15 Astonishing Facts About Styxosaurus – The Sea’s Mysterious Giant
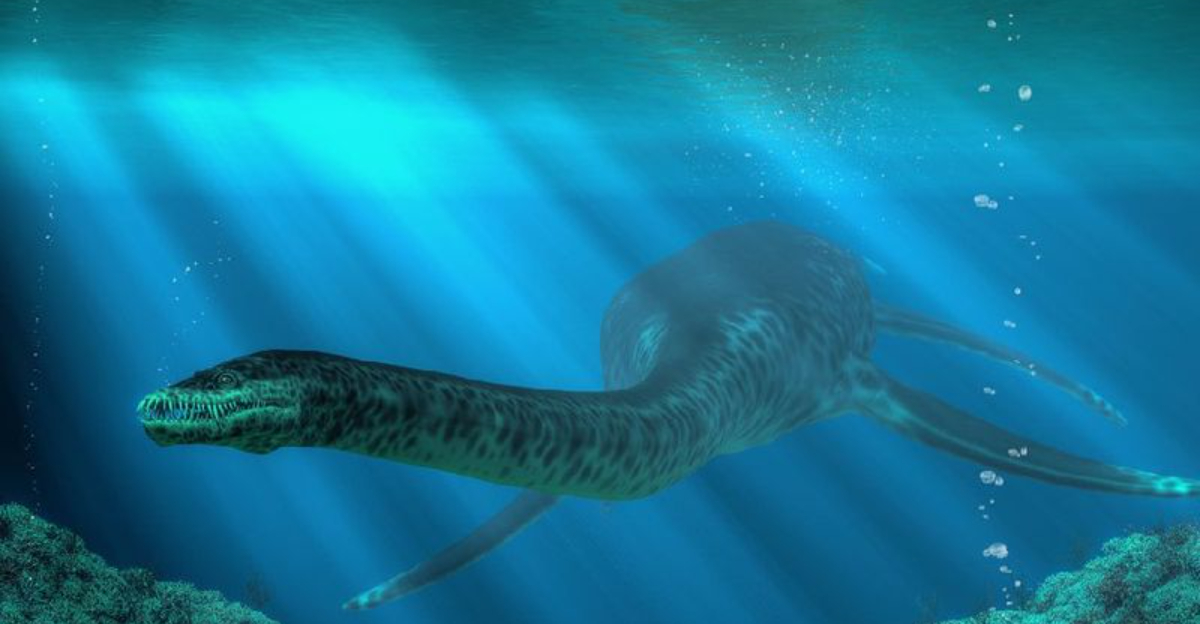

Imagine a creature swimming through ancient seas with a neck longer than a giraffe’s and powerful flippers that could propel it through water like a torpedo. The Styxosaurus was exactly this kind of remarkable marine reptile that lived during the Late Cretaceous period.
These fascinating plesiosaurs have captured the imagination of paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike with their unique adaptations and mysterious lifestyles.
1. Ruler Of Ancient Oceans
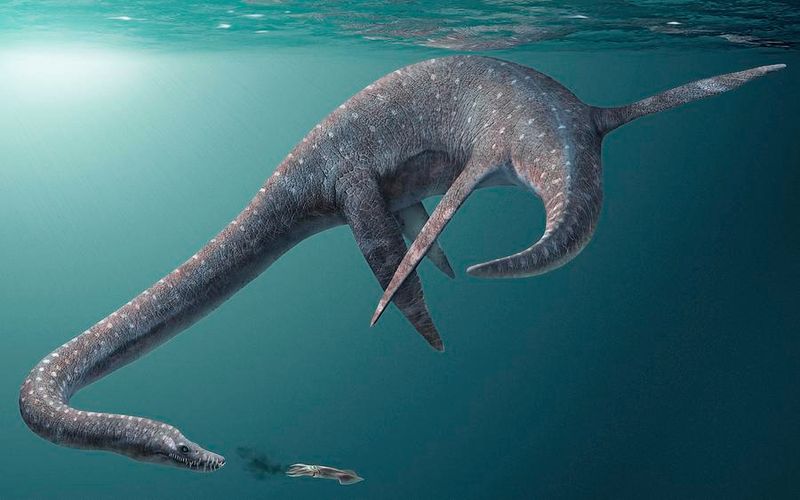

