26 Animals That Are Surprisingly At The Bottom Of The Food Chain

In the intricate web of life, every creature has its place, and some find themselves at the very bottom of the food chain.
These animals play vital roles in their ecosystems, often serving as crucial sources of energy for higher predators. From tiny insects to small amphibians, these animals may be at the bottom, but they are far from insignificant.
1. Grasshoppers
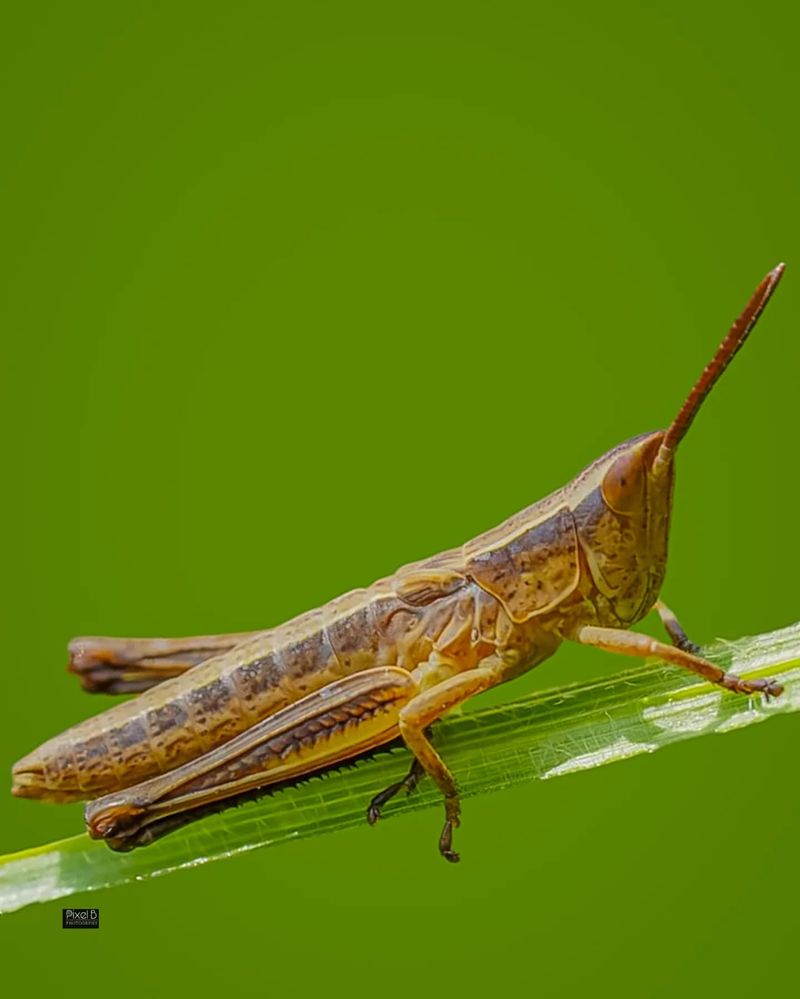

Grasshoppers are common insects found in various habitats, from grasslands to forests. Known for their powerful hind legs, grasshoppers are excellent jumpers, which helps them evade predators and explore their environment.
These herbivorous insects play a significant role in their ecosystems by feeding on plants and serving as a primary food source for birds, reptiles, and small mammals. Grasshoppers contribute to the balance of plant life and help maintain the health of their habitats.
2. Ants
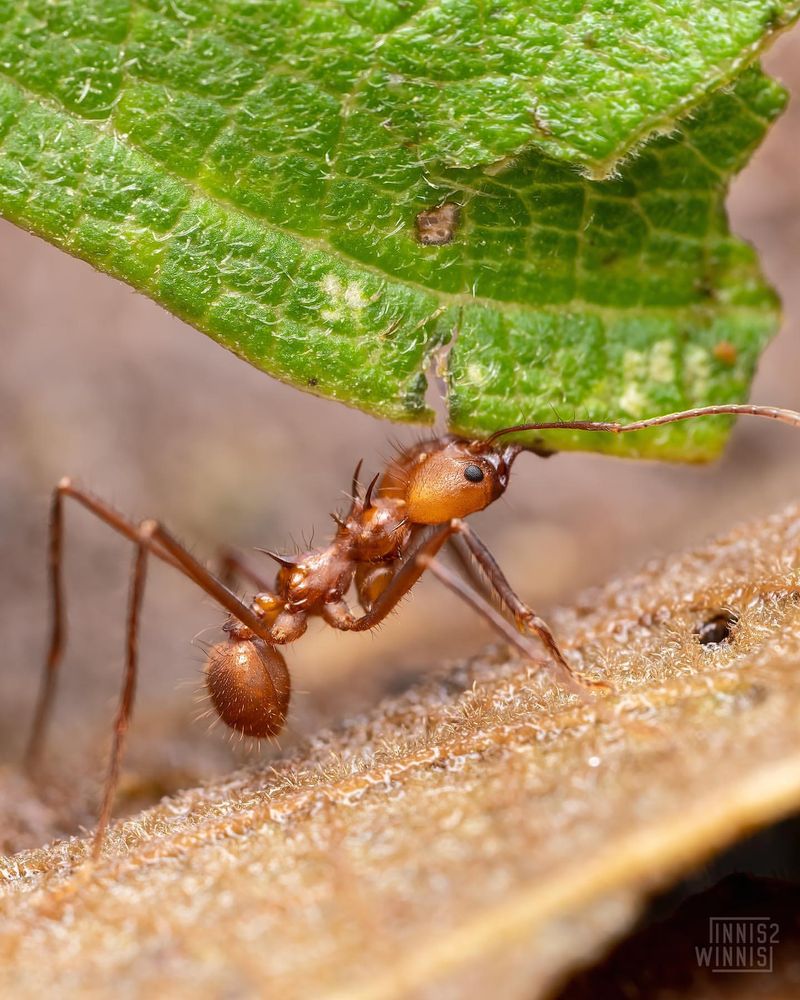

Ants are fascinating insects that can be found in nearly every corner of the Earth. Although they are small in size, ants are known for their incredible strength and teamwork.
Living in highly organized colonies, ants play a significant role in their ecosystems by aerating the soil and recycling nutrients.
These industrious insects are also a vital food source for numerous animals, including birds, anteaters, and other small mammals. Ants’ ability to adapt to various environments makes them indispensable players in their habitats.
3. Krill
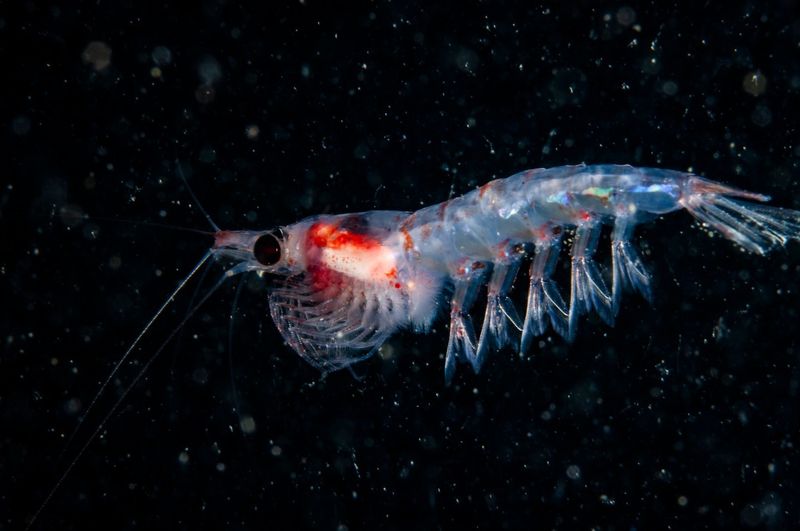

