17 Animals With Unbelievable Hearing That Will Astonish You

Some animals have the kind of hearing that would leave any audiophile green with envy.
From listening to frequencies we can’t even fathom to detecting the faintest of sounds, these creatures rely on their extraordinary hearing to survive, hunt, and communicate.
1. Elephant Seal
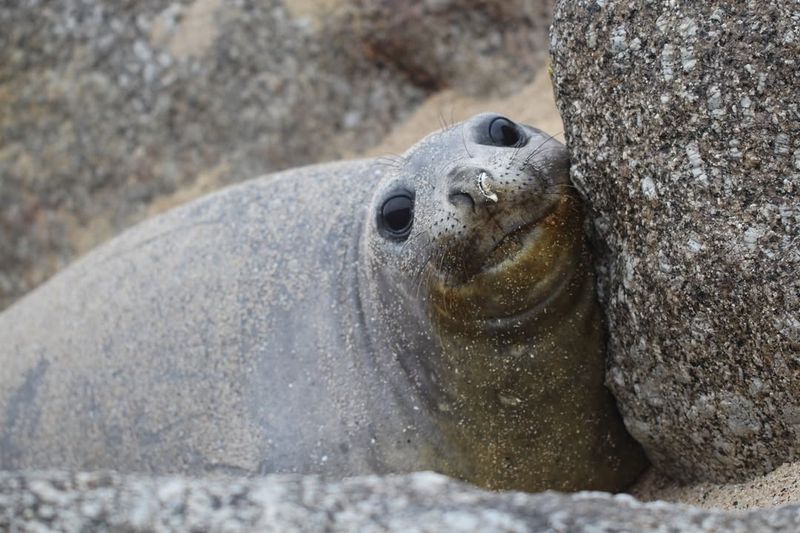

Elephant seals have incredible hearing that helps them stay safe and communicate in the vast, open ocean. They can hear low-frequency sounds from miles away, which is vital for detecting predators and other seals.
Their large ears are perfectly adapted for hearing underwater, and they can pick up on sounds from up to 30 miles away, giving them a significant advantage when navigating their environment.
2. Tiger
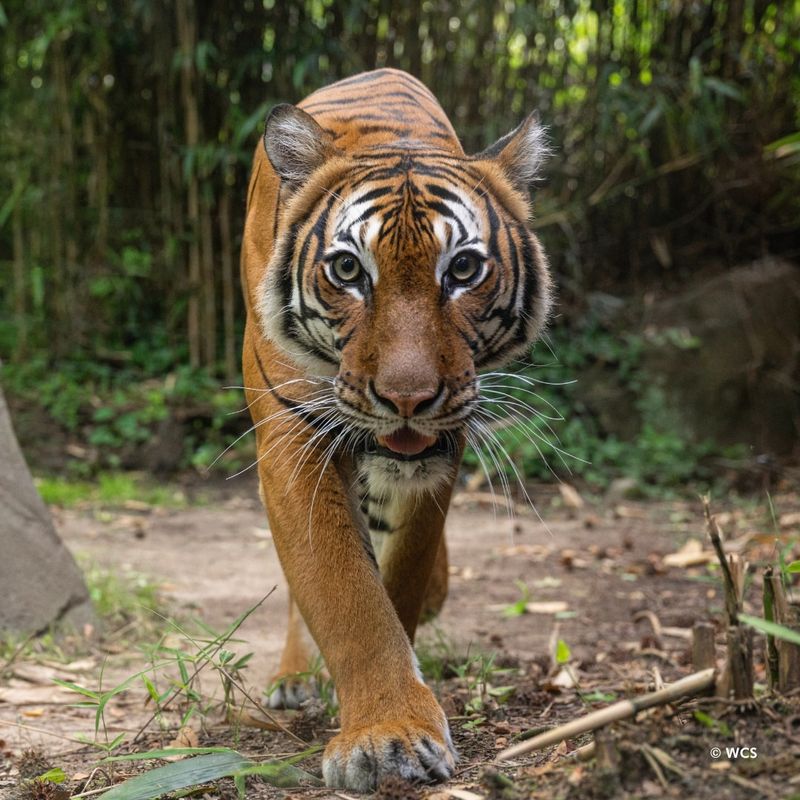

