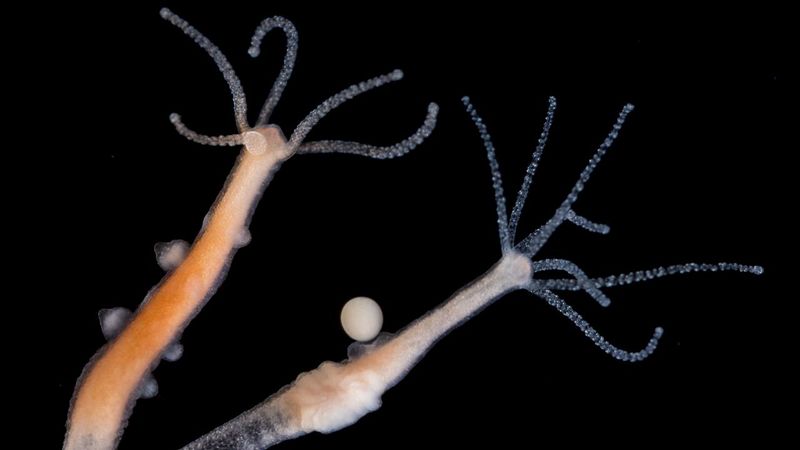
Hydras are small, freshwater organisms that belong to the phylum Cnidaria. They are renowned for their incredible regenerative abilities, capable of completely regenerating a new individual from just a small fragment of their body.
This remarkable feature is due to their high proportion of stem cells that can differentiate into any cell type. In laboratory settings, hydras are significant for studying regeneration and cellular differentiation.
Their ability to continually renew their cells provides insights into aging and immortality, as they do not appear to undergo senescence. Hydras’ regenerative capacity makes them a model organism for researchers exploring cellular biology and regeneration.
Understanding their mechanisms could lead to breakthroughs in regenerative medicine, offering potential therapies for age-related diseases and injuries. Their simplicity and regenerative prowess highlight the extraordinary capabilities of even the most diminutive life forms.
9. Crayfish
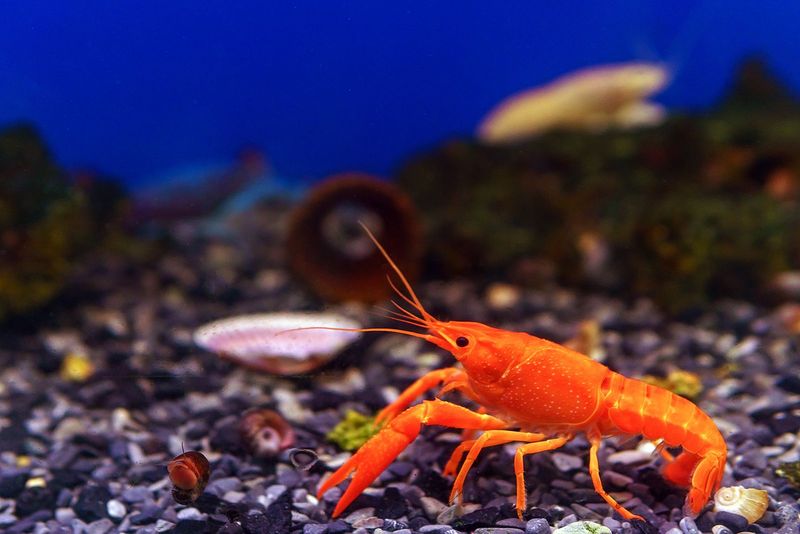

Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans known for their ability to regenerate lost appendages, including claws and antennae. This regeneration is vital for their survival, enabling them to recover from predatory attacks and continue foraging and mating.
The process relies on a complex interplay of cellular and molecular events, resulting in the regrowth of lost parts over time. In their aquatic environments, crayfish play crucial roles in maintaining the ecosystem by controlling algae and detritus levels.