Krill are small, shrimp-like crustaceans that swarm in massive numbers in oceans around the world. These tiny creatures are a crucial component of the marine food web, serving as the primary diet for many larger animals, such as whales, seals, penguins, and fish.
Their abundance and nutritional value make krill an essential part of the diet for many species, helping sustain the vast marine life diversity. Despite their size, krill collectively have a massive impact on ocean ecosystems.
4. Earthworms
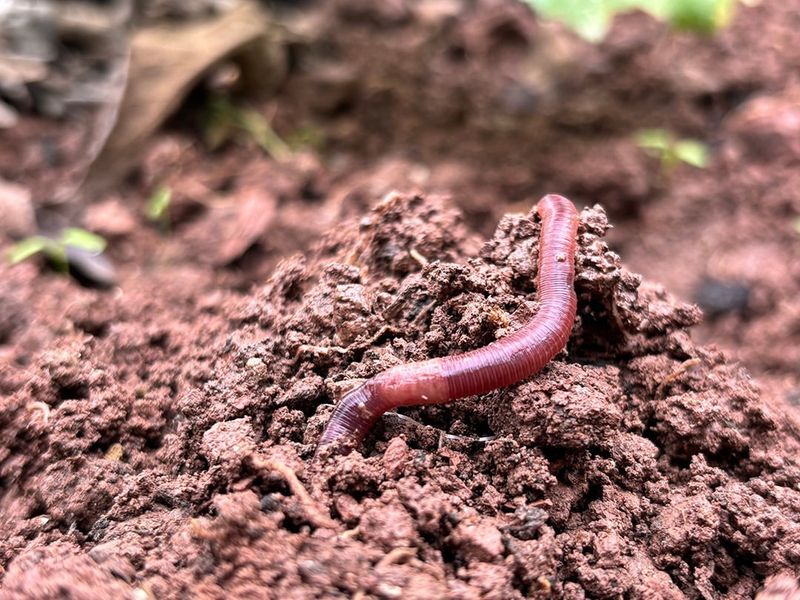

Earthworms are essential soil dwellers that play a crucial role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. As they burrow through the earth, they aerate the soil, facilitating the growth of plants by allowing air and water to reach plant roots.
Earthworms consume organic material, breaking it down and enriching the soil with nutrients. This process is vital for plant growth and the overall health of gardens and agricultural fields. In doing so, earthworms support the base of the terrestrial food chain.
5. Mealybugs
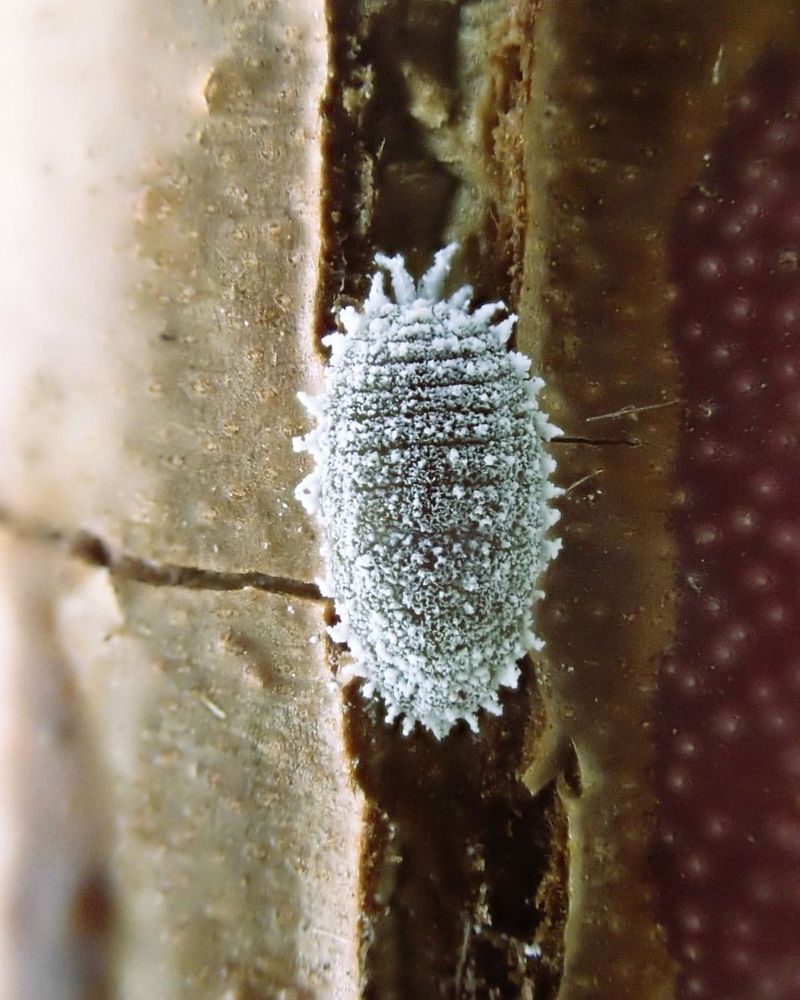