Swimming through prehistoric waters about 85-70 million years ago, Styxosaurus dominated the Western Interior Seaway that split North America in two. This massive marine reptile wasn’t actually a dinosaur but belonged to a group called plesiosaurs.
Unlike dinosaurs who ruled the land, these creatures evolved specifically for life at sea.
2. Giraffe Of The Sea
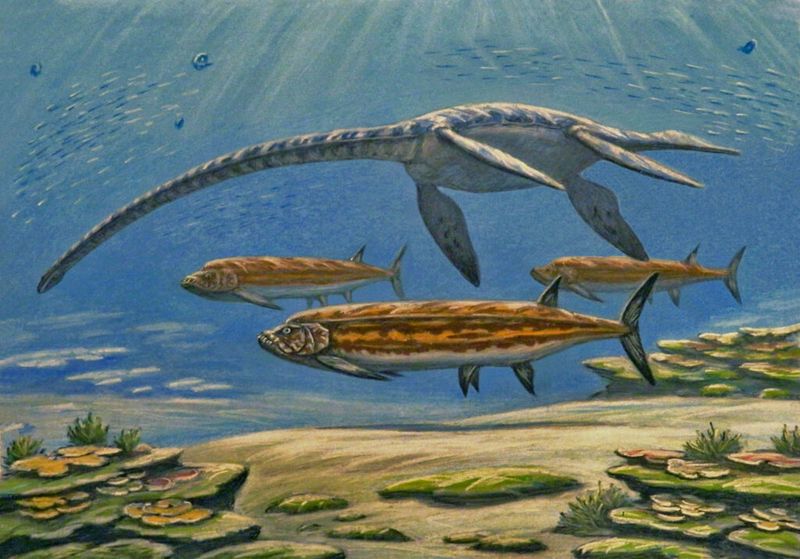

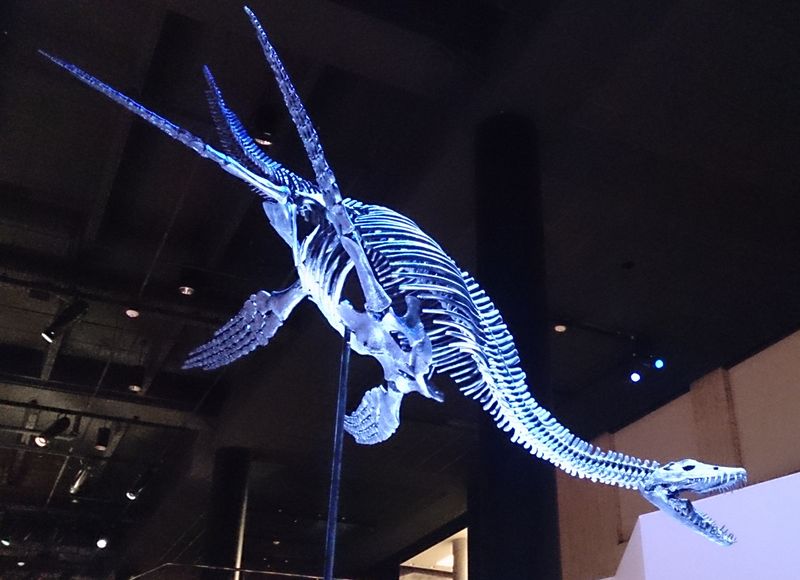
Talk about neck goals! Styxosaurus sported an incredibly long neck containing up to 70 vertebrae. For comparison, humans have just 7 neck vertebrae.
This extraordinary adaptation allowed it to sneak up on prey from below, swinging that flexible neck to snatch fish before they knew what hit them. Imagine a submarine with a built-in fishing pole!
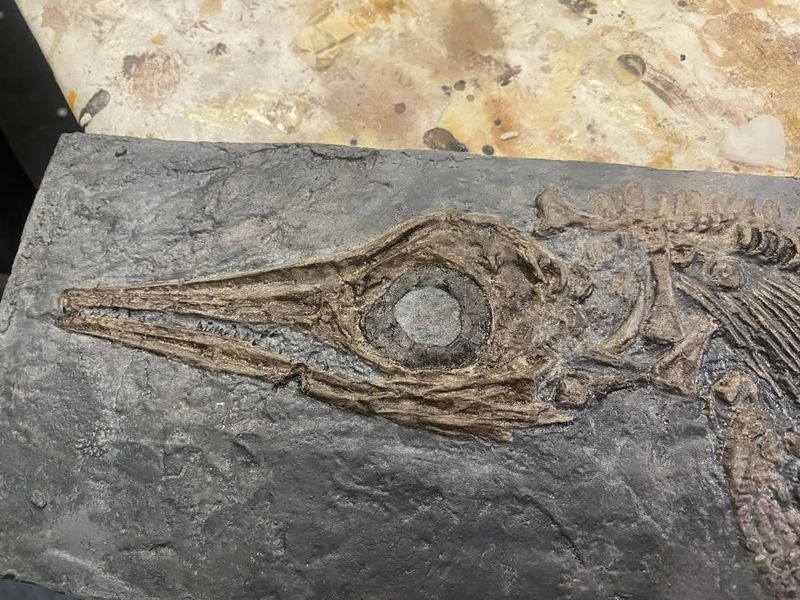
3. Pebble-Packing Predator