The study of crayfish regeneration has significant implications for understanding tissue regeneration in more complex organisms, including humans. Research into their regenerative mechanisms may unlock new approaches to regenerative medicine and limb restoration.
Their ability to regrow complex structures exemplifies the resilience and adaptability found in crustaceans and presents exciting possibilities for biological research.
10. Salamander
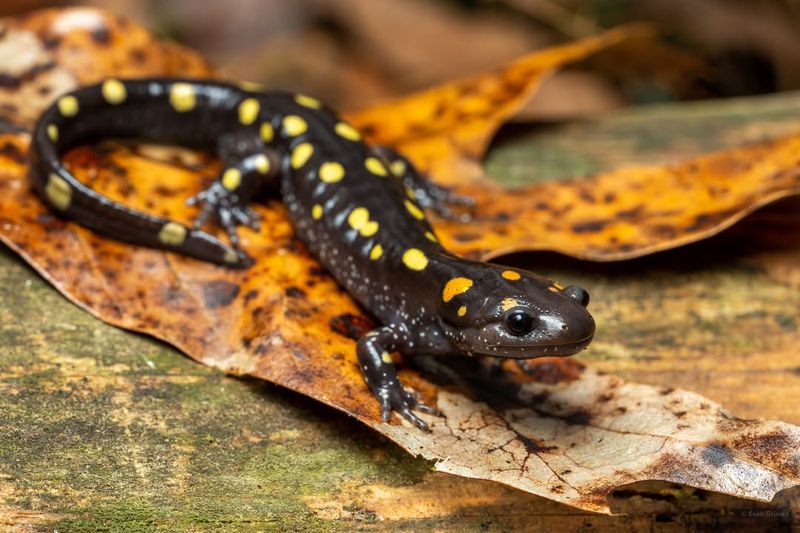

Salamanders are amphibians well-known for their extraordinary regenerative abilities, capable of regenerating limbs, tails, and even parts of their spinal cords and hearts. This ability provides them with a significant survival advantage, allowing them to recover from injuries that would be catastrophic for other animals.
These creatures thrive in moist, forested environments where they play essential roles in controlling insect populations. The regenerative properties of salamanders have made them subjects of extensive scientific research, with the aim of applying these findings to human medicine.
Understanding the cellular and molecular pathways involved in salamander regeneration could lead to breakthroughs in treating spinal cord injuries and heart diseases.
Their impressive regenerative capabilities continue to inspire advancements in the field of regenerative biology, highlighting the potential for healing and recovery in nature.
11. Flatworm
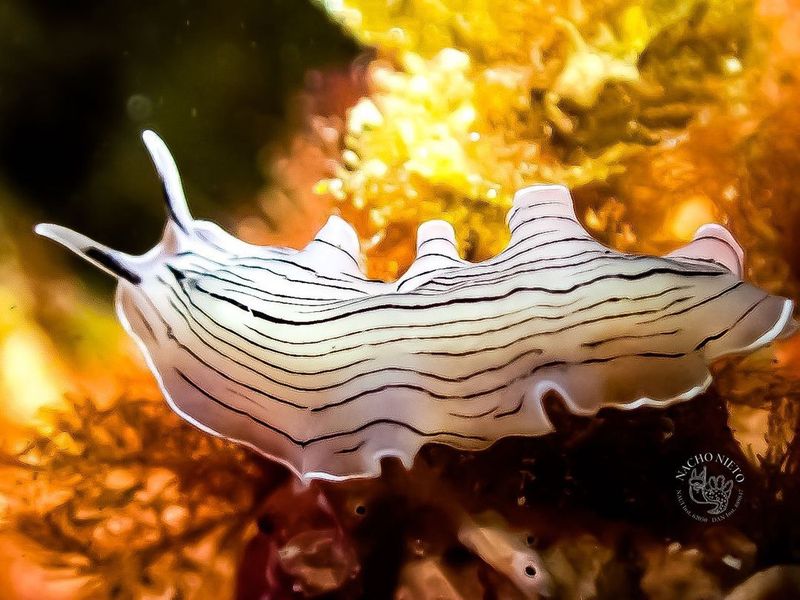

Flatworms, particularly planarians, are renowned for their remarkable regenerative abilities, capable of reforming their entire bodies from small fragments. This ability is due to the presence of stem cells called neoblasts, which can differentiate into any cell type needed for regeneration.