Mealybugs are small, sap-sucking insects commonly found on plants in gardens and greenhouses. Known for their soft, white, waxy coating, mealybugs can often be spotted on the undersides of leaves.
These pests feed on plant sap, which can weaken plants and lead to reduced growth. However, they also serve as a food source for various predatory insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings.
6. Termites
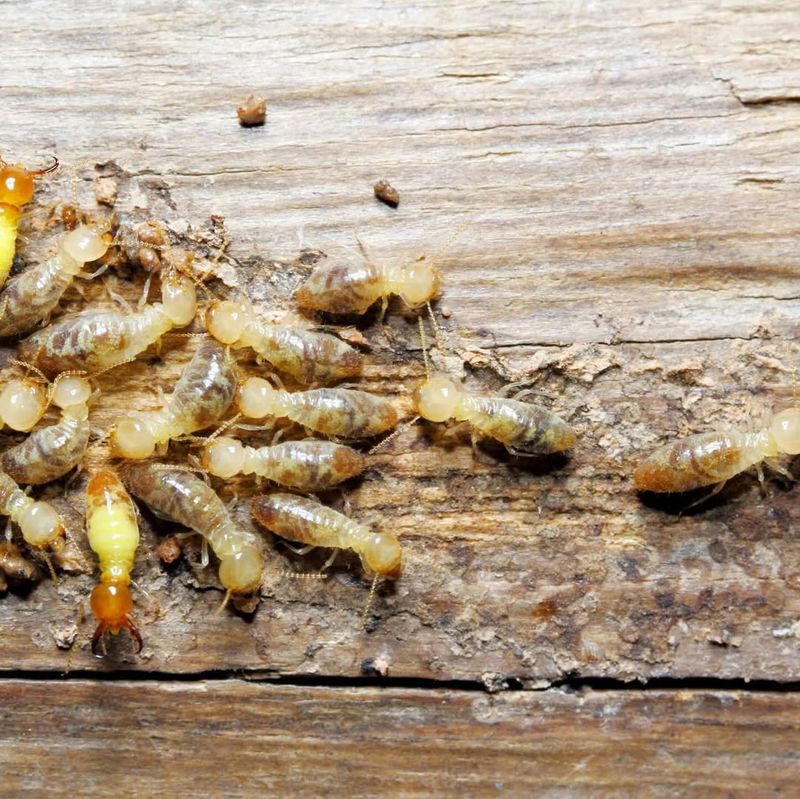

Termites are small, social insects that thrive in colonies, often within mounds or wooden structures. Known for their role in decomposition, termites break down dead plant materials, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
These industrious insects are particularly vital in tropical ecosystems, where they contribute to soil formation and fertility. By breaking down tough plant fibers, termites enable other organisms to access essential nutrients.
7. Algae Eaters
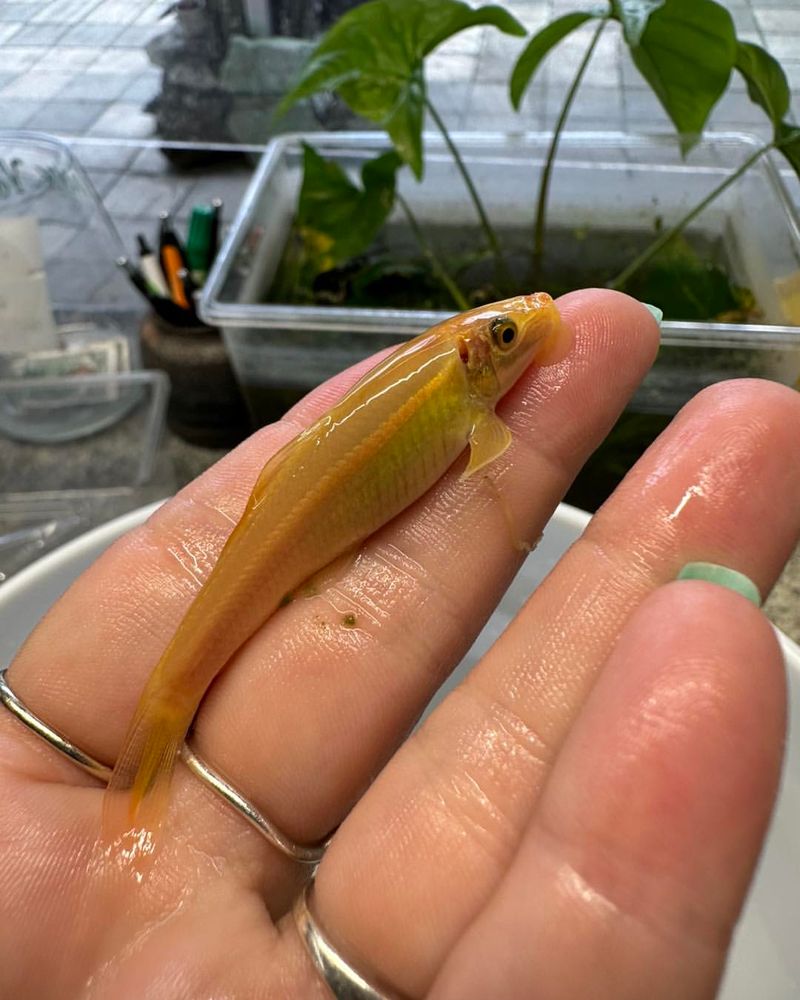

Algae eaters are organisms that consume algae, playing a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems by controlling algae growth. These creatures can range from small invertebrates to larger fish, each contributing to the balance of their environments.
By feeding on algae, these organisms prevent overgrowth that can lead to oxygen depletion in water bodies, ensuring the survival of other aquatic life. Algae eaters are essential for maintaining clear and healthy waters.
8. Plankton
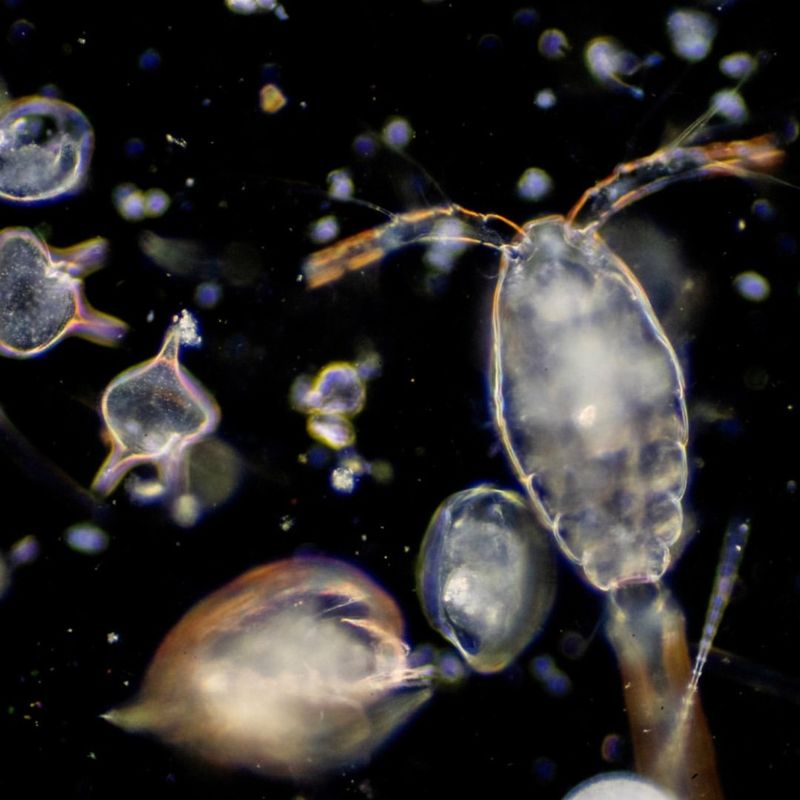

