14 Fascinating Animals That Are Completely Hairless

Animals without hair or fur captivate our curiosity with their unique adaptations and appearances. While hair often provides insulation and protection, these fascinating creatures thrive without it.
From creatures of the deep sea to those navigating arid landscapes, each has evolved distinct strategies to survive and thrive.
1. Pangolin
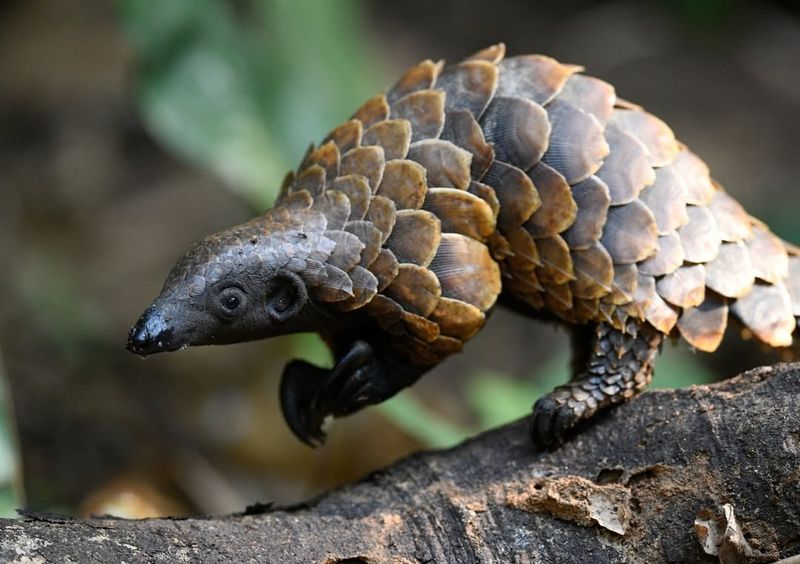

Though many think of pangolins as armored mammals, they’re also completely hairless under their protective scales.
Their keratin-covered bodies are adapted for digging and self-defense. With a tongue longer than their body and no hair in sight, they’re among nature’s most curious creations.
2. Elephant Seal
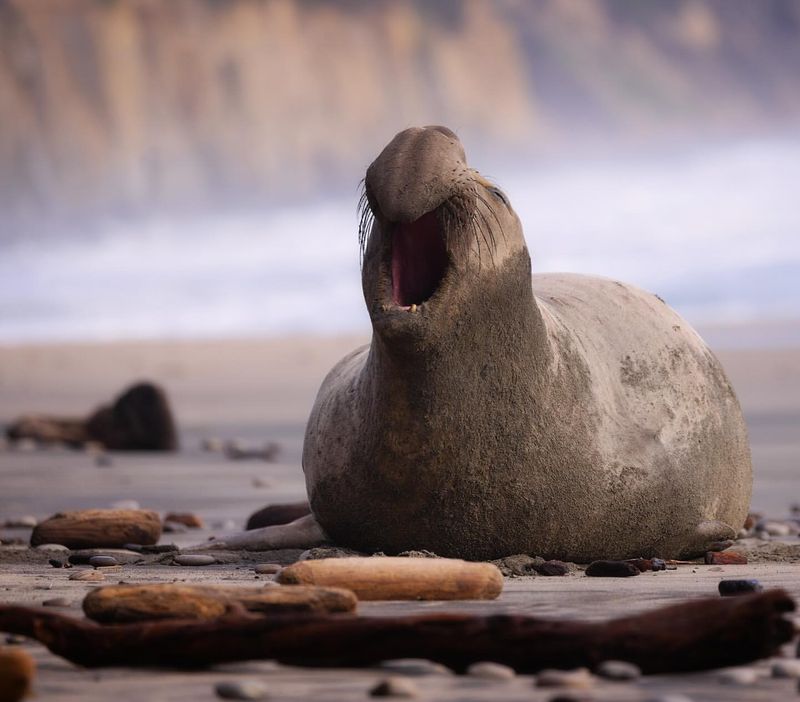