Ever swallowed stones on purpose? Styxosaurus did! Scientists have discovered specimens with smooth stones called gastroliths in their stomach cavities.
These weren’t accidental snacks – they likely helped balance the animal’s buoyancy or aided digestion by grinding food, similar to how modern birds use gizzard stones. Some specimens contained over 250 polished stones!
4. Built For Speed
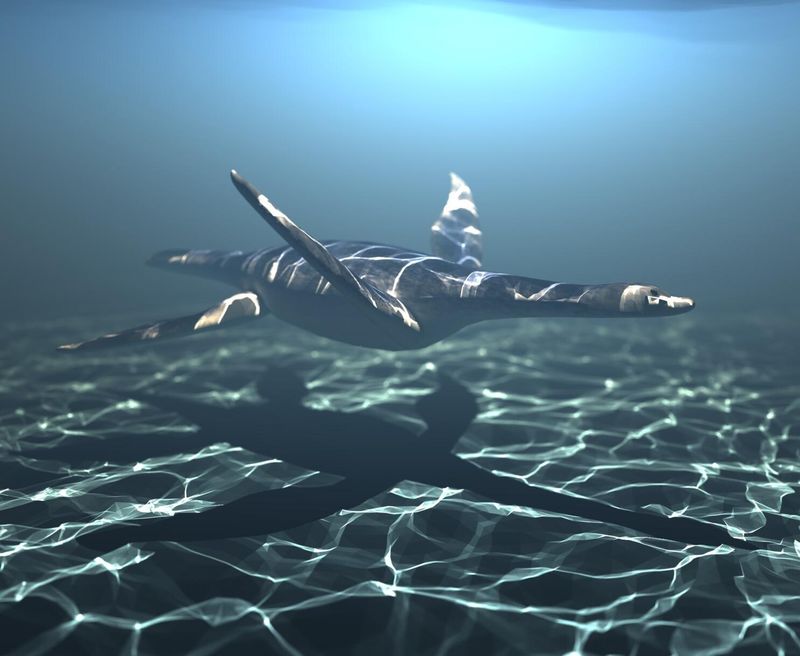

With four powerful flipper-like limbs, Styxosaurus cut through water like an underwater race car. These specialized limbs evolved from legs into hydrodynamic paddles perfect for generating thrust.
The front flippers were typically larger than the back ones, creating a swimming style similar to modern sea turtles but with even more power and speed.
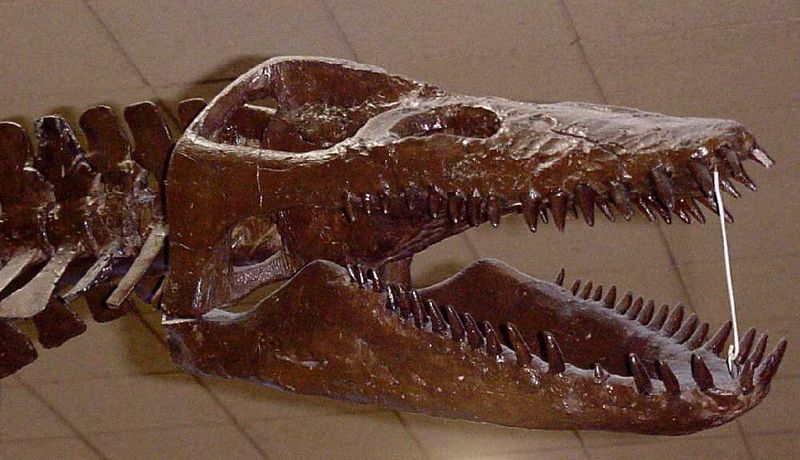
5. Toothy Traps