Plankton are tiny, often microscopic organisms that float in water bodies across the globe. These small creatures are the foundation of aquatic ecosystems, serving as the primary food source for many marine animals, including fish and whales.
Despite their size, plankton play a monumental role in maintaining the balance of oceanic life. Plankton can be divided into two main categories: phytoplankton, which are plant-like and perform photosynthesis, and zooplankton, which are animal-like and consume other plankton.
9. Bee larvae
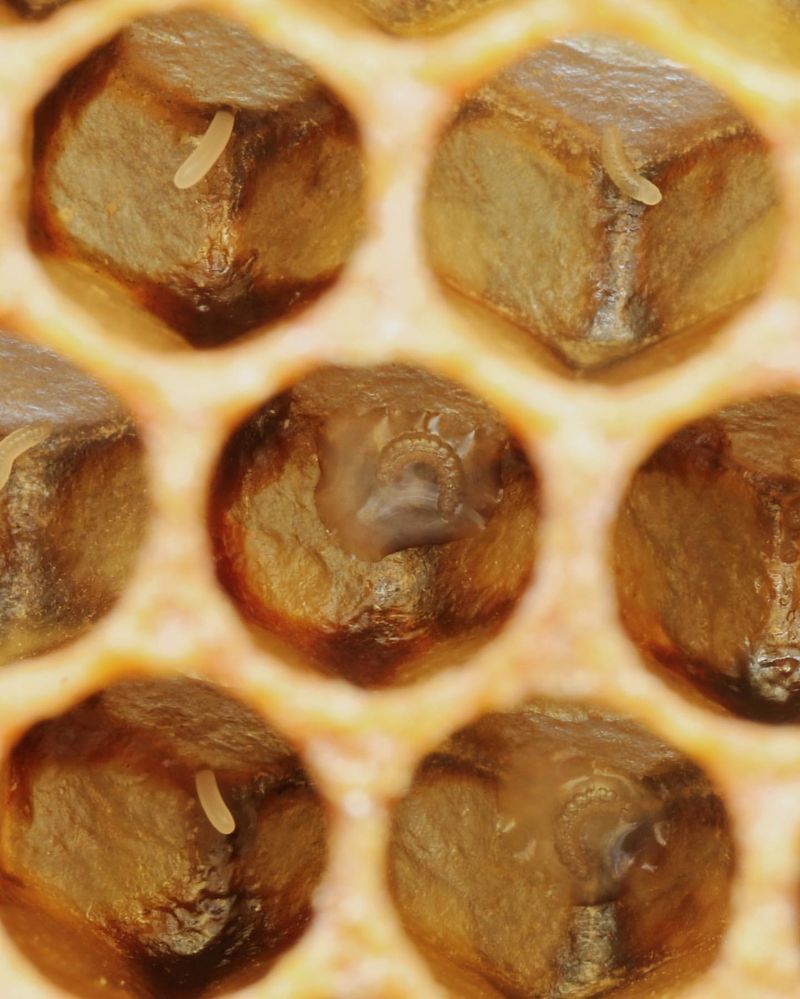

Bee larvae are the developing young of bees, nurtured within the protective cells of a honeycomb. These larvae are crucial to the survival and continuity of bee colonies, growing into the pollinators we rely on for food production.
Inside the hive, bee larvae are cared for by worker bees, feeding them a diet rich in royal jelly and nectar. This nourishment supports their development into adult bees, ready to take on the world.
10. Brine Shrimp
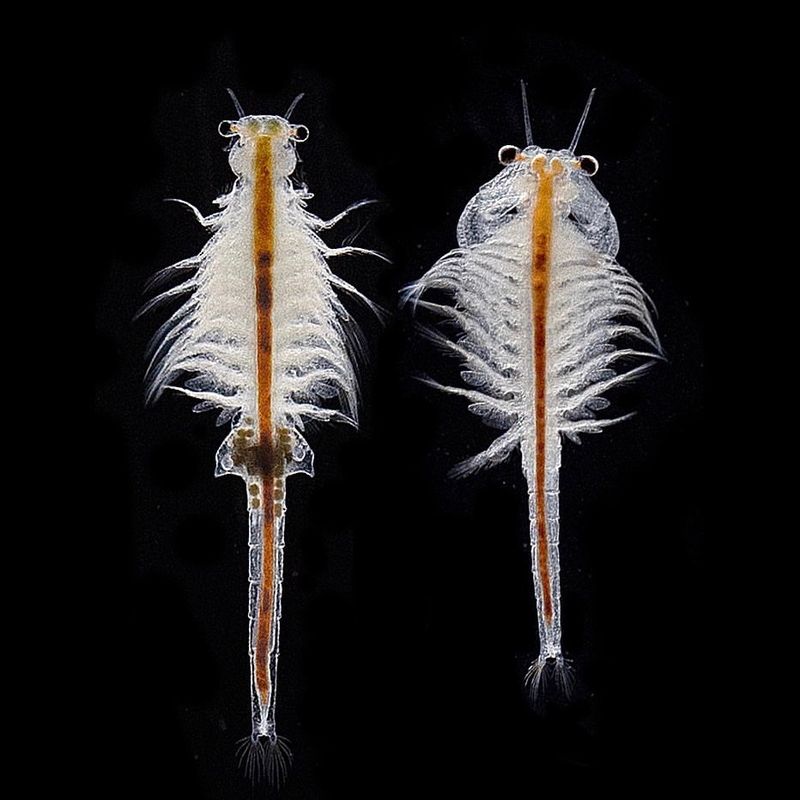