Despite their name, elephant seals are sleek and completely hairless in appearance, with thick blubber replacing fur for insulation.
These massive marine mammals are known for their size, deep vocalizations, and fierce mating battles. Their smooth, oily skin helps them glide effortlessly through the ocean.
3. Naked Mole Rat
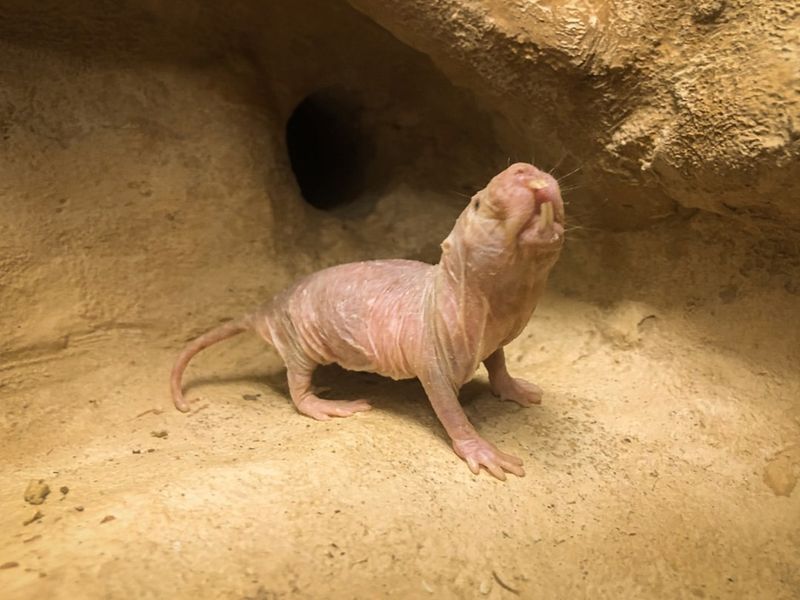

With wrinkled pink skin and large protruding teeth, the naked mole rat is one of the strangest-looking mammals on Earth.
Living underground in eusocial colonies, they’re incredibly resilient to pain and even cancer. Their hairless bodies help them navigate tight, warm tunnels with ease.
4. Fish
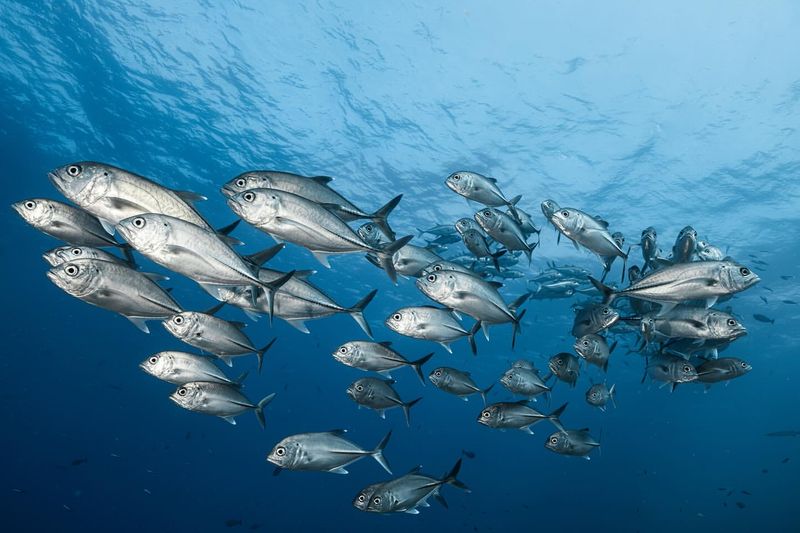