Tigers possess highly sensitive hearing that helps them track prey in dense jungles or grasslands. They can hear sounds at frequencies as high as 64 kHz, which aids them in detecting the slightest rustle of prey.
This acute hearing is crucial for their hunting strategy, allowing them to hone in on their target with precision before launching a stealthy attack. Their ability to hear even faint sounds gives them the edge as apex predators.
3. Elephant
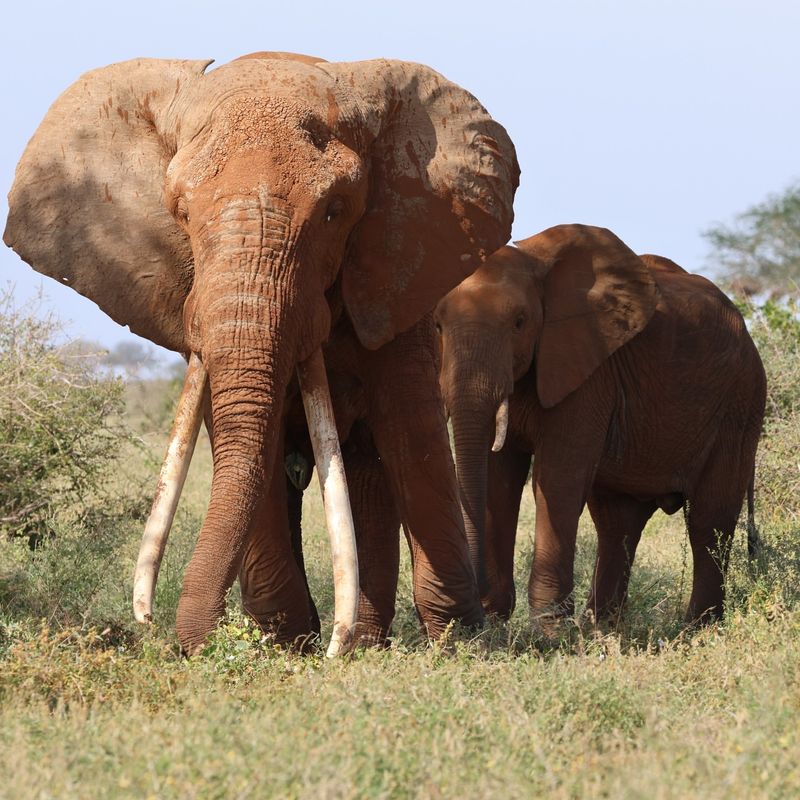

Elephants are known for their massive size, but their hearing is equally impressive. These gentle giants can hear frequencies as low as 14 Hz, far below the range that humans can hear.
This allows them to detect sounds from miles away, including the low-frequency vibrations that travel through the ground. They even use this incredible hearing to communicate with each other over great distances using infrasound.
4. Greater Wax Moth
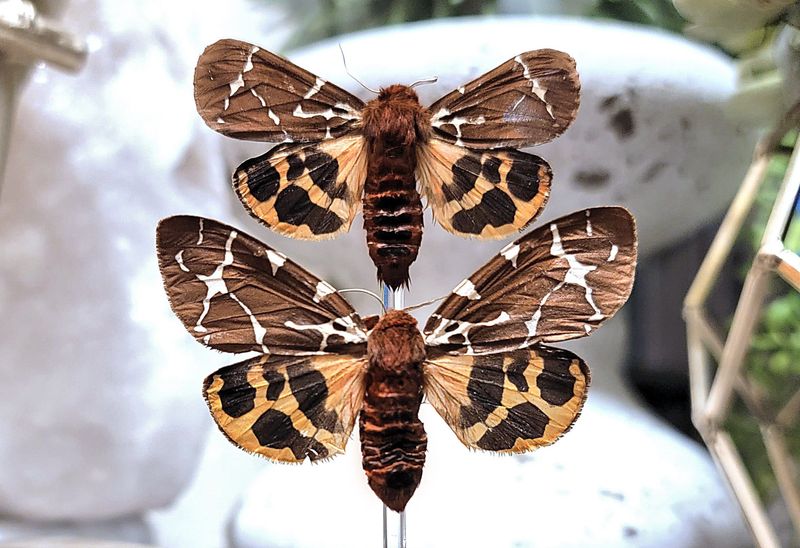

The greater wax moth might be tiny, but it has the ability to hear ultrasonic frequencies at a range far beyond human capabilities.
In fact, its hearing is so finely tuned that it can detect the echolocation calls of bats, which helps it avoid being preyed upon. Its tiny ears, located on its abdomen, can hear frequencies that would blow your mind—over 300 kHz!
5. Owl
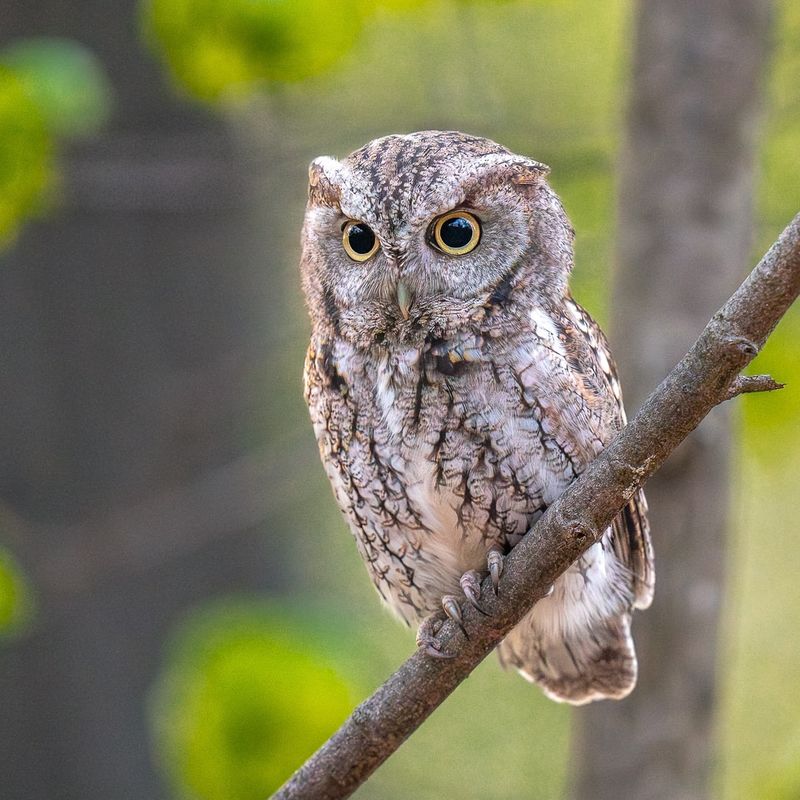