Brine shrimp, often known as “sea monkeys,” are tiny crustaceans found in saltwater lakes and ponds. These resilient creatures thrive in extreme conditions, withstanding high salinity levels that few other organisms can tolerate.
Despite their small size, brine shrimp are an essential food source for a variety of birds and fish. Their ability to survive in harsh environments makes them invaluable to the ecosystems they inhabit.
11. Daphnia
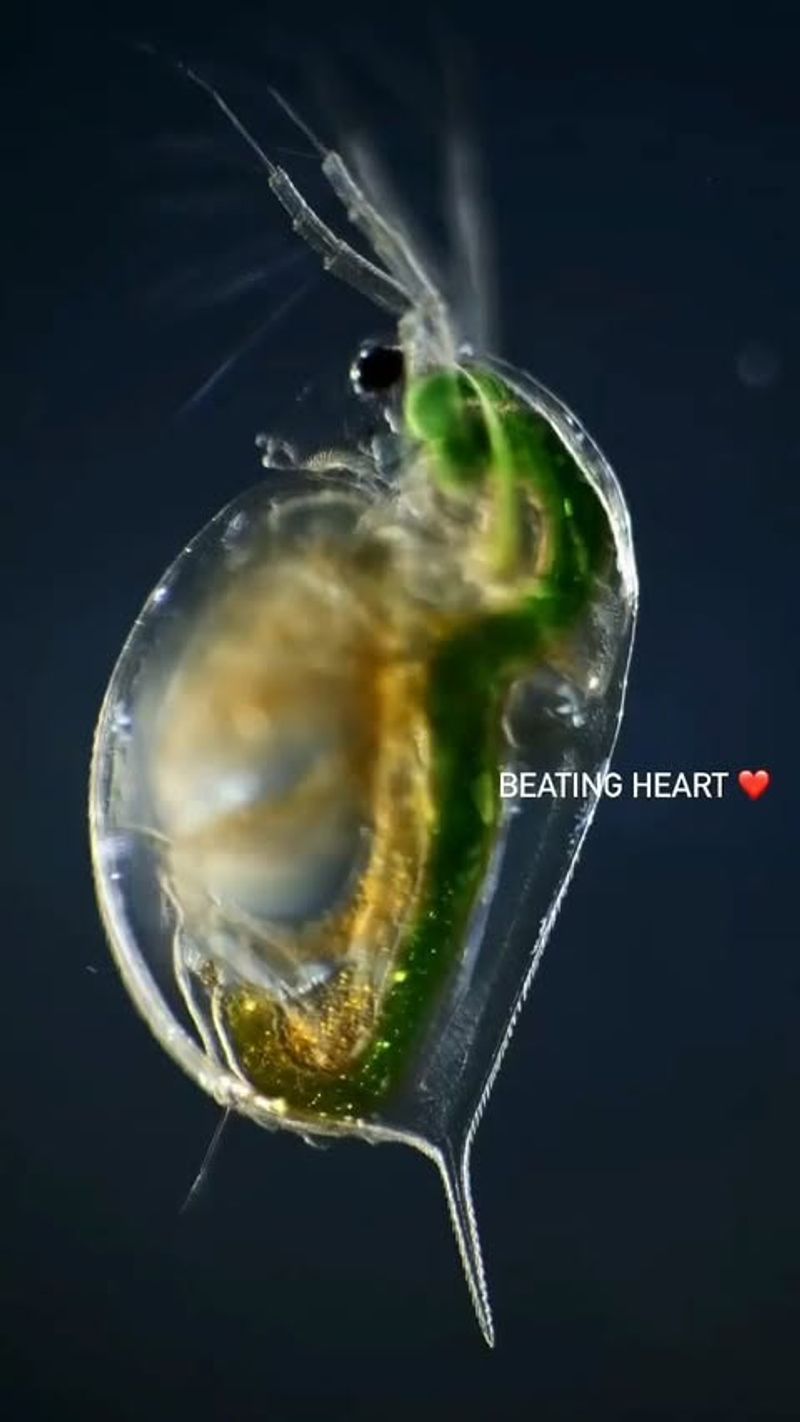
Daphnia, often referred to as “water fleas,” are small, planktonic crustaceans found in freshwater environments. These transparent creatures are a key component of aquatic ecosystems, serving as a primary food source for fish and other aquatic animals.
Daphnia are filter feeders, consuming algae and bacteria, which helps maintain water quality and clarity. Their presence in water bodies is a good indicator of ecosystem health.
12. Sea Urchins
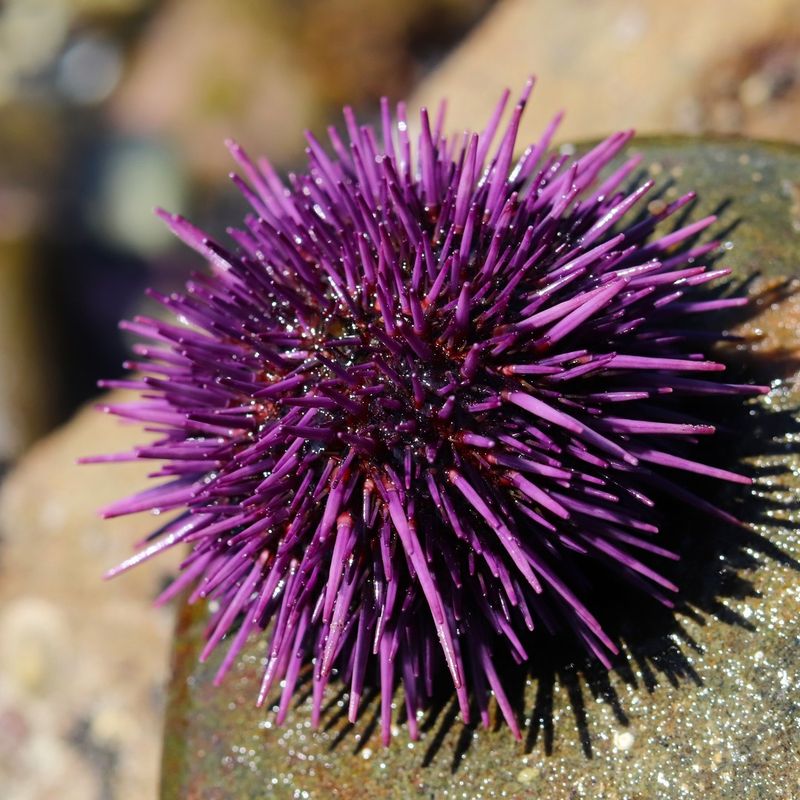

Sea urchins are spiny, globular animals found on the ocean floor, often among coral reefs and rocky shorelines. These echinoderms play a significant role in marine ecosystems by feeding on algae and helping control its growth.
By grazing on algae, sea urchins prevent overgrowth that can smother coral reefs and disrupt marine habitats. This grazing activity is crucial for maintaining the health and diversity of coral reef ecosystems.
13. Limpets
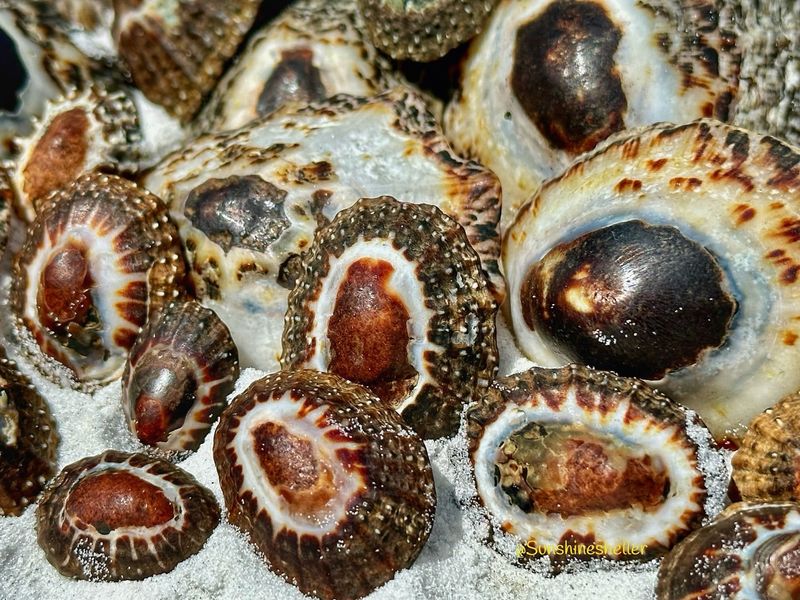