These creatures inhabit various environments, from freshwater to terrestrial habitats, where they play roles in controlling pest populations. The study of flatworms provides insights into the mechanisms of regeneration and stem cell biology, with the potential to influence human regenerative medicine.
Research into flatworm regeneration may lead to novel approaches in tissue engineering and regenerative therapies.
Their ability to restore entire body structures underscores the extraordinary regenerative capabilities inherent in even the simplest organisms, offering a deeper understanding of biological processes.
12. Octopus
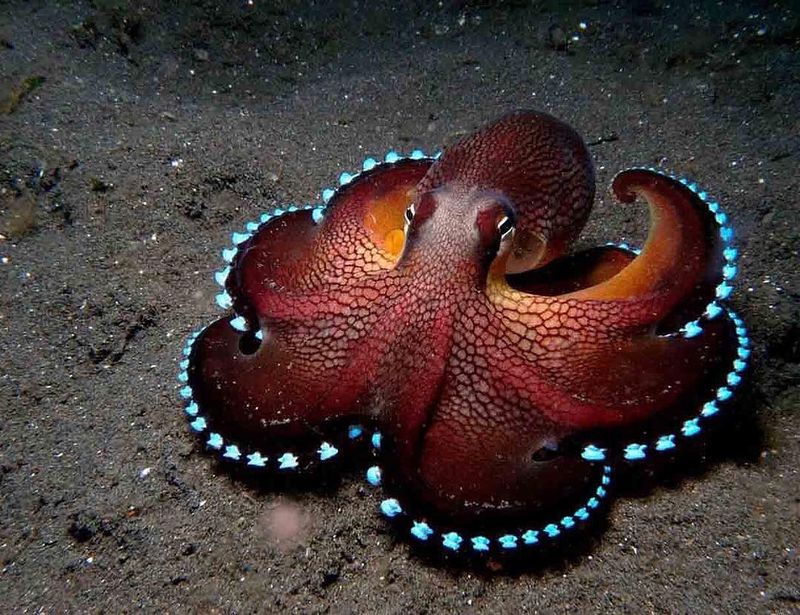

Octopuses are intelligent marine invertebrates known for their ability to regenerate lost arms. This capability is not only essential for survival but also enables them to continue their complex behaviors such as hunting and camouflage.
Each regenerated arm can regain its full functionality, including nerve and muscle connections, within several weeks. In their natural habitats, octopuses are crucial predators that help maintain the balance of marine ecosystems.
Their regenerative abilities have intrigued scientists, who study them to understand the underlying cellular and genetic processes. The potential applications of understanding octopus regeneration extend to regenerative medicine and neurobiology.
By exploring how octopuses regrow their limbs, researchers hope to gain insights into nerve regeneration and recovery processes. These fascinating creatures exemplify the incredible adaptability and resilience of marine life, with regeneration being a key aspect of their survival strategy.