Forget your dentist’s warnings about sharp objects – Styxosaurus had a mouth full of needle-like teeth perfectly designed for snagging slippery prey. Unlike cutting or crushing teeth found in other predators, these interlocking spikes formed living fish traps.
Once caught between those pointy dental daggers, escape was nearly impossible for unfortunate fish and squid.
6. Named After The Underworld
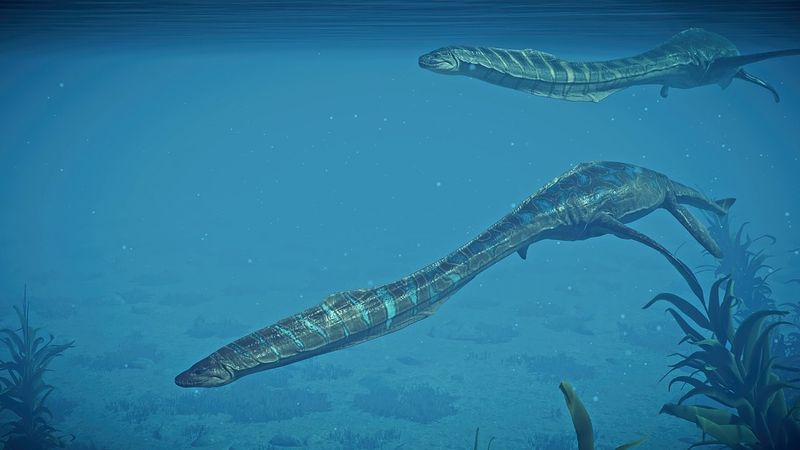

Why such a spooky name? Styxosaurus gets its name from the River Styx of Greek mythology—the boundary between Earth and the Underworld.
When paleontologist Samuel Paul Welles named it in 1943, he thought this mysterious creature from the deep deserved a name connecting it to mythological waters. The full name translates roughly to “reptile from the River Styx.”
7. Monster-Sized Measurements
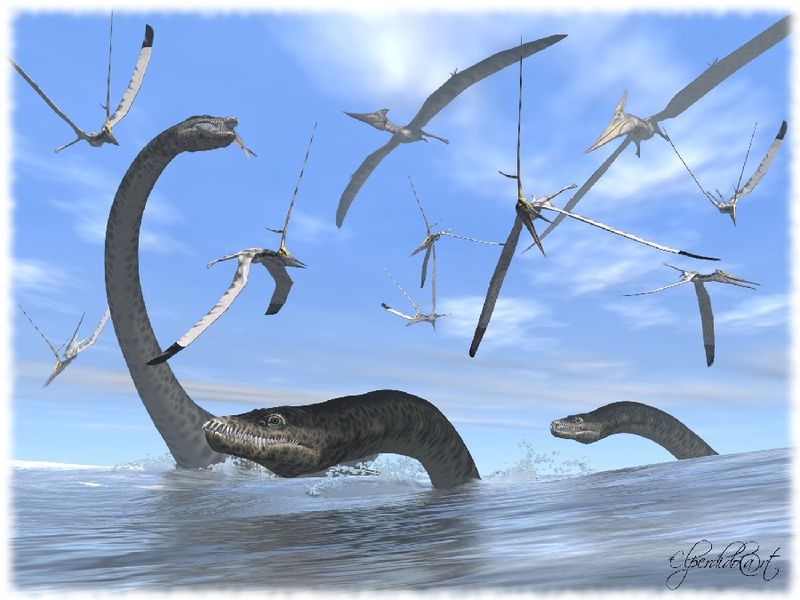