Limpets are small, marine mollusks with conical shells, commonly found clinging to rocks along coastlines. These sturdy creatures are herbivores, feeding primarily on algae that grow on rocky surfaces.
By grazing on algae, limpets help control its growth, maintaining the balance of intertidal ecosystems. Their feeding habits prevent algal overgrowth, which can impact other marine species that share their habitat.
14. Snails

Snails are small, slow-moving mollusks with a coiled shell, found in various environments, from gardens to forests. These creatures are known for their methodical pace and fascinating biology, including their ability to retract into their shells for protection.
Snails are herbivores, feeding on plant material and playing a role in decomposition and nutrient cycling. Their activities contribute to soil health and plant growth by breaking down organic matter.
15. Larval Fish
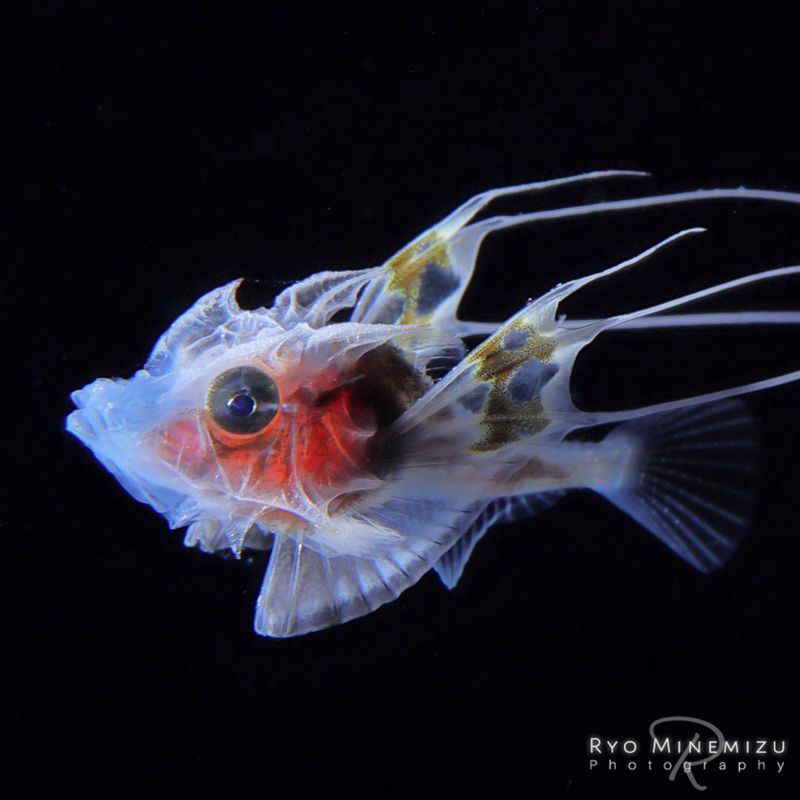

Larval fish are the early developmental stage of fish, found in various aquatic environments. These tiny creatures drift with ocean currents, feeding on plankton as they grow and develop into adult fish.
Despite their vulnerability, larval fish are a crucial component of marine food webs. They serve as prey for a range of marine animals, including larger fish and seabirds.
16. Leafcutter Bees
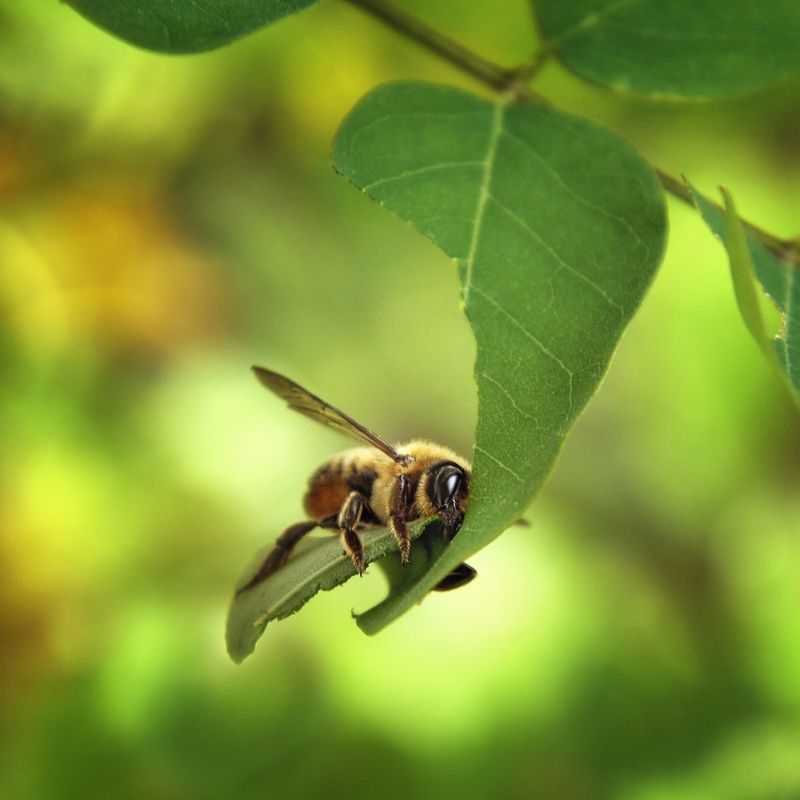

Leafcutter bees are fascinating creatures, often overlooked in the grand scheme of nature. These diminutive architects are found in backyards, diligently cutting leaves to build their nests.
Though they possess the ability to sting, they are non-aggressive and rarely pose a threat to humans.
Despite their industrious nature, leafcutter bees are at the mercy of many predators, ranging from birds to larger insects. Their primary defense is their camouflage, blending seamlessly with the greenery.
17. Caterpillars
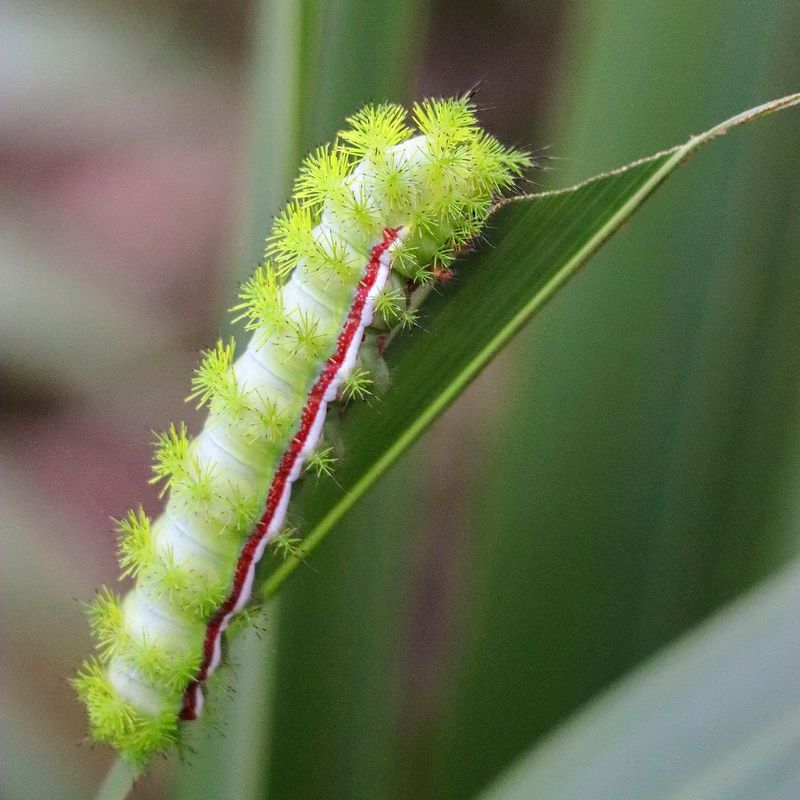