Most fish are completely hairless by nature, relying on scales and mucus-covered skin to protect them in aquatic environments.
From vibrant reef dwellers to deep-sea predators, their smooth bodies are built for streamlined swimming. Hair simply isn’t part of the underwater design.
5. Frog
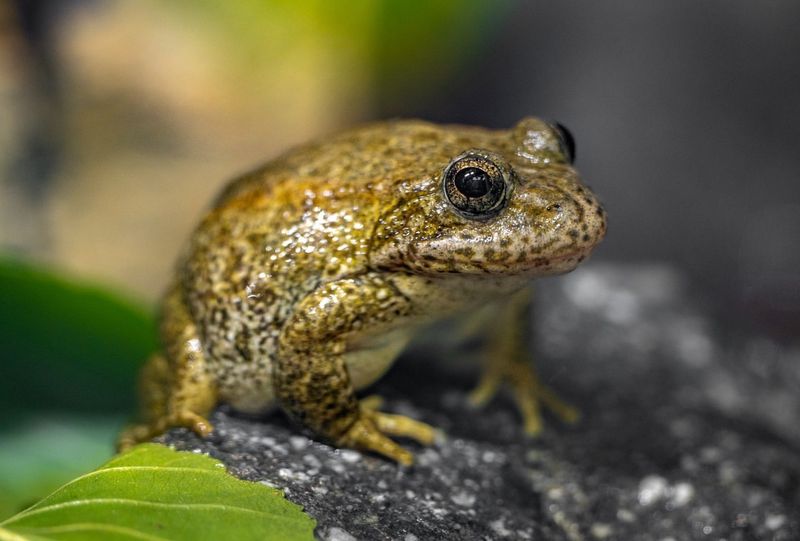

Frogs have soft, permeable skin that absorbs water and oxygen, making hair an unnecessary feature.
Their slick, shiny skin plays a vital role in their survival, especially in moist habitats. It’s one reason they need to stay near water to thrive.
6. Tortoise
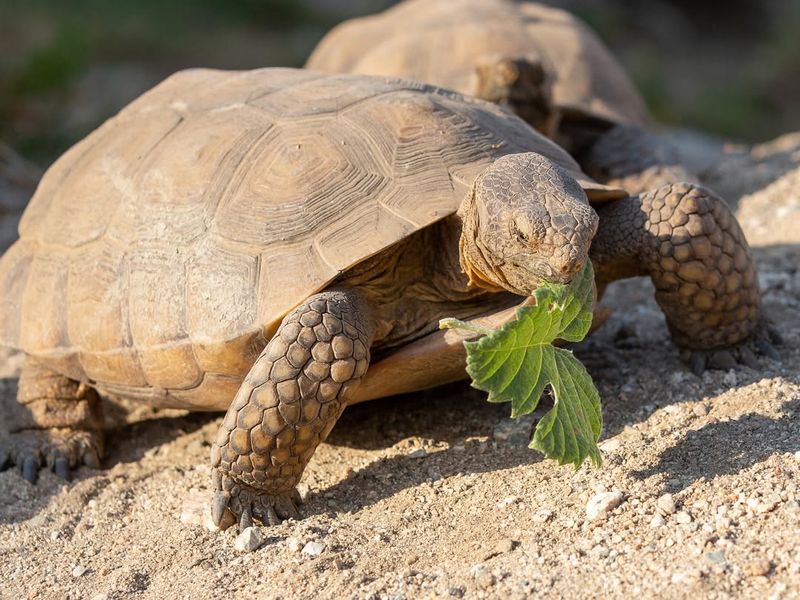

Tortoises are famous for their hard shells and scaly skin, but they’re also entirely hairless.
Their tough exterior protects them from predators and harsh climates. With their slow, steady movements and bald charm, they’ve fascinated humans for centuries.
7. Alligator
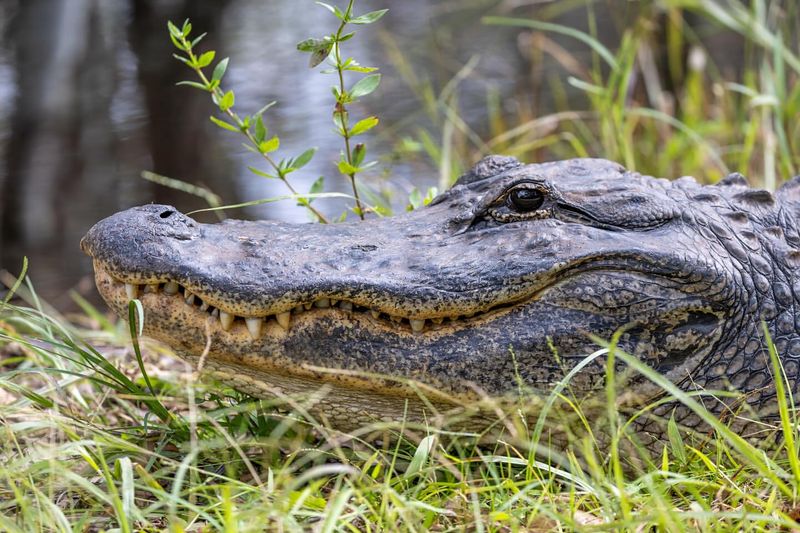