Stretching up to 40 feet from snout to tail – about the length of a school bus – Styxosaurus was an impressive sight. Its neck alone could reach nearly 20 feet!
Despite this enormous size, the creature’s head was surprisingly small, only about the size of a medium dog’s. This dramatic proportion between tiny head and massive body created one of nature’s most unusual silhouettes.
8. Air-Breathing Ocean Dweller
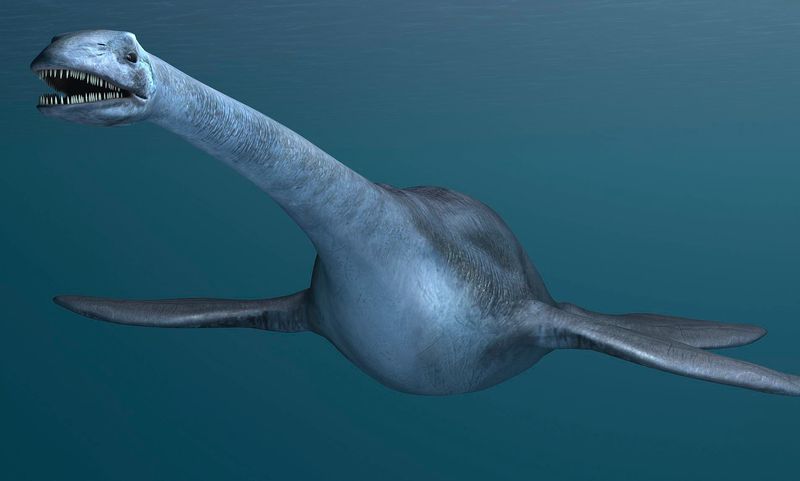

Unlike fish, Styxosaurus couldn’t breathe underwater. As a reptile, it needed to surface regularly for air, similar to modern whales and dolphins.
This air-breathing adaptation suggests these creatures evolved from land-dwelling ancestors who returned to the sea. Imagine the sight of these long-necked giants periodically poking their heads above the waves for a breath!
9. American Treasure
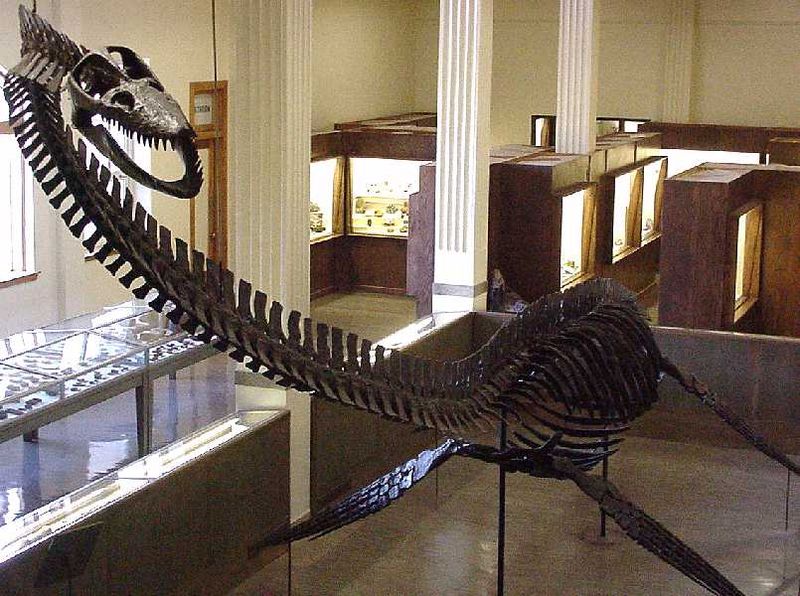

Most Styxosaurus fossils have been unearthed across the American Midwest, particularly in Kansas, South Dakota, and Wyoming. These areas were once covered by a vast inland sea.
The most famous specimen, discovered in Kansas in 1952, is nicknamed “Styx” and features an incredibly well-preserved skeleton with stomach stones intact. It’s now a star attraction at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles.
10. Prehistoric Parenting Mystery
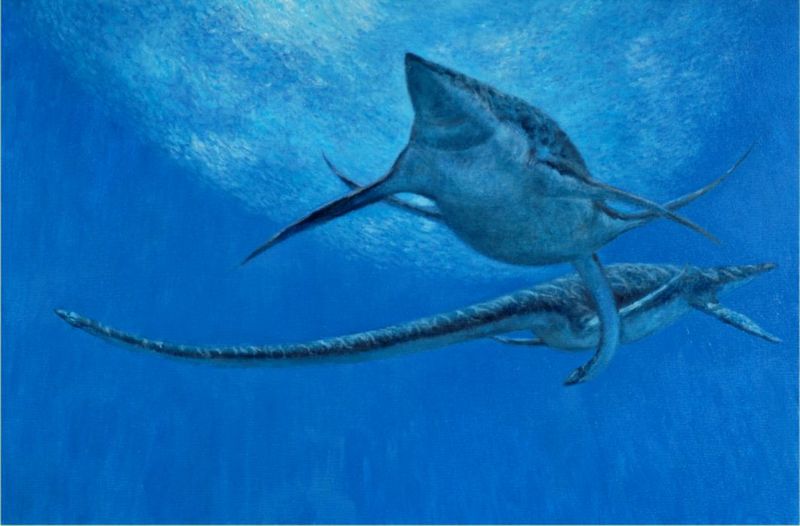