Caterpillars are the larval stage of butterflies and moths, found crawling on leaves and plants. These voracious eaters play a vital role in their ecosystems by consuming plant material and serving as a primary food source for birds and other predators.
As they munch on leaves, caterpillars contribute to plant population control and nutrient cycling. Their presence is crucial for maintaining the balance of plant and animal interactions in their habitats.
18. Fairy Shrimp
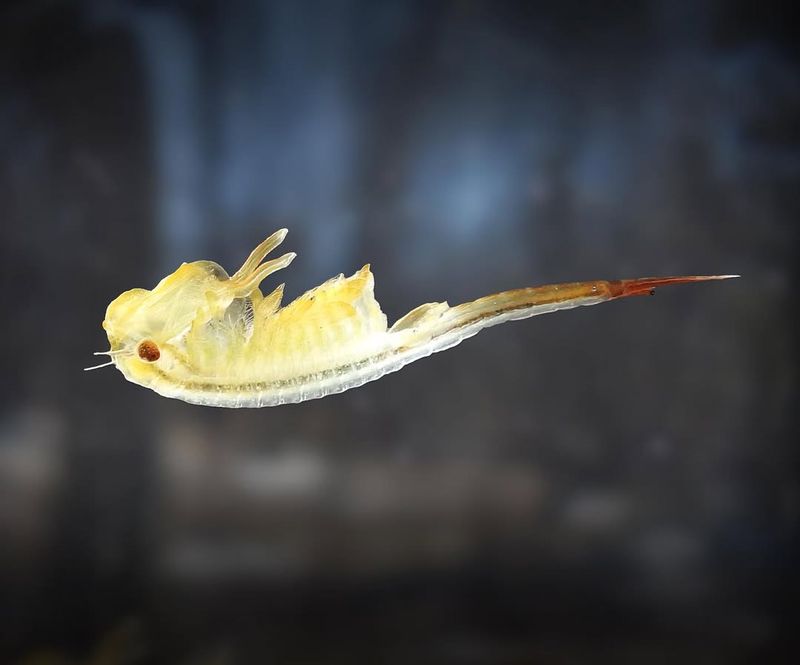

These translucent creatures, often less than an inch long, flit gracefully through their watery homes. Despite their ethereal appearance, they are essential components of their ecosystem.
Living short lives, fairy shrimp are critical food sources for birds, amphibians, and other aquatic creatures. Their eggs can endure harsh climates, waiting for the perfect conditions to hatch, ensuring their survival through successive generations.
19. Aphids
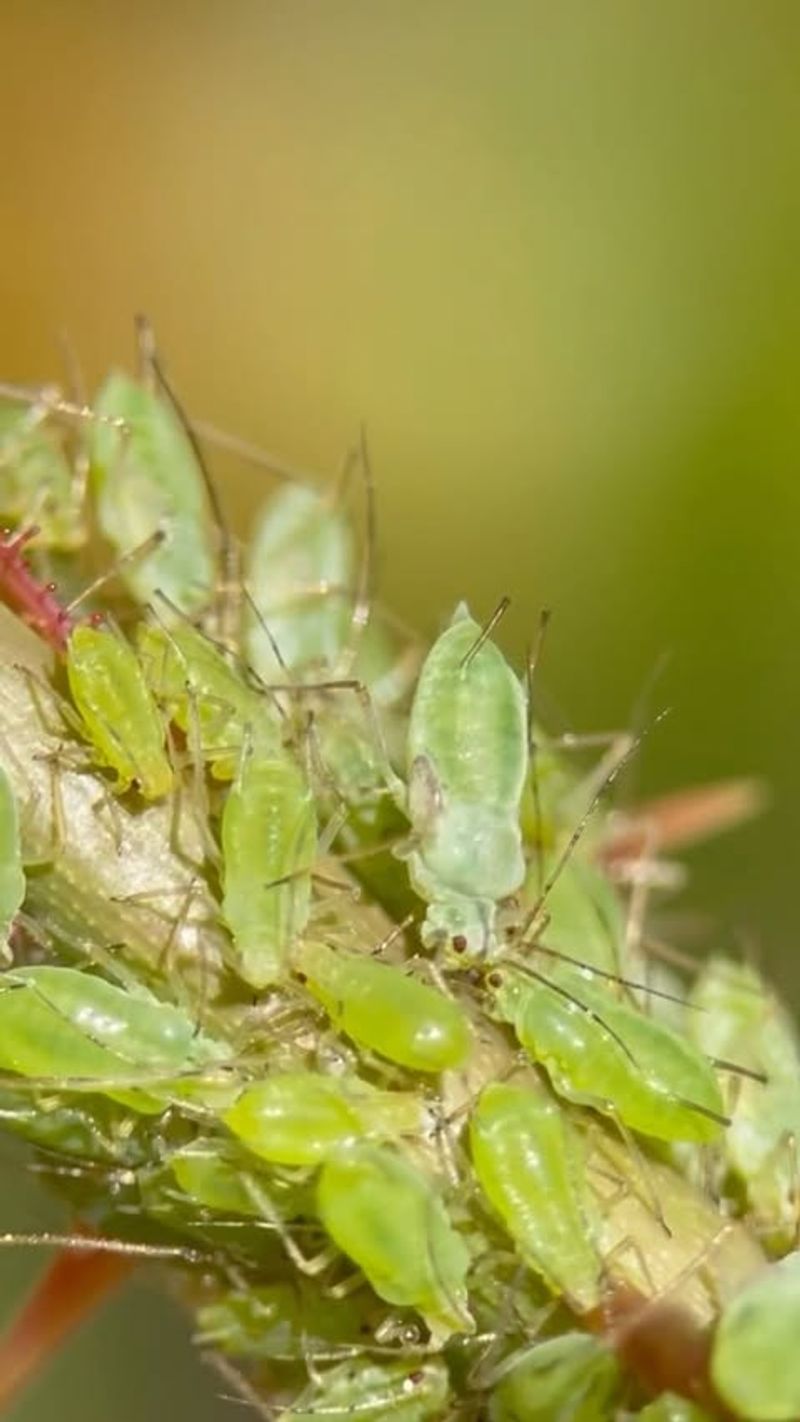