Alligators sport thick, armor-like scales instead of fur, making them one of the most fearsome and ancient-looking reptiles around.
Their tough, hairless hides are perfect for surviving in swampy environments. They’ve ruled the wetlands for millions of years—no hair required.
8. Snake
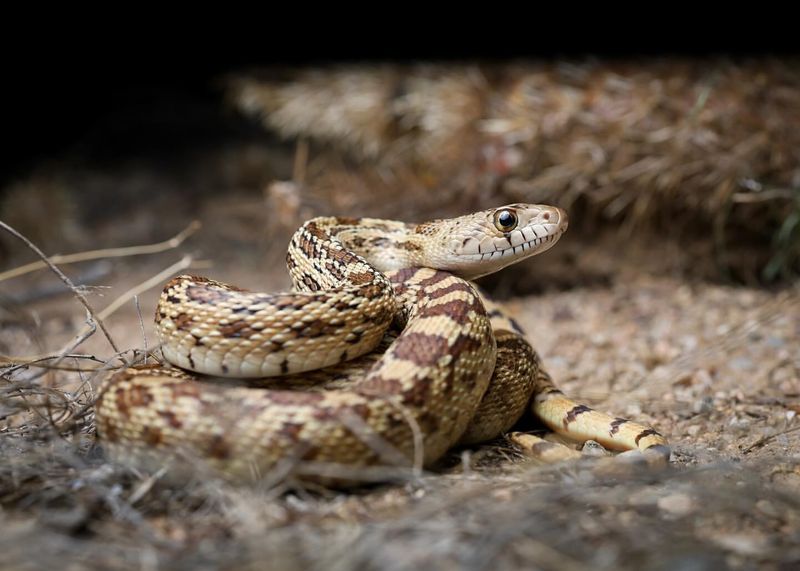

Slithery and sleek, snakes are the ultimate hairless hunters.
Their scale-covered bodies help them move silently across land and water. With no need for fur, snakes rely on heat-sensing pits and camouflage to thrive in nearly every environment.
9. Whales
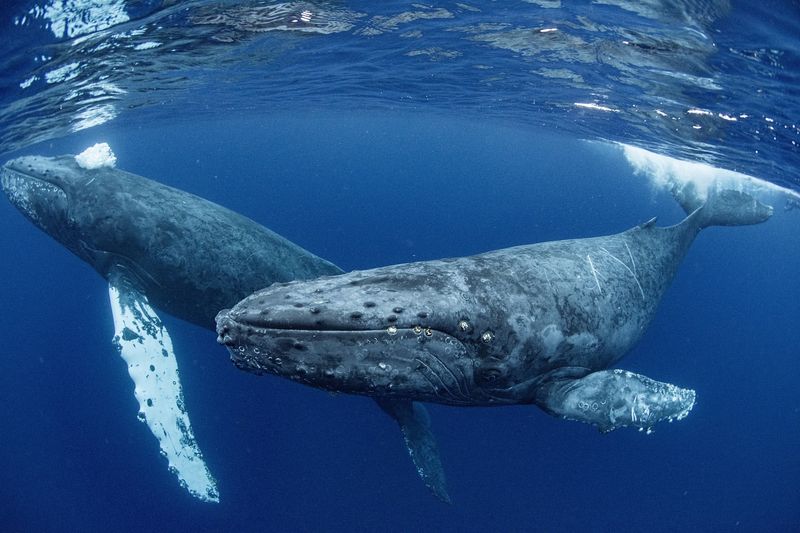

