23 Incredible Creatures Found More Than A Mile Underwater
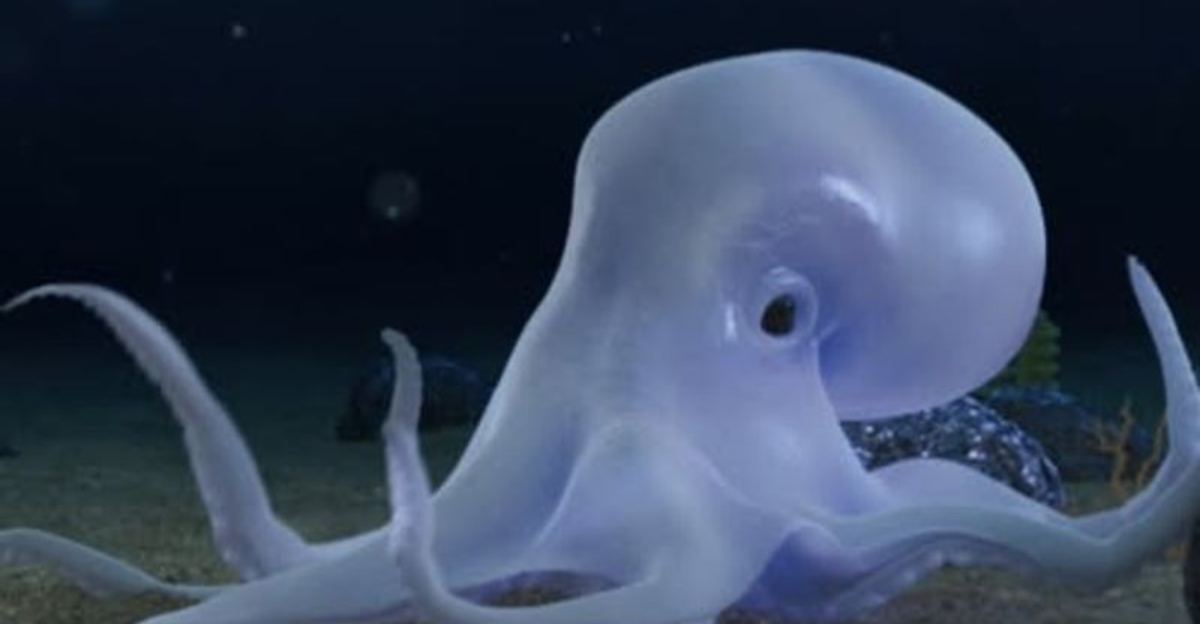

The deep sea, a mysterious realm more than a mile beneath the ocean’s surface, is home to some of the planet’s most fantastical creatures. Scientists, equipped with advanced technology, have ventured into these depths to uncover astonishing life forms that defy imagination.
Each discovery sheds light on the incredible adaptability and biodiversity of deep-sea ecosystems. Let’s explore such creatures, each unique in its adaptations and allure.
1. Deep-Sea Cusk-Eel
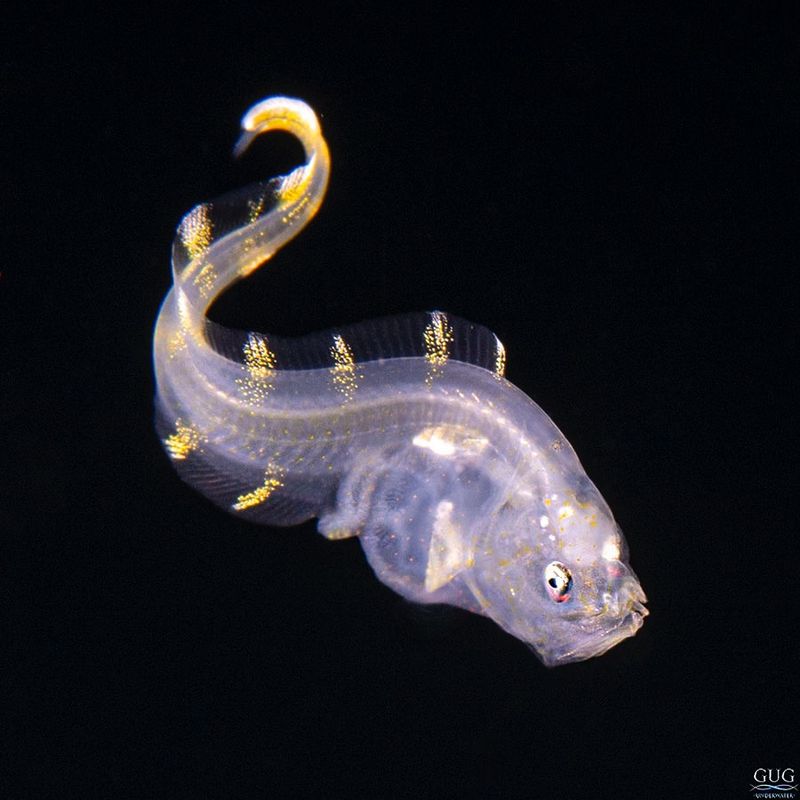

The Deep-Sea Cusk-Eel is a fascinating creature found at depths greater than a mile underwater. Known for its eel-like appearance, it has adapted to the harsh conditions of the deep sea by developing a robust, streamlined body that allows it to navigate through the deep, dark waters. This eel feeds on smaller fish and invertebrates, and its ability to withstand the pressure and cold of the deep ocean makes it an incredible example of adaptation.
2. Giant Tube Worm
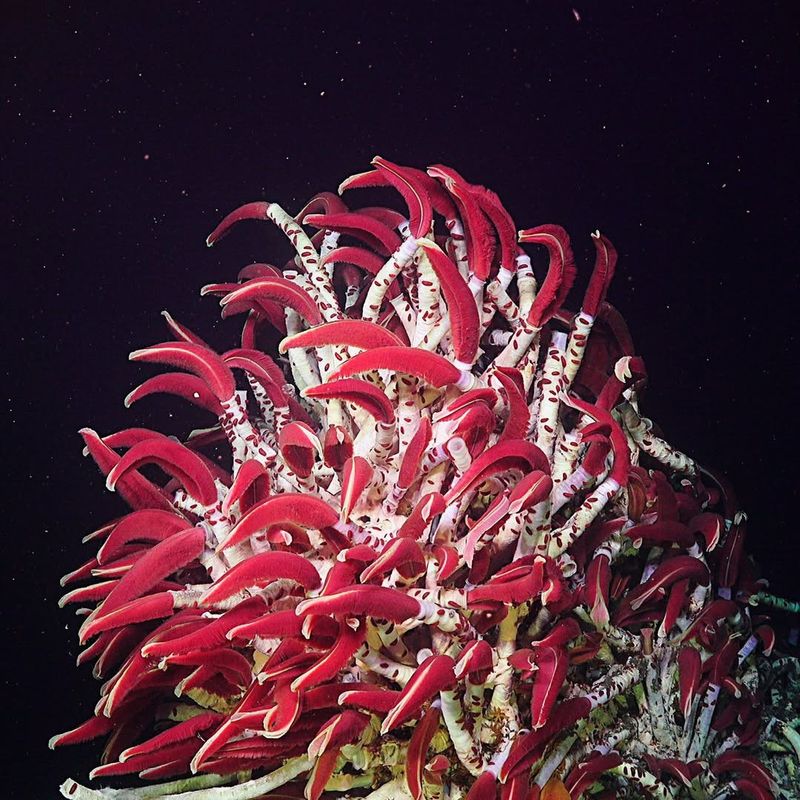