Owls are some of the best nocturnal hunters, and their exceptional hearing plays a big role in their success. With their ability to hear prey moving in complete darkness, owls can pinpoint sounds with incredible precision.
Their asymmetrical ears—one higher than the other—help them triangulate sounds, allowing them to hear even the slightest rustle of a mouse from up to 100 feet away.
6. Bat
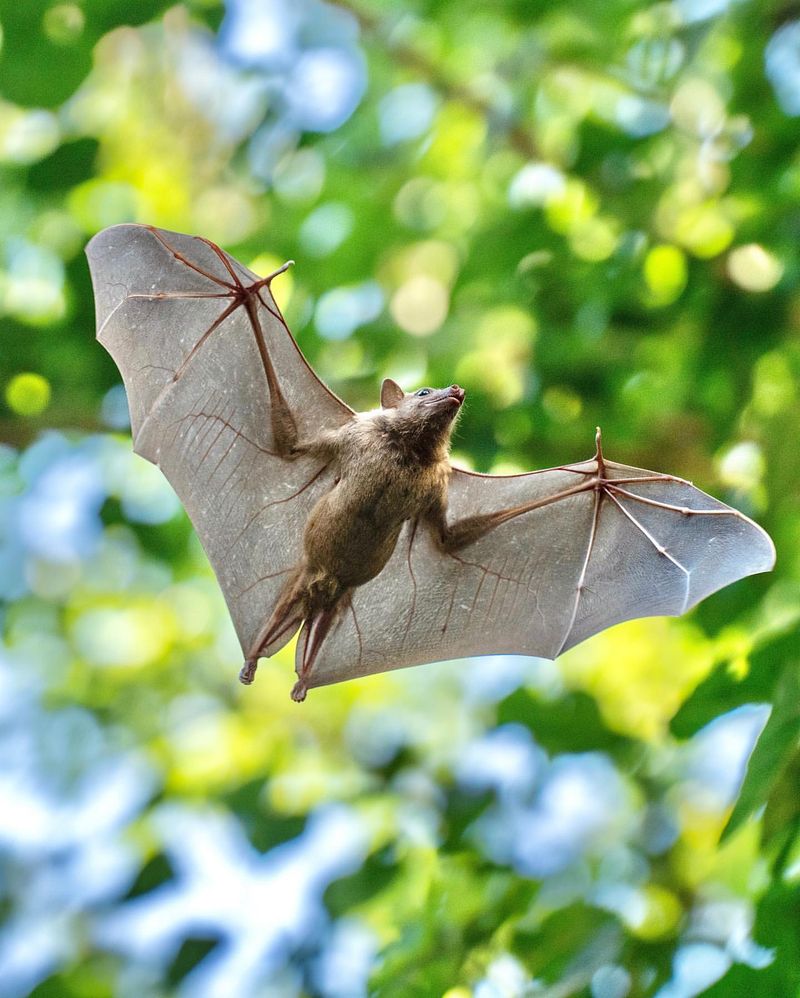

Bats are the masters of echolocation, using sound waves to navigate and hunt in total darkness. They can emit high-frequency sounds and listen to the echoes bouncing off objects, helping them locate insects and even navigate complex environments.
Some species can hear frequencies up to 100,000 Hz, far beyond what humans can even comprehend.
7. Porpoise
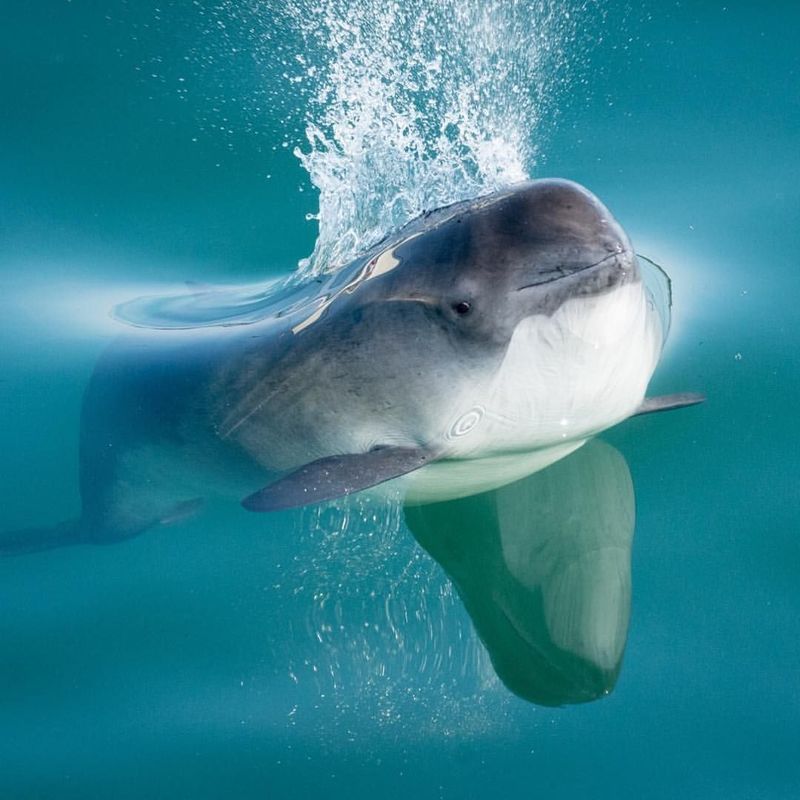