Did Styxosaurus lay eggs or give live birth? This remains one of paleontology’s unsolved mysteries. Most reptiles lay eggs, but since Styxosaurus lived entirely in water, egg-laying would have been challenging.
Many scientists believe they likely gave live birth like modern sea snakes and certain lizards. Future fossil discoveries of pregnant specimens might one day solve this puzzle!
11. Survival Through Climate Change
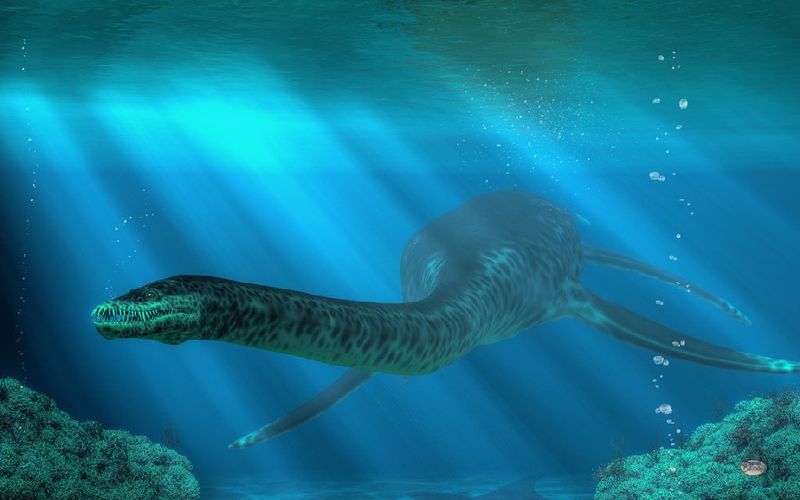

Talk about adaptable! Styxosaurus survived through significant climate shifts during the Late Cretaceous period. While other marine species disappeared, these resilient reptiles thrived as oceans warmed and sea levels fluctuated.
Their ability to hunt various prey and potentially migrate between different water depths may have been key survival advantages during environmental upheaval.
12. Dinner Menu: Mostly Seafood
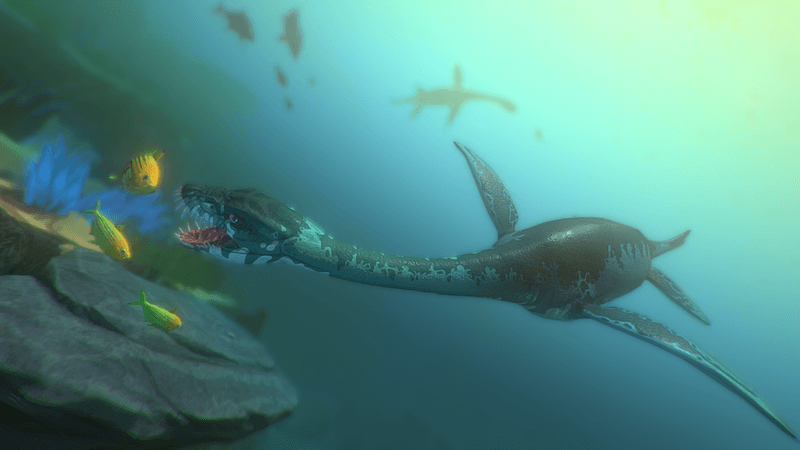
With specialized hunting adaptations, Styxosaurus primarily feasted on fish, squid, and ammonites (prehistoric shelled creatures similar to nautilus). Fossil evidence reveals their diet through preserved stomach contents.
Their hunting strategy likely involved surprising prey from below, using that remarkable neck to strike quickly. Some specimens show they occasionally supplemented their diet with smaller marine reptiles—talk about an apex predator!
13. Eyes Above Water
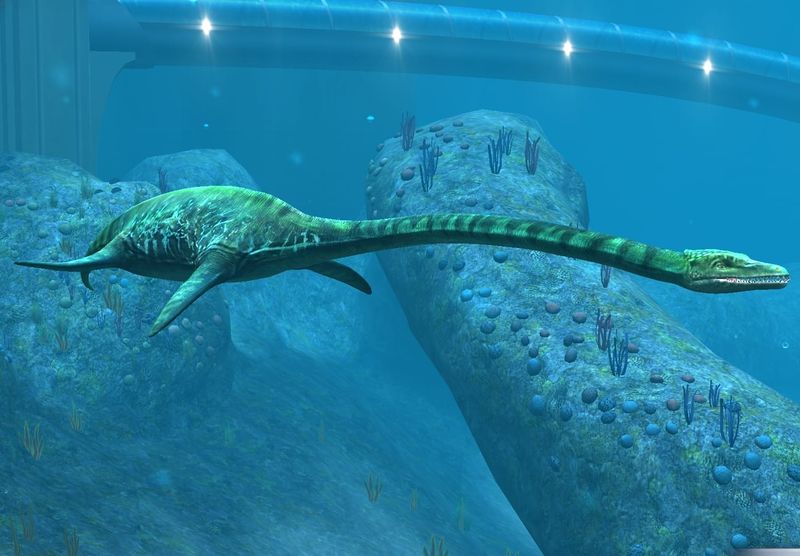