Found around hydrothermal vents more than a mile underwater, the Giant Tube Worm is an extraordinary creature that thrives in extreme conditions.
These worms live in complete darkness and survive by forming symbiotic relationships with bacteria that convert chemicals from the vents into energy. This adaptation allows them to thrive in a completely hostile environment, where sunlight does not reach.
3. Bioluminescent Jellyfish
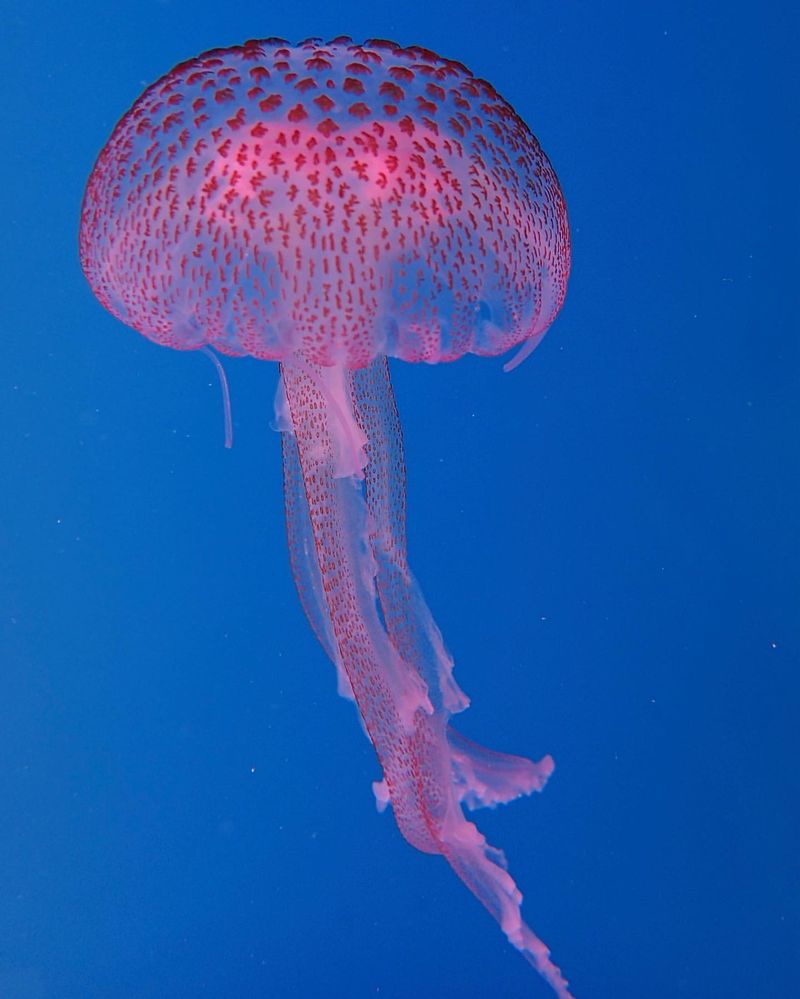

This captivating creature dazzles with its ethereal glow, producing light through a chemical reaction known as bioluminescence. Found over a mile deep, the bioluminescent jellyfish uses its light to attract prey and communicate with others of its kind.
Imagine a soft, glowing orb moving gracefully through the inky blackness, its tendrils trailing behind like delicate streamers. These jellyfish are not just organisms but living art, mesmerizing any who are lucky enough to witness them.
4. Giant Squid
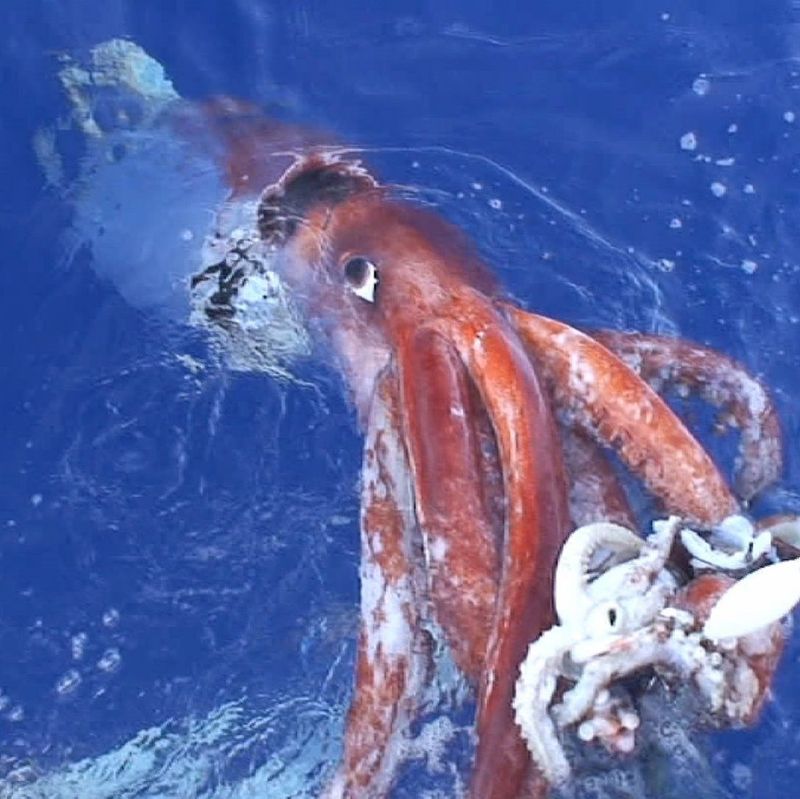

Few creatures inspire as much awe and mystery as the giant squid. With eyes the size of dinner plates and tentacles that can stretch over 40 feet, this elusive giant has been the source of maritime legends for centuries.
Dwelling in the deep, the giant squid has adapted to its dark habitat with remarkable eyesight, allowing it to spot prey in near-total darkness.
5. Deep-Sea Anglerfish
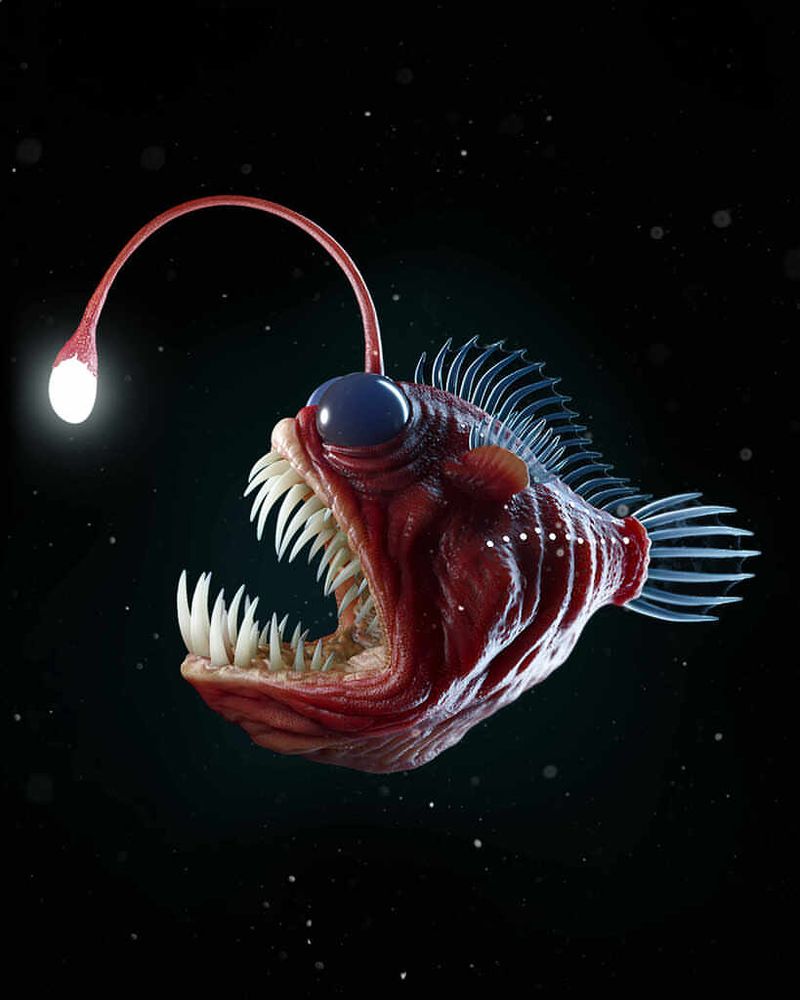