Porpoises have a highly developed sense of hearing, essential for navigating and hunting underwater. They can detect a wide range of frequencies and use echolocation to find food in the dark depths of the ocean.
These intelligent mammals can hear sounds up to 150 kHz, far beyond the hearing range of humans or most other marine creatures.
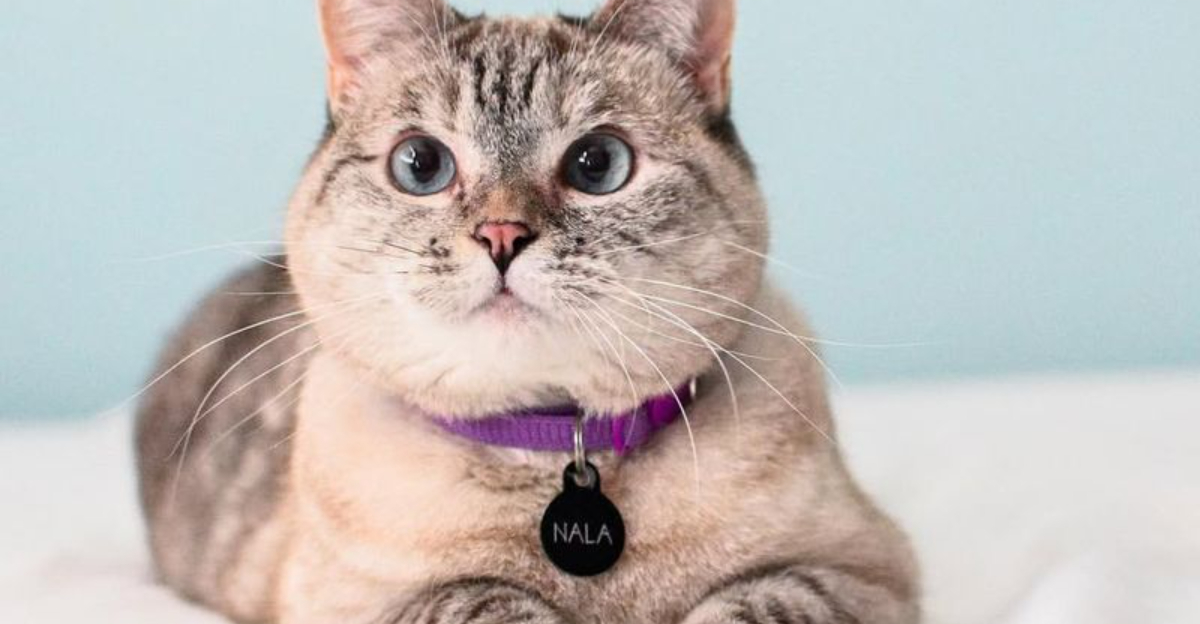
8. Cat
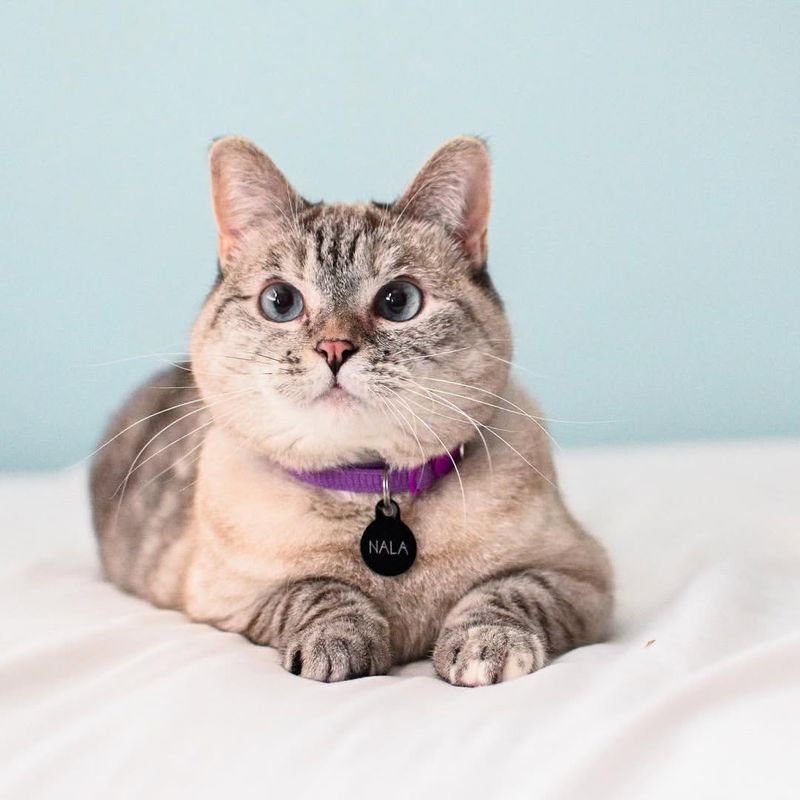