13. Newt
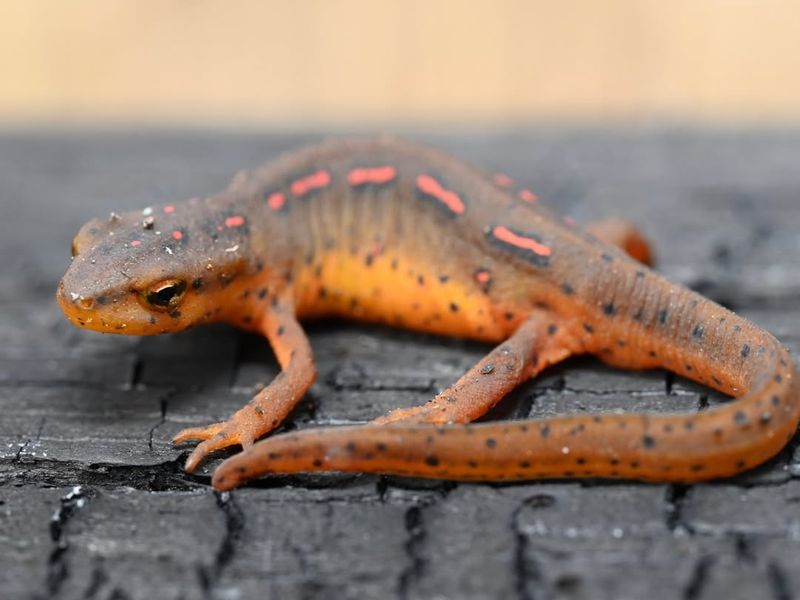

Newts, a type of salamander, are celebrated for their remarkable regenerative capabilities, including the regeneration of limbs, tails, jaws, and even parts of their eyes and hearts.
This ability is particularly important for survival, allowing them to recover from predatory encounters and environmental challenges. In their aquatic and terrestrial habitats, newts help control insect populations and contribute to the ecological balance.
The study of newt regeneration offers insights into the complex cellular processes involved in tissue regrowth, with potential implications for human medicine.
Researchers are particularly interested in how newts manage to regenerate eye structures, hoping to apply these findings to vision restoration therapies. The regenerative prowess of newts continues to inspire scientific inquiry, demonstrating the profound potential for healing and renewal in the natural world.
14. Spiny Lobster
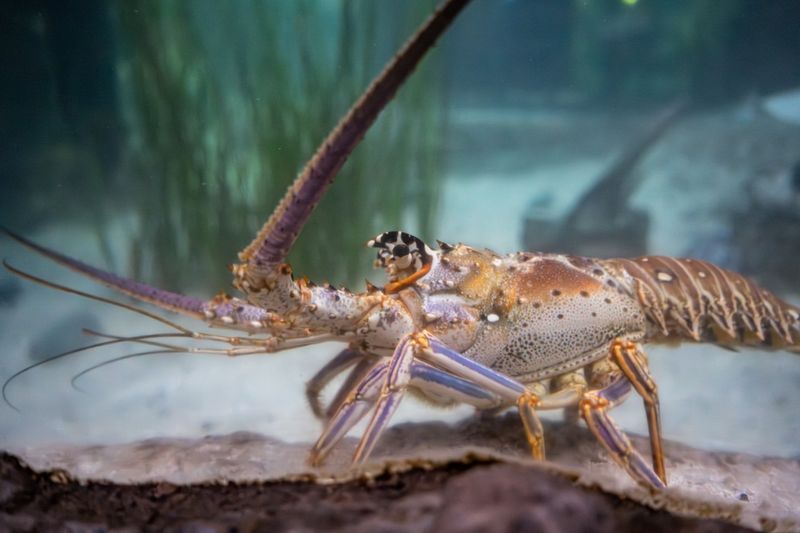

Spiny lobsters are marine crustaceans known for their ability to regenerate lost antennae and other appendages. This regenerative power is crucial for their survival, as these structures are essential for sensing the environment and defending against predators.
The regeneration process involves complex developmental pathways that allow the replacement of lost parts. In their ocean habitats, spiny lobsters play a role in maintaining the balance of the marine ecosystem by being both predators and prey.
Studying their regenerative abilities contributes to our understanding of crustacean biology and offers insights into potential applications in regenerative medicine. The ability of spiny lobsters to regenerate complex structures highlights the remarkable adaptive capabilities of marine organisms.
By exploring these processes, scientists aim to uncover the secrets of regeneration that could one day benefit human medicine. Their resilience in the face of environmental challenges showcases the ingenuity of evolutionary biology.