Though they descend from land mammals, whales lost their fur over time to become the smooth, blubber-coated giants we know today.
Their hairless bodies help them conserve energy and move through water efficiently. Some retain tiny hair follicles near their mouths—but nothing like a traditional coat.
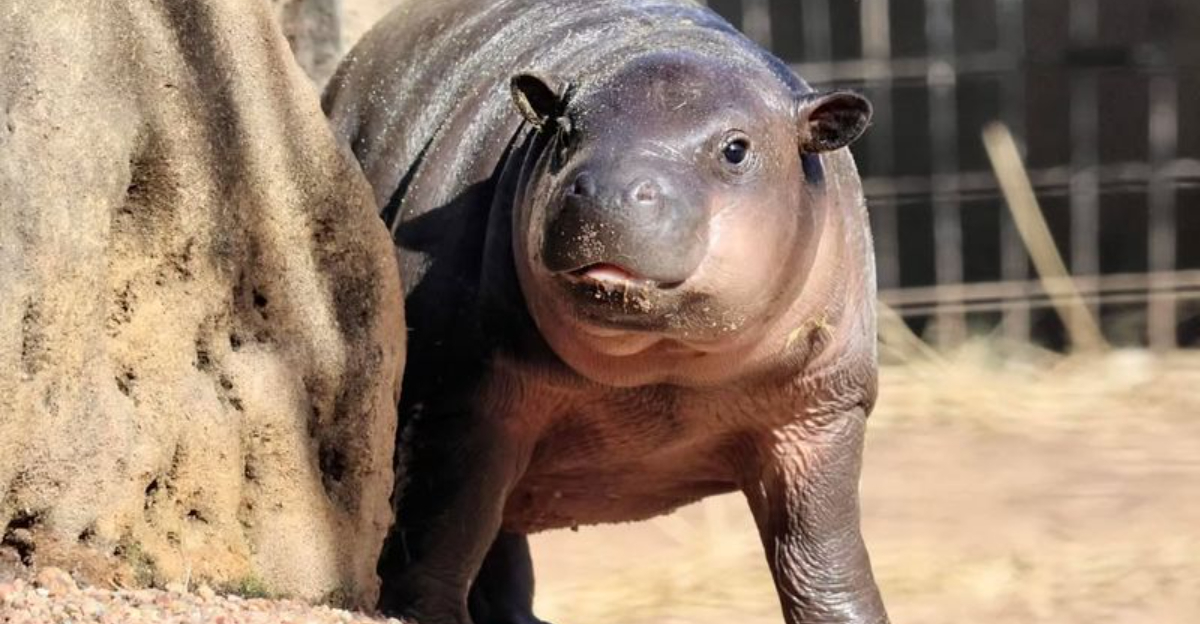
10. Hippo
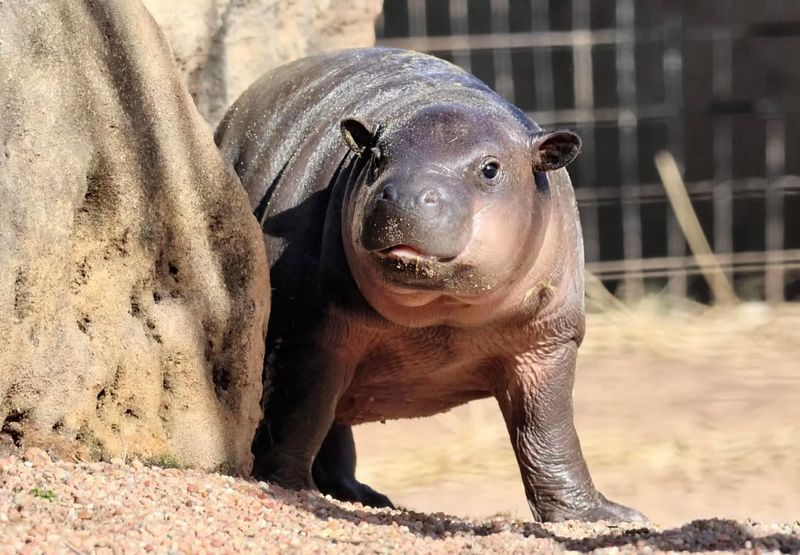