The deep-sea anglerfish is perhaps one of the most fantastical and terrifying creatures found in the ocean depths. Known for its menacing appearance and unique hunting strategy, this fish lures prey using a bioluminescent lure that extends from its forehead.
Hidden in the shadows, the anglerfish remains motionless, waiting for unsuspecting prey to be drawn to its light. Once close, the anglerfish snaps its powerful jaws shut, capturing its next meal.
6. Vampire Squid
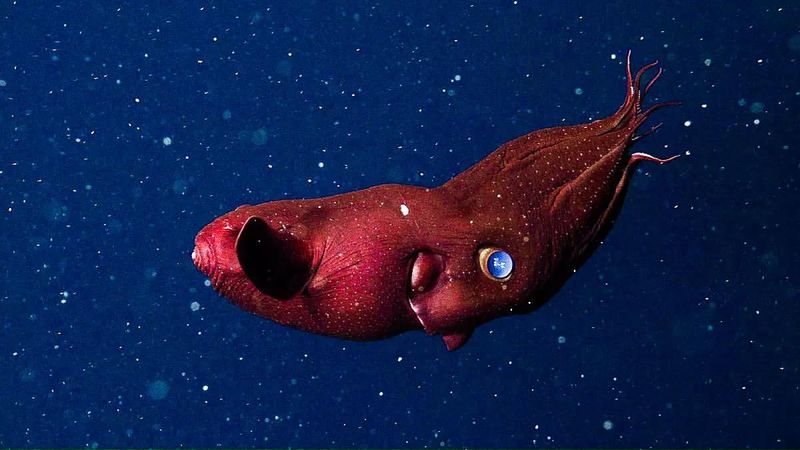

Contrary to its menacing name, the vampire squid is a gentle creature of the deep. Its blood-red eyes and cloak-like webbing give it a mystical appearance, as it drifts through dark waters using minimal energy.
This squid is uniquely adapted to the oxygen-poor environment of the deep sea, using specialized gills to extract oxygen efficiently. Unlike its aggressive relatives, the vampire squid feeds on marine detritus, collecting falling organic matter with its filamentous arms.
7. Goblin Shark
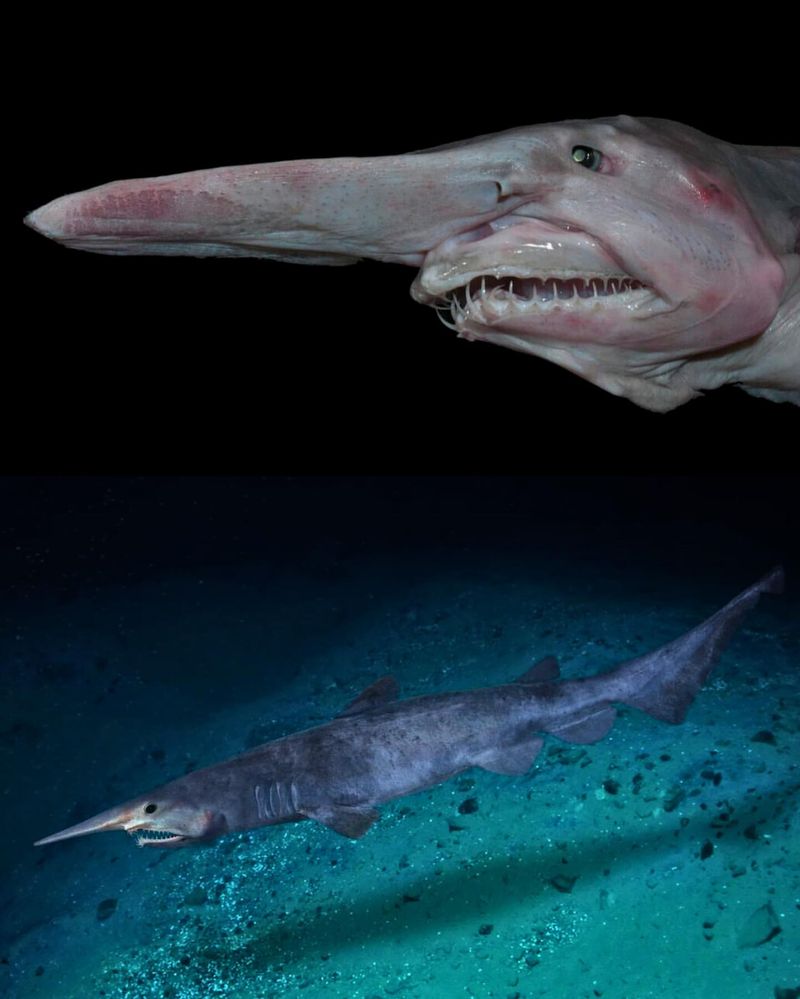

With a face only a mother could love, the goblin shark is one of the more bizarre residents of the deep sea. Its long, protruding snout and unique jaw structure set it apart from other sharks, giving it a truly otherworldly appearance.
Goblin sharks use their elongated snouts to sense the electrical fields of prey, a useful adaptation in their dark, murky habitat. When prey is detected, the shark’s jaws extend forward at lightning speed, capturing the unsuspecting victim.
8. Yeti Crab
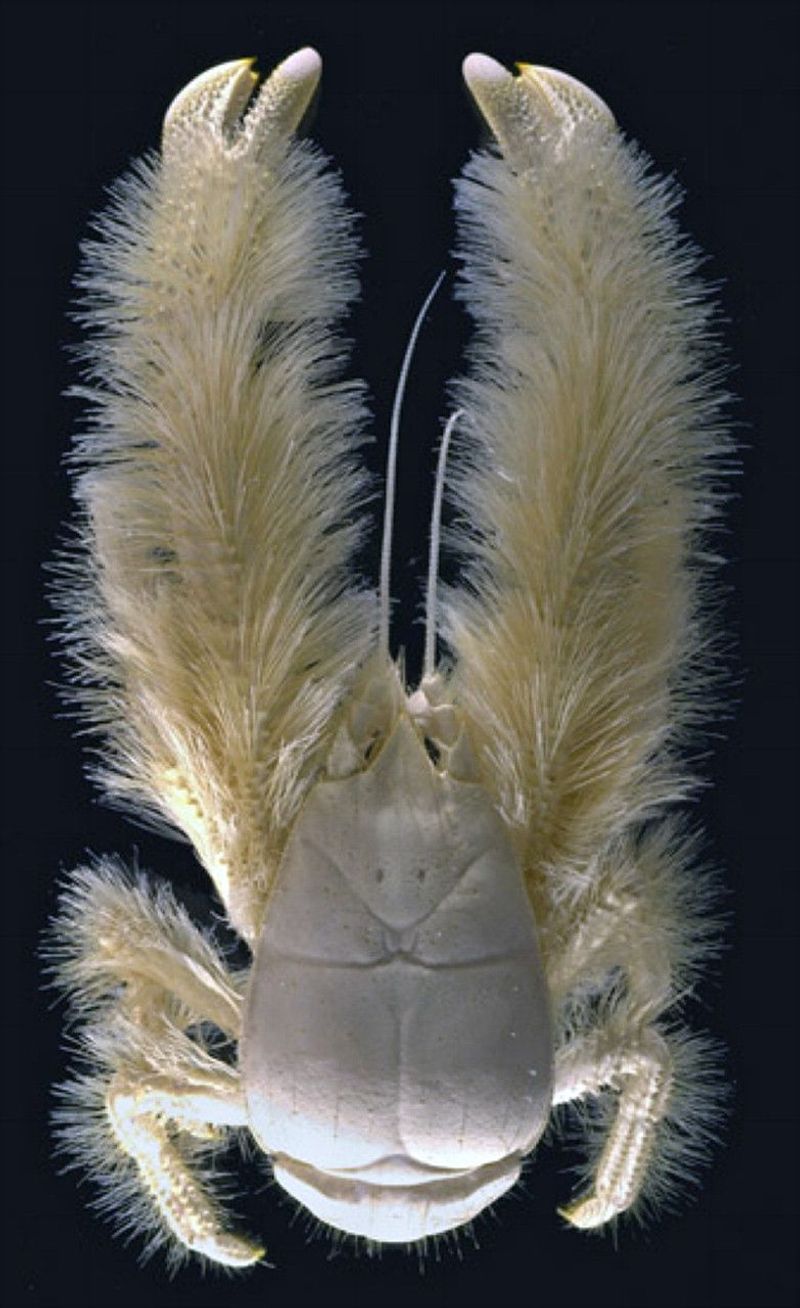