Cats have incredible hearing that allows them to detect even the faintest sounds, especially at high frequencies. Their ears can rotate 180 degrees, helping them pinpoint sounds from nearly every direction.
A cat’s hearing range extends from 48 Hz to 85 kHz, allowing them to catch the high-pitched sounds of small rodents that we can’t even hear.
9. Dog
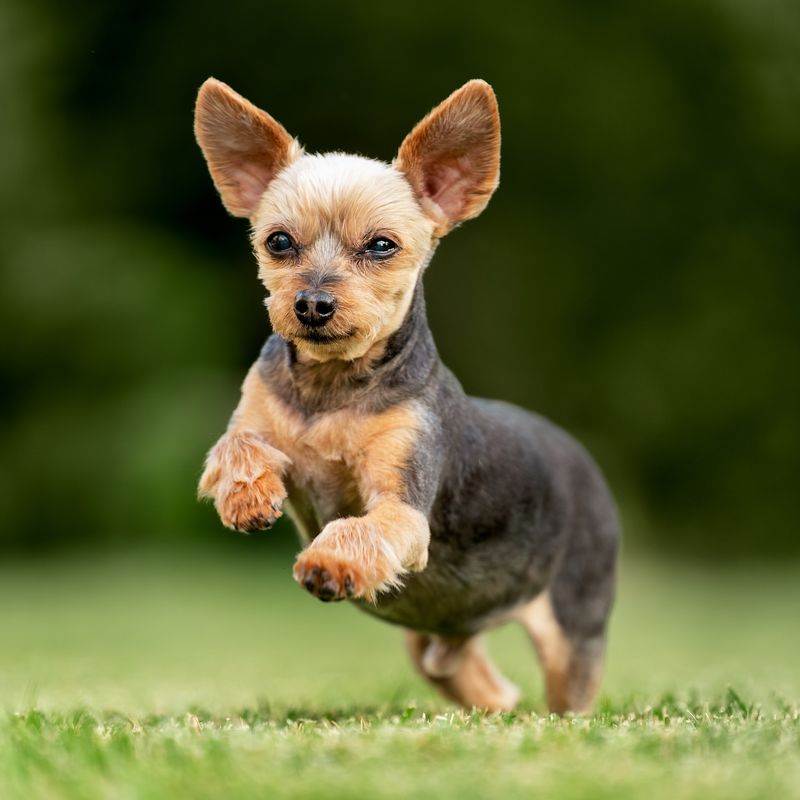

Dogs’ hearing is far superior to ours, capable of detecting frequencies as high as 65,000 Hz—well beyond the human range of hearing. This allows them to hear things like the high-pitched sound of a dog whistle or the distant sound of footsteps.
Their sensitive ears are not just a survival tool, but also a key reason why they excel as service animals and companions.
10. Dolphin
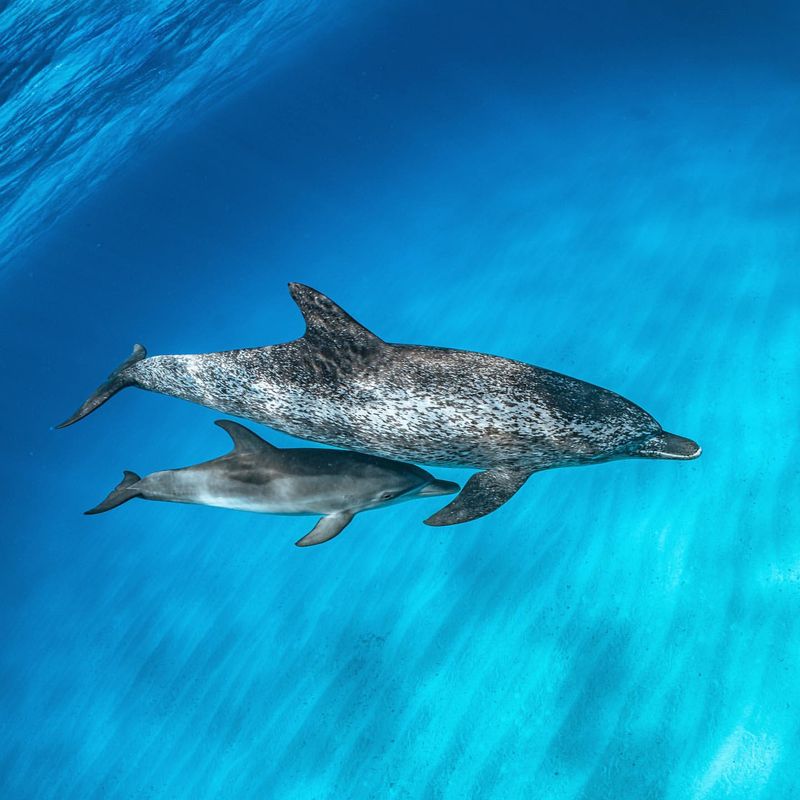