The hippo’s thick, hairless skin is adapted to intense sun and frequent immersion in water.
They secrete a natural sunscreen that gives their skin a shiny appearance and prevents burns. Despite their bulk, their sleek bodies help them swim with surprising agility.
11. Armadillo
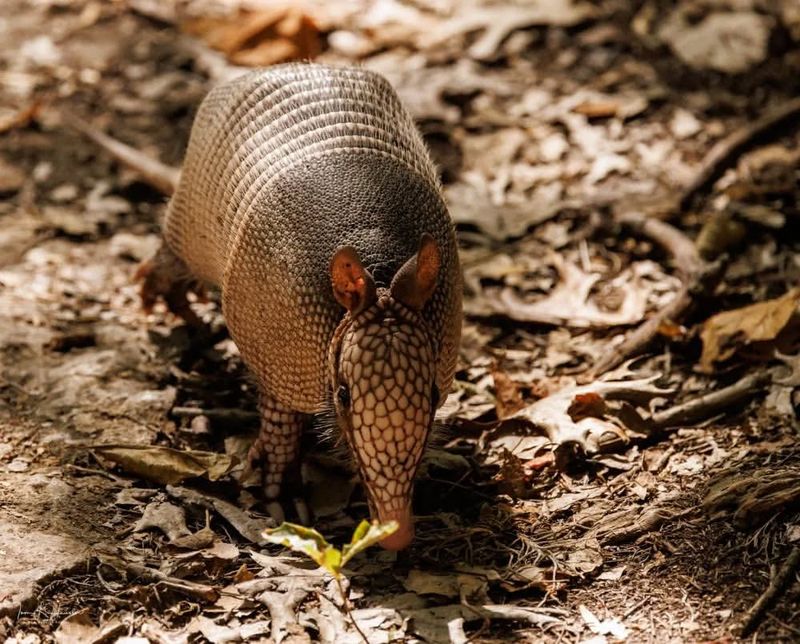

Covered in bony armor and leathery skin, armadillos are virtually hairless mammals with a prehistoric look.
Their smooth shell acts like a natural defense against predators. While they may have sparse hairs on their undersides, their signature look is all scale and no fluff.
12. Leatherback Turtle
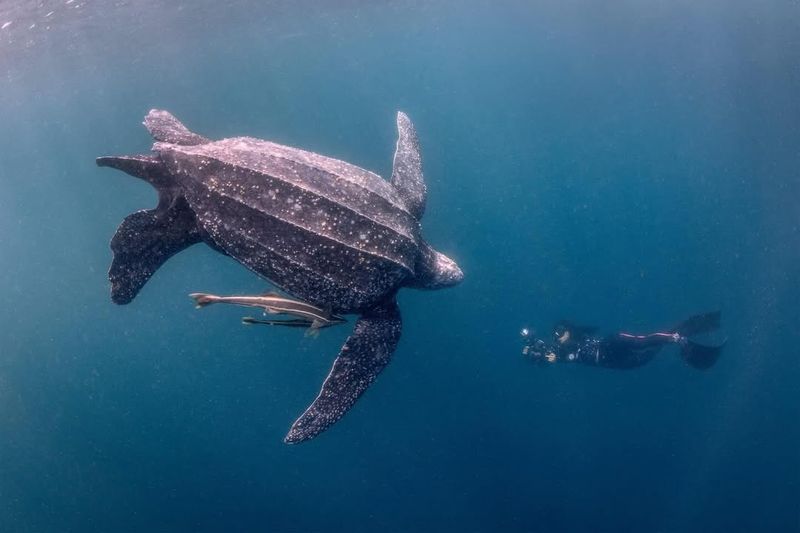