Discovered near hydrothermal vents, the yeti crab is a fascinating crustacean with a peculiar appearance. Named for its hairy pincers, which resemble the mythical yeti, this crab thrives in one of the ocean’s most extreme environments.
The yeti crab’s furry pincers are more than just decorative; they host bacteria that the crab farms as a food source, waving its pincers in nutrient-rich waters to cultivate its next meal.
9. Dumbo Octopus
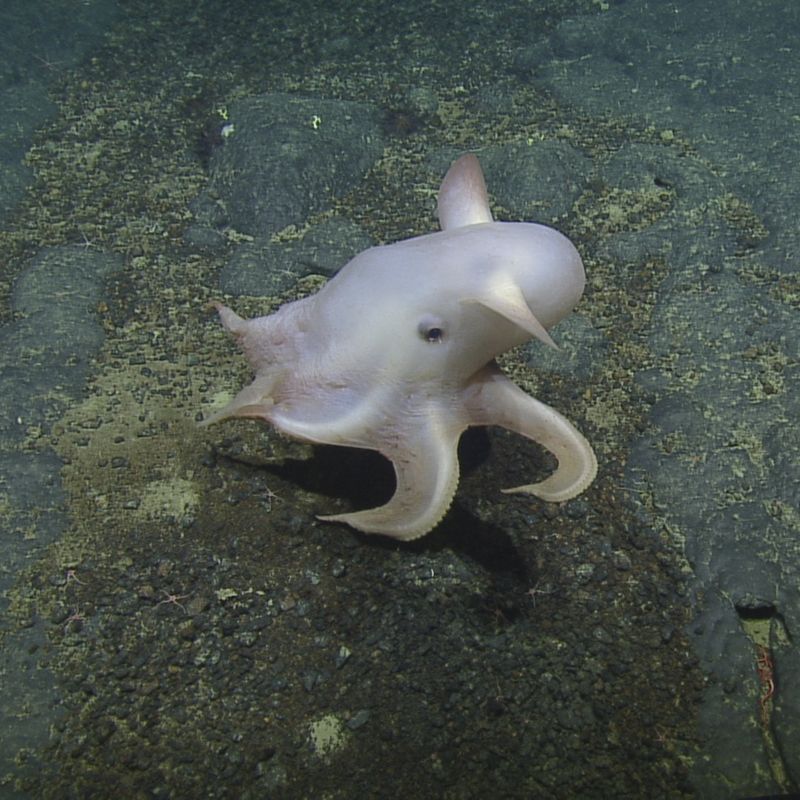

With its ear-like fins resembling the Disney character, the dumbo octopus is as charming as it is unique. Found in the deep ocean, this octopus glides gracefully through the water, using its fins to navigate the dark depths.
Unlike many of its relatives, the dumbo octopus doesn’t squirt ink to escape predators. Instead, it relies on its agility and the ability to hover in place, moving with a gentle, undulating motion that is a marvel to behold.
10. Deep-Sea Dragonfish
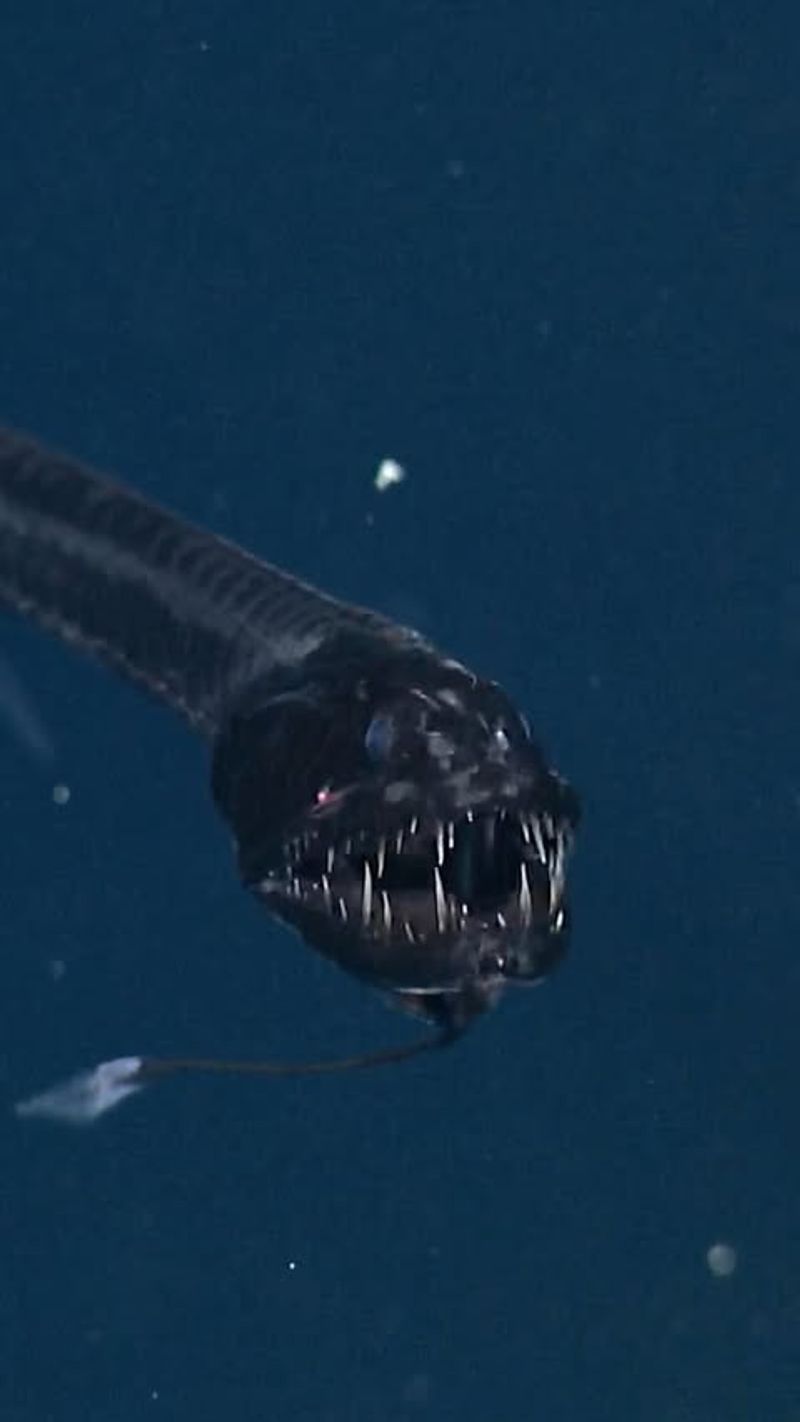