Positioned at the top of its skull, Styxosaurus’s eyes allowed it to spot potential threats while keeping most of its body safely submerged. This adaptation resembles modern crocodiles’ eye placement.
Combined with nostrils located high on the snout, these features let Styxosaurus breathe and see while minimally exposing itself – perfect for both hunting and avoiding becoming someone else’s lunch!
14. Extinct Without Dinosaurs

Though they swam alongside the age of dinosaurs, Styxosaurus and all plesiosaurs vanished during the same mass extinction event that wiped out non-avian dinosaurs 66 million years ago. The asteroid impact dramatically altered ocean chemistry and food chains.
Without this catastrophic event, these remarkable marine reptiles might have continued evolving into even more specialized forms.
15. Loch Ness Inspiration
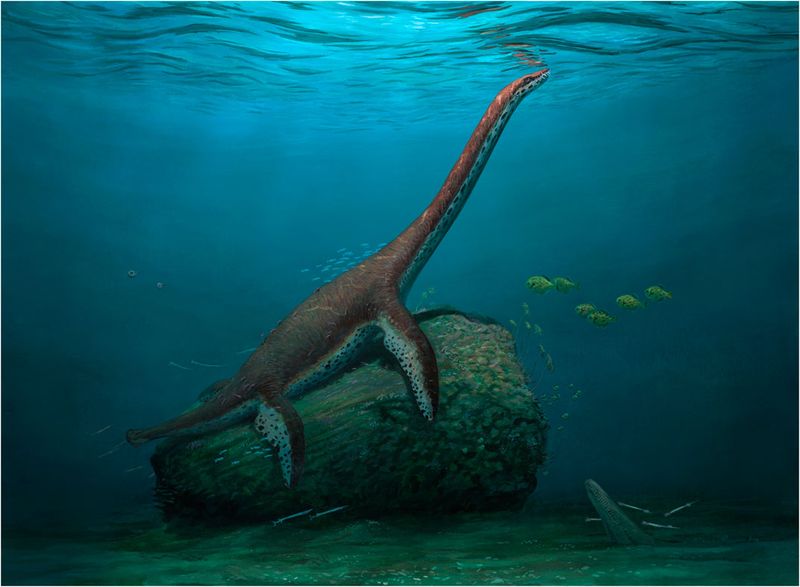

Ever heard of Nessie? The iconic image of the Loch Ness Monster with its long neck and flippers bears a striking resemblance to Styxosaurus and other plesiosaurs.
Many cryptozoologists and monster enthusiasts have suggested that if any prehistoric creature somehow survived extinction to inspire modern lake monster sightings, a plesiosaur like Styxosaurus would be the perfect candidate!