Unlike most sea turtles, leatherbacks have a leathery, rubbery shell instead of hard plates.
Their skin and shell are completely hairless and help them dive to extreme depths. These gentle giants can grow over 6 feet long and are built for endurance, not appearance.
13. Dolphin
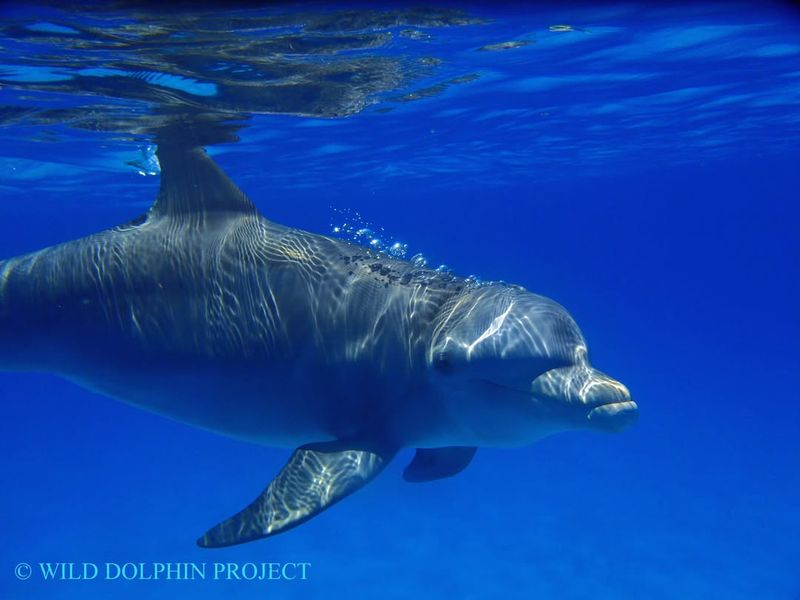

Dolphins are completely hairless, except for a few bristles that fall off shortly after birth.
Their smooth skin allows for fast swimming and frequent surface breaches. They’re known for intelligence, grace, and a sleek appearance that’s all muscle and no fur.
14. Sphynx Cat
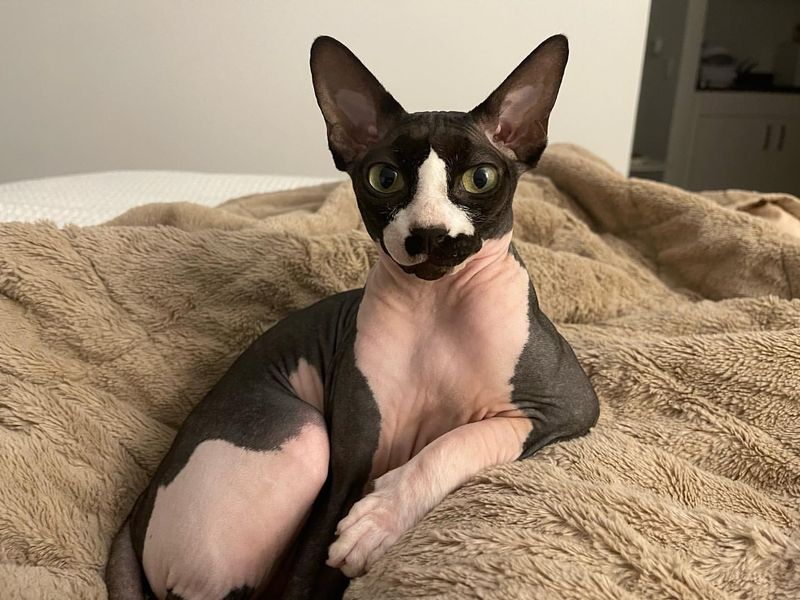
Unlike most cats, the Sphynx is covered in fine, barely noticeable fuzz instead of fur, giving it a smooth, suede-like texture.
These affectionate and quirky cats make up for their lack of hair with bold personalities. Their unique look continues to turn heads and spark conversation.