The deep-sea dragonfish is a fearsome predator of the deep, equipped with long fangs and a bioluminescent barbel that it uses to lure prey. Its slender, eel-like body allows it to navigate the dark waters with ease.
This fish’s ability to produce light is not just for hunting; it also uses bioluminescence to communicate and camouflage itself, blending into the faint light filtering down from above.
11. Barreleye Fish
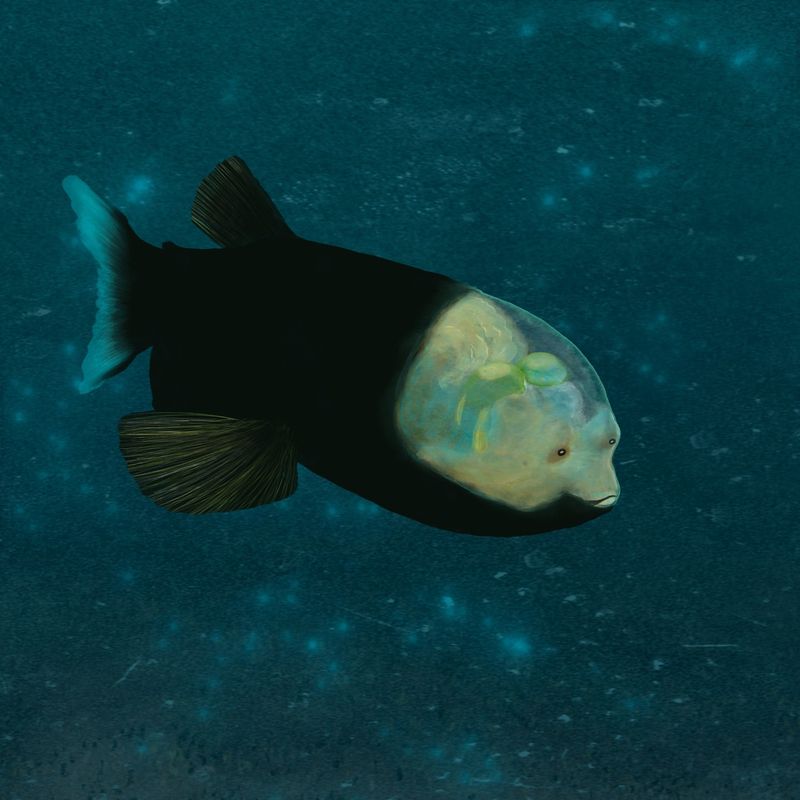

The barreleye fish is a true marvel of the deep sea, with its transparent head and tubular eyes that can look upwards through its skull. This adaptation allows it to detect prey silhouetted against the faint light from above.
Living in the midwater depths, the barreleye fish’s unique adaptations help it survive in a challenging environment where food is scarce. Its transparent head reduces its visibility to predators, while its specialized eyes give it an edge in spotting prey.
12. Pelican Eel
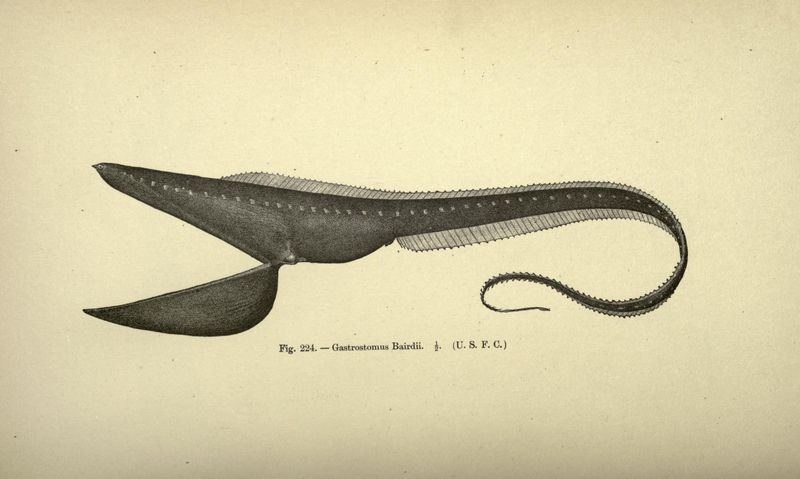
The pelican eel is a peculiar creature of the deep, known for its enormous mouth that can expand to engulf prey almost half its size. This adaptation allows it to consume a wide variety of prey in the sparse deep-sea environment.
Despite its intimidating appearance, the pelican eel is not an aggressive predator. It relies on its large mouth to opportunistically capture whatever food drifts its way, making it a unique and efficient feeder.
13. Glass Squid
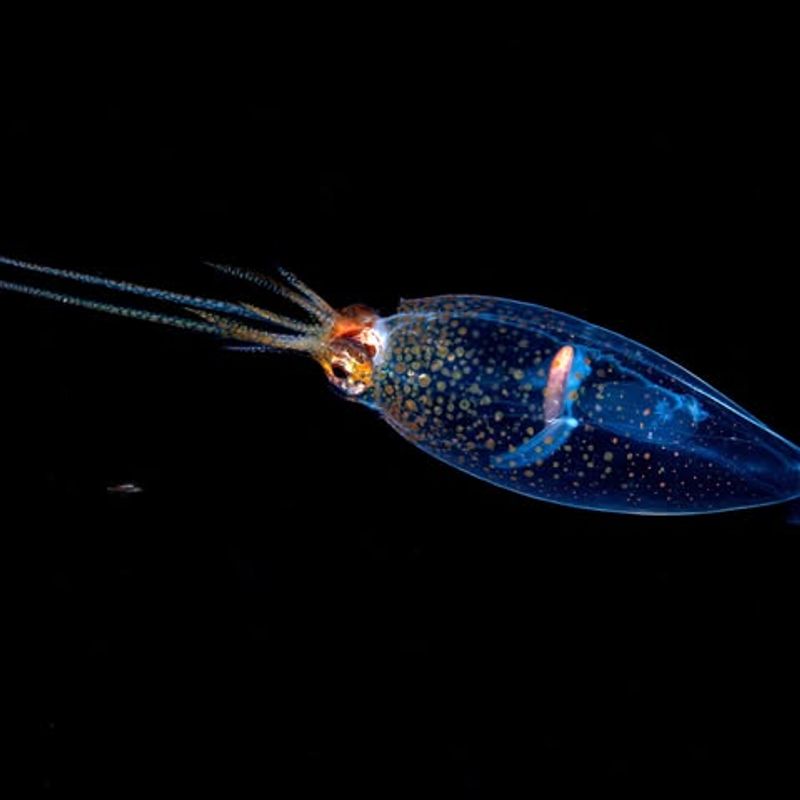

The glass squid is a remarkable creature, with a transparent body that renders it nearly invisible in the deep ocean. This adaptation helps the squid avoid predators in the treacherous depths where it dwells.
Its transparency is not its only unique feature; the glass squid also has the ability to bioluminesce, producing light to communicate, camouflage, and confuse predators. This multifaceted use of light is essential for survival in the dark ocean.
14. Gulper Eel
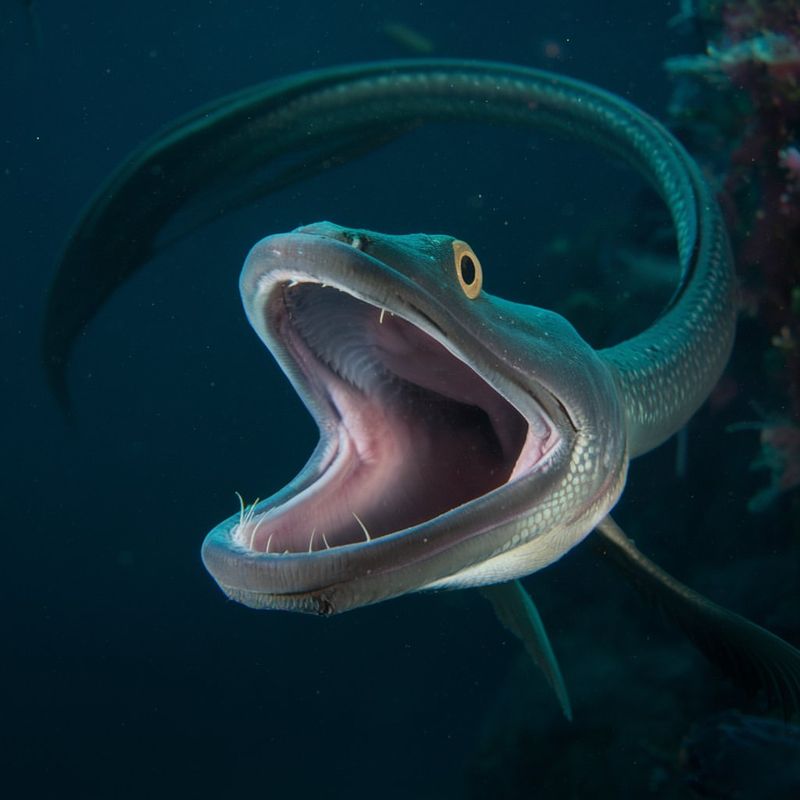