Dolphins rely heavily on their hearing to communicate and hunt in the deep, dark waters where visibility is limited.
They can detect high-frequency sounds up to 150 kHz, allowing them to use echolocation to locate prey and navigate their environment. Their extraordinary hearing is one of the main reasons why they are such efficient predators and social creatures.
11. Horse
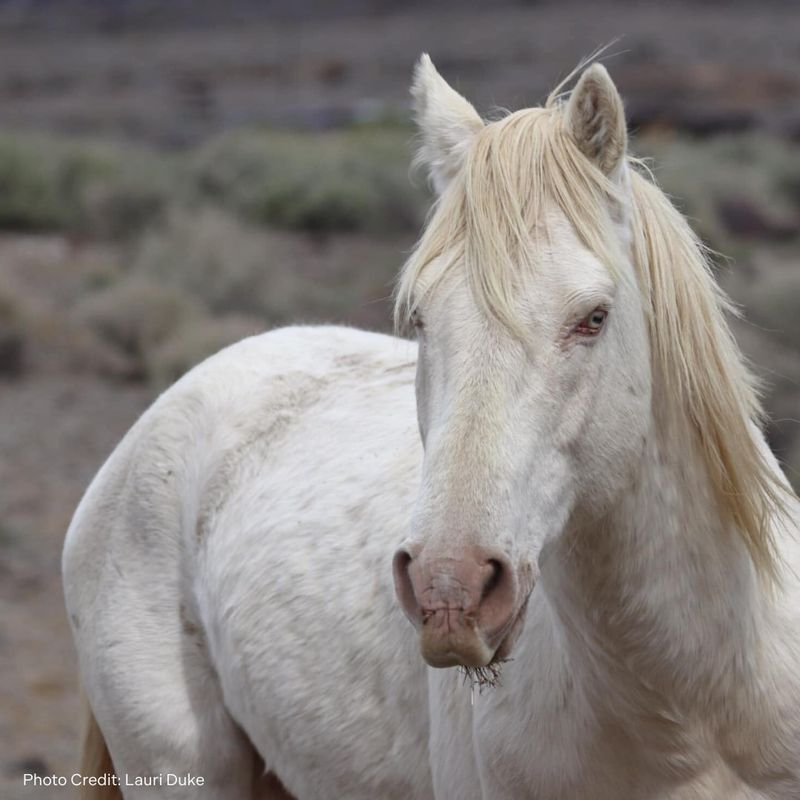

Horses have a remarkable sense of hearing, capable of picking up frequencies from 55 Hz to 33 kHz. Their large, mobile ears can rotate independently to help them listen to sounds from all directions.
This keen sense of hearing helps them detect potential danger in the wild and stay aware of their surroundings in domestic settings as well.
12. Mouse
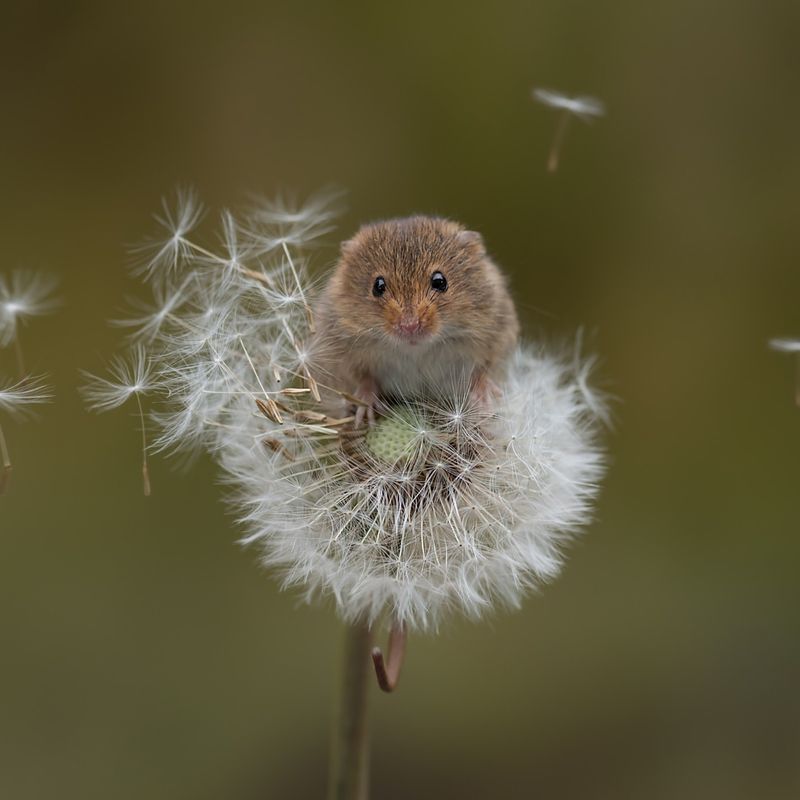