The gulper eel, also known as the pelican eel, is a fascinating deep-sea fish with an enormous mouth capable of swallowing prey much larger than itself. This adaptation allows it to exploit a wide range of food sources in the nutrient-poor depths.
Its long, slender body and expandable stomach make the gulper eel a highly efficient predator, able to store food for later digestion. This is crucial in an environment where meals can be few and far between.
15. Sea Pig
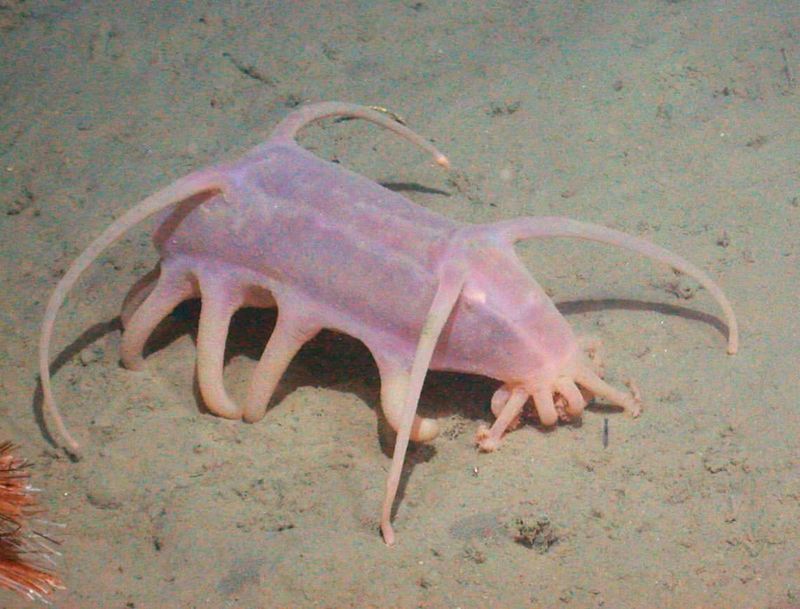

The sea pig, a type of sea cucumber, is a curious inhabitant of the deep-sea floor. Its plump, pink body and tube-like feet allow it to crawl along the ocean bed, scavenging for organic matter.
Sea pigs play a vital role in the deep-sea ecosystem by recycling nutrients and contributing to the carbon cycle. Their feeding activity helps maintain the delicate balance of the benthic community.
16. Brittle Star
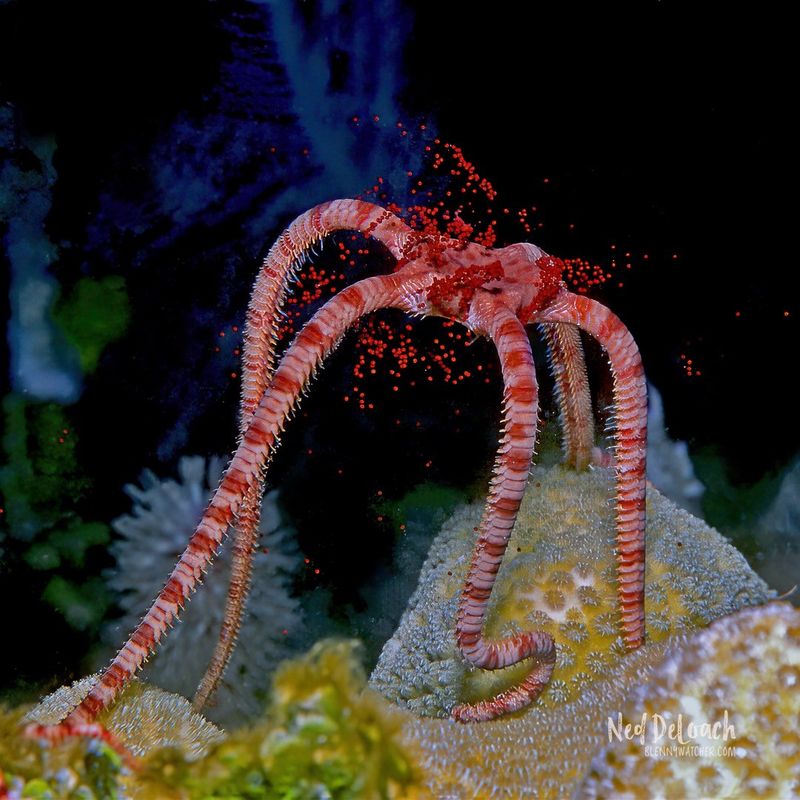

Brittle stars are closely related to starfish and are known for their long, flexible arms that enable them to move gracefully across the ocean floor. These echinoderms are highly adaptable, able to thrive in a variety of deep-sea environments.
Their arms, often adorned with spines, are used for locomotion and feeding. Brittle stars capture food particles from the water, contributing to the nutrient cycling in the deep ocean.
17. Sea Spider
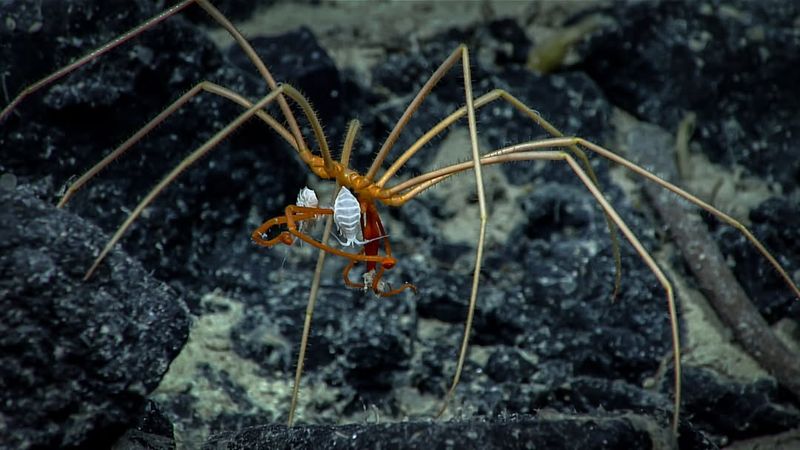

Sea spiders, with their long, spindly legs and small bodies, are an intriguing group of marine arthropods found in deep-sea environments. Despite their name, they are not true spiders but share a superficial resemblance.
These creatures use their legs to move across the ocean floor, where they feed on soft-bodied invertebrates. Their unique physiology, including a reduced body size and elongated legs, allows them to thrive in the cold, high-pressure environment of the deep sea.
18. Zombie Worm
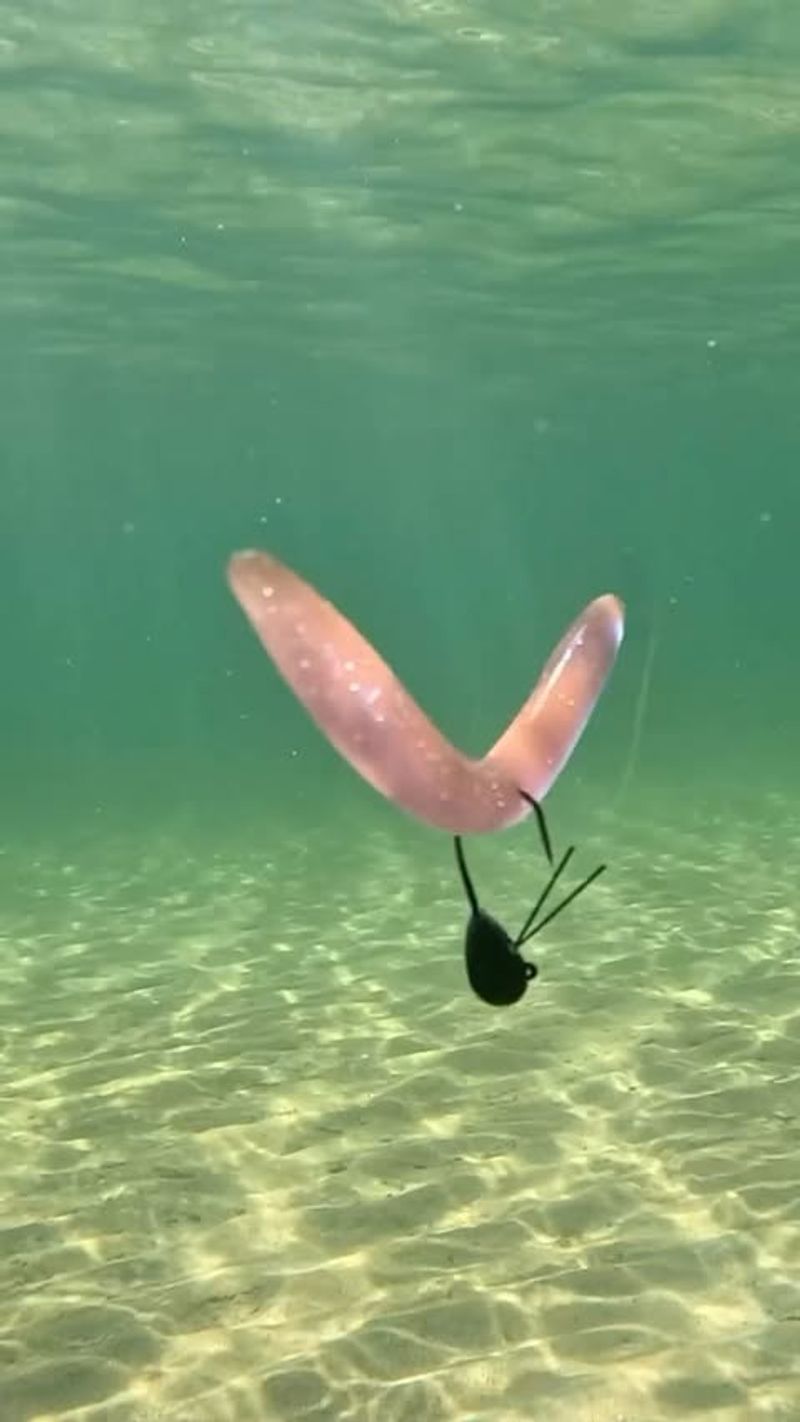

The zombie worm, also known as Osedax, is a remarkable creature that feeds on the bones of dead whales on the ocean floor. These worms lack a mouth and gut, relying instead on symbiotic bacteria to digest bone material.
Their feathery plumes, which resemble roots, allow them to absorb nutrients from the bones, supporting their growth in an otherwise nutrient-poor environment. These adaptations make zombie worms key players in the decomposition process of whale carcasses.
19. Chimaera
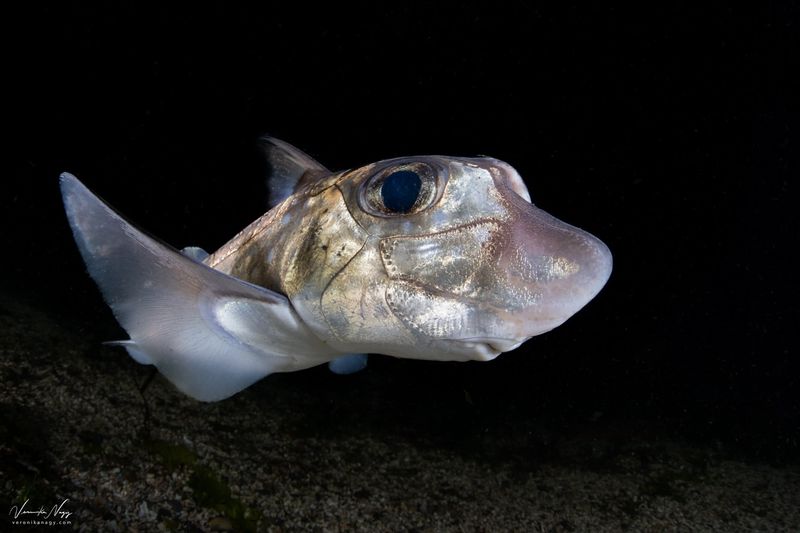

Chimaeras, also known as ghost sharks, are cartilaginous fish that inhabit the deep ocean. Their smooth bodies and elongated snouts give them an eerie appearance, reminiscent of ancient fish from millions of years ago.
These creatures are equipped with special sensory organs that help them detect prey in the dark, cold waters of the deep sea. Their diet primarily consists of small fish and invertebrates.
20. Black Swallower
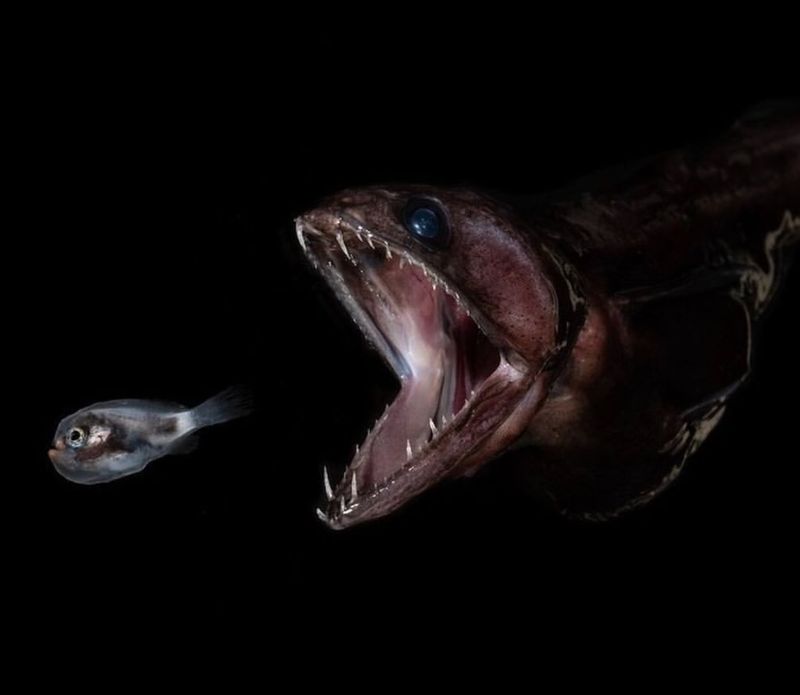

The black swallower is a deep-sea fish known for its ability to consume prey much larger than itself, thanks to its highly expandable stomach. This adaptation allows it to capitalize on the infrequent opportunities for food in the deep sea.
Despite its small size, the black swallower is a formidable predator, capable of capturing and digesting prey several times its size. Its ability to store food for extended periods is crucial in an environment where meals are rare.
21. Deep-Sea Jellyfish
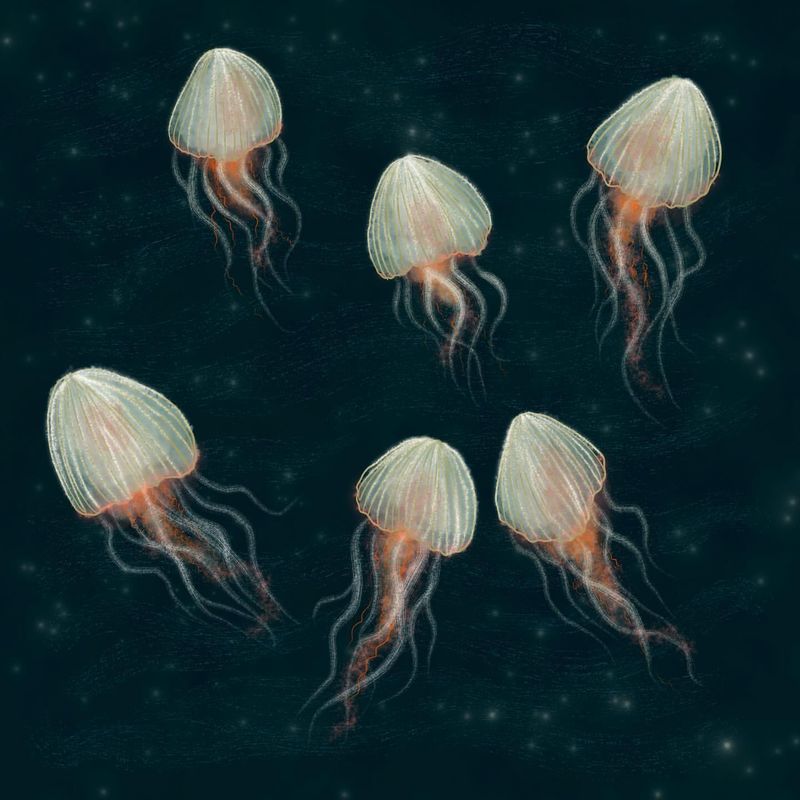