Mice have exceptionally sensitive hearing, especially in the higher frequency range. They can hear frequencies up to 90 kHz, which is much higher than what humans can detect.
This helps them detect ultrasonic vocalizations from other mice and evade predators, especially when they need to react quickly to sounds from predators like owls.
13. Rat
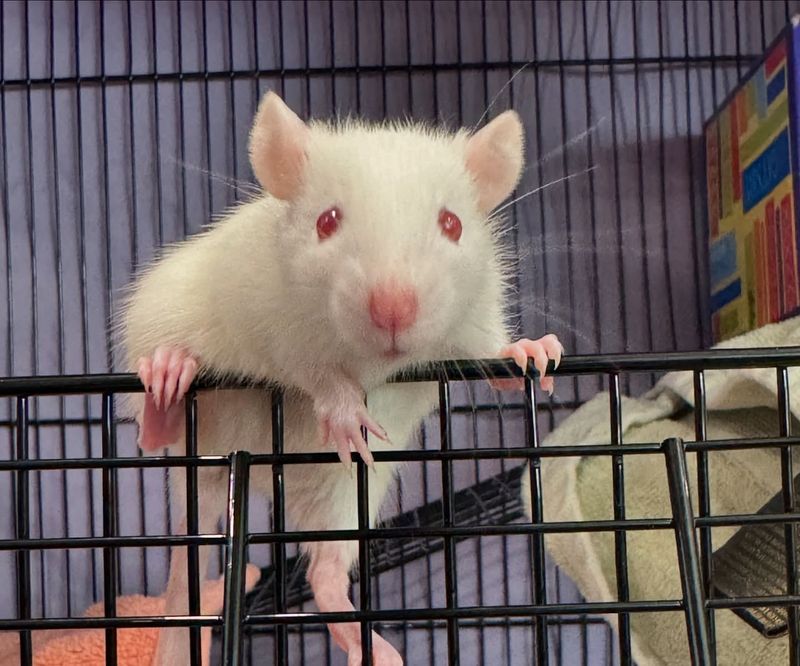
Rats, like their mouse relatives, have an incredible ability to hear sounds in the ultrasonic range. They can detect frequencies up to 90 kHz and use this ability to communicate with each other through high-pitched squeaks.
This fine-tuned hearing also helps them avoid predators and navigate their environment with incredible efficiency.
14. Pigeon
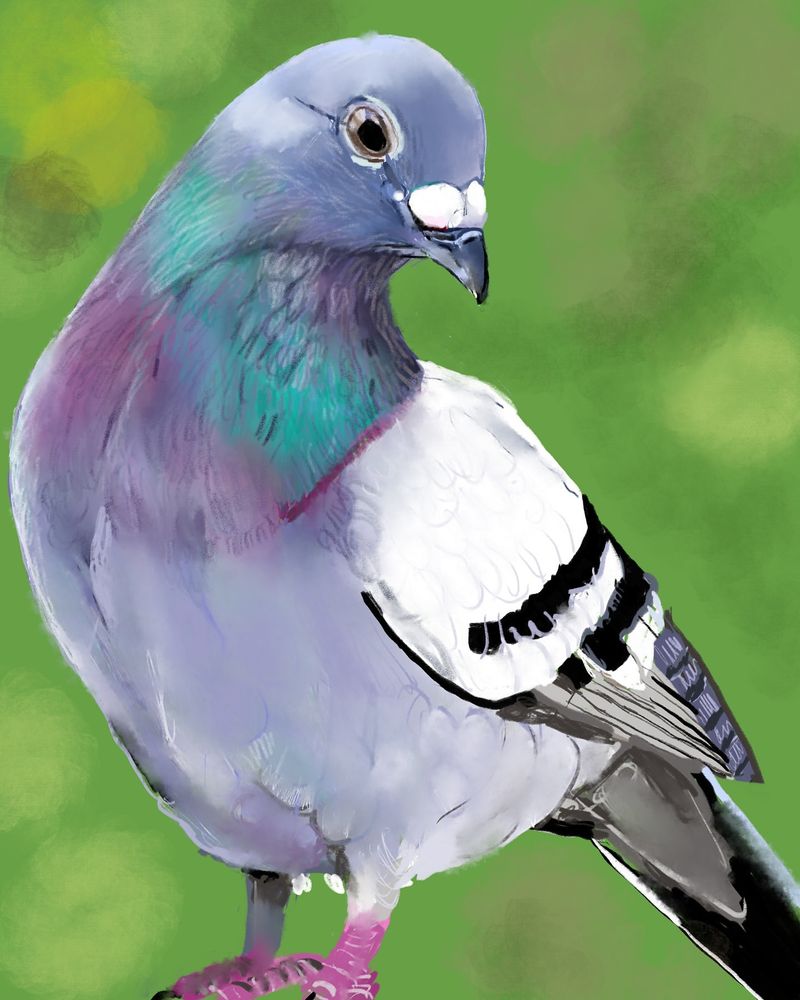

Pigeons have an impressive ability to hear sounds at lower frequencies, particularly those below the range that humans can perceive.
Their hearing is key to their ability to navigate, as they can detect infrasound—low-frequency sound waves—that are often associated with weather patterns, changes in the environment, and even earthquakes.
15. Fennec Fox
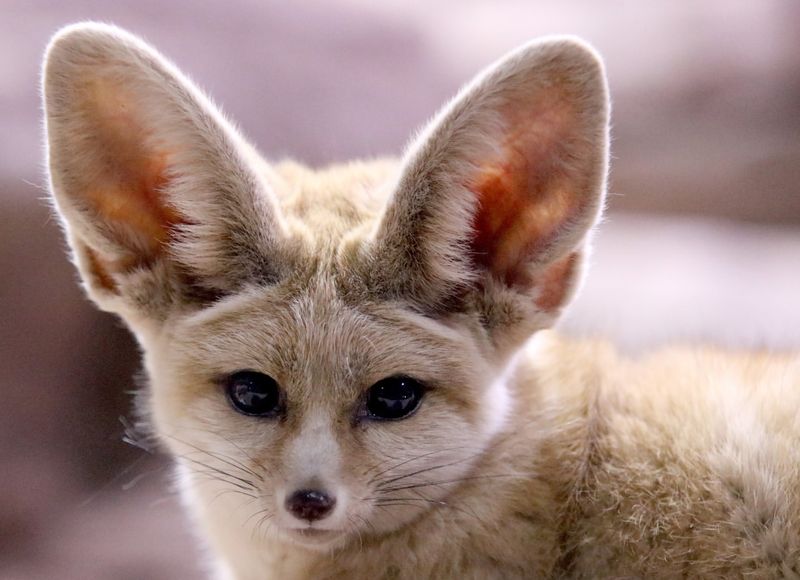