Deep-sea jellyfish are mesmerizing creatures, known for their bioluminescent displays and graceful movements. Their long, flowing tentacles can capture prey and evade predators in the dark ocean depths.
Bioluminescence is a key adaptation for these jellyfish, allowing them to communicate, attract mates, and deter predators. This ability to produce light is an essential survival strategy in the pitch-black environment of the deep sea.
22. Basket Star
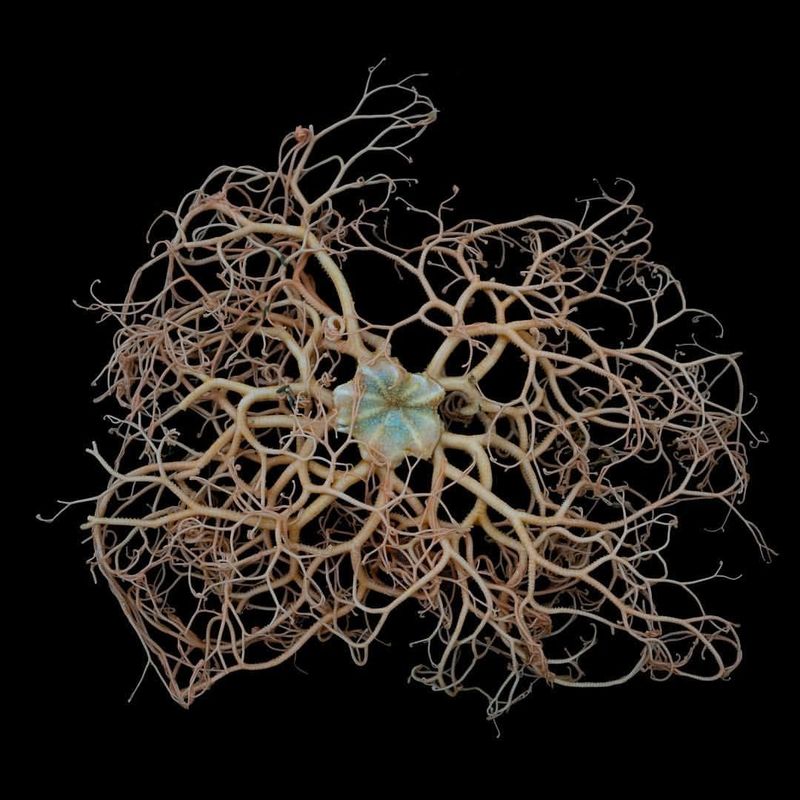
Basket stars are a type of brittle star known for their intricately branched arms, which can extend out like a delicate lacework. These arms are used to capture plankton and other small organisms from the water column.
Found in the deep sea, basket stars are well-adapted to their environment, using their arms to filter feed in nutrient-poor waters. Their unique morphology allows them to maximize the capture of food particles while remaining anchored to the ocean floor.
23. Deep-Sea Octopus
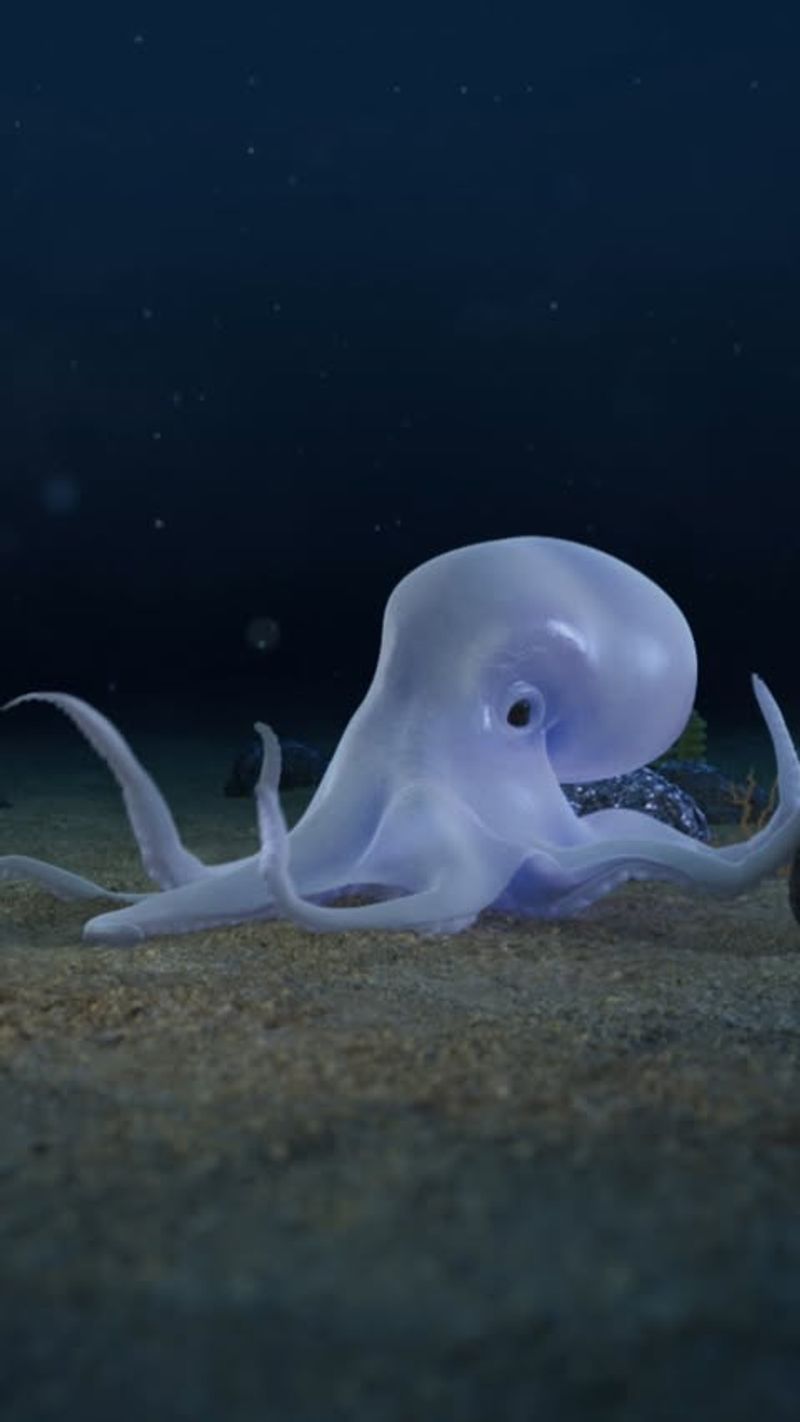

Deep-sea octopuses are fascinating creatures, known for their intelligence and adaptability. Their eight arms, lined with sensitive suckers, allow them to explore and manipulate their environment with precision.
These octopuses have evolved to thrive in the cold, high-pressure depths of the ocean, where they use their keen senses to locate prey and avoid predators. Some species are capable of bioluminescence, providing both camouflage and communication in the dark waters.