The fennec fox has enormous ears relative to its body size, and this helps it hear sounds in the desert environment where it lives.
Their hearing is incredibly sensitive, allowing them to hear small creatures moving beneath the sand. This specialized hearing helps them hunt and stay aware of potential threats in their arid surroundings.
16. Kangaroo Rat
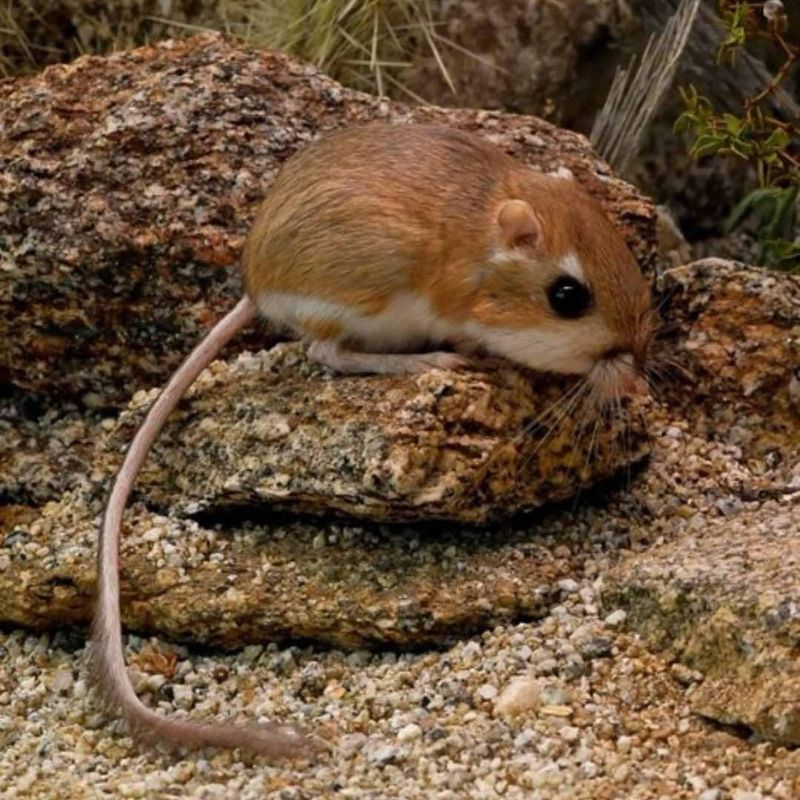

The kangaroo rat, a small desert rodent, has an acute sense of hearing that allows it to detect predators from far away.
Their large ears help them hear the faintest sounds in the desert, and they can often hear the footsteps of predators like owls or coyotes long before they approach. Their sensitive hearing is crucial for survival in such a harsh environment.
17. Beluga Whale
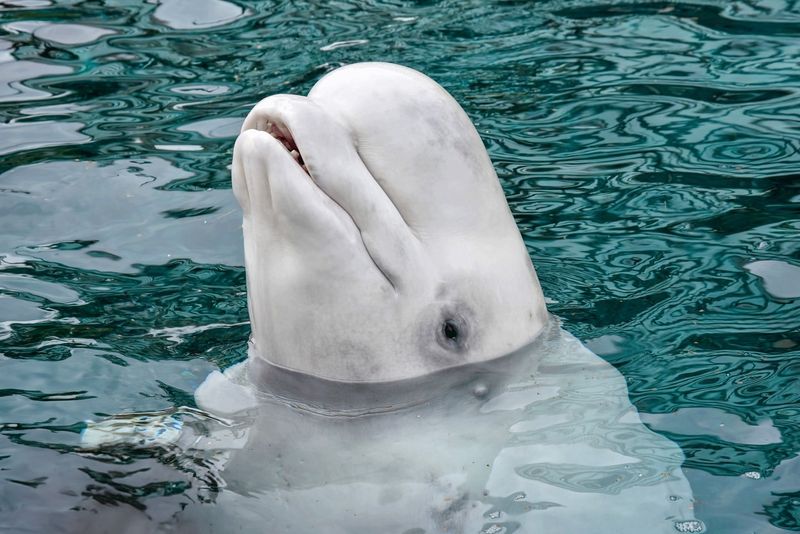

Beluga whales are known for their “canaries of the sea” vocalizations, but their hearing is just as remarkable.
These whales use sound for communication and navigation, and their hearing is so finely tuned that they can detect sounds from other whales and even human-made noises from miles away. They can hear frequencies between 1 and 120 kHz, allowing them to thrive in their Arctic habitats.