Aphids are small, sap-sucking insects commonly found on plants in gardens and fields. Known for their rapid reproduction, these pests can quickly form large colonies on the undersides of leaves.
While they can cause damage to plants by feeding on their sap, aphids also serve as a primary food source for various predatory insects, such as ladybugs and parasitic wasps.
20. Pill Bugs
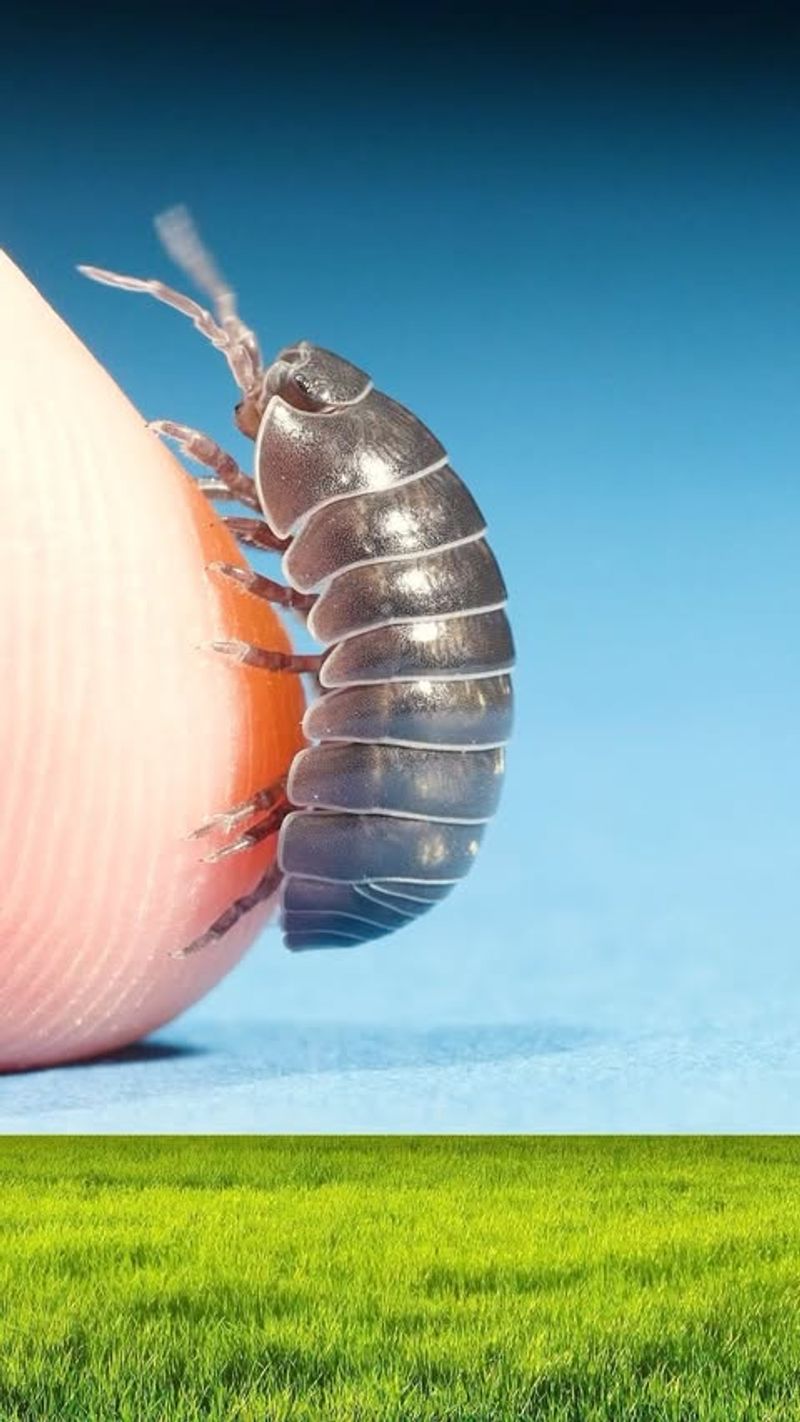

Pill bugs, also known as roly-polies, are small terrestrial crustaceans found in damp environments, such as under logs and rocks. Despite their resemblance to insects, pill bugs are crustaceans and play a significant role in decomposition.
These creatures feed on decaying organic matter, breaking it down and recycling nutrients back into the soil. This activity aids in soil health and fertility, supporting plant growth.
21. Clams
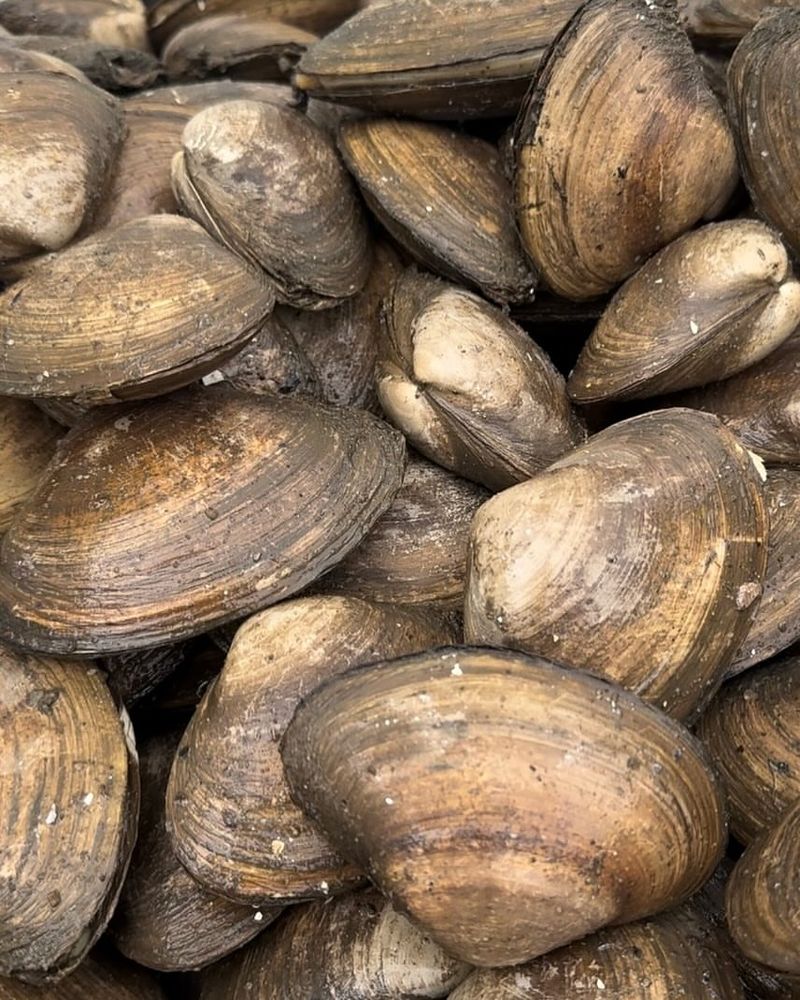

Clams are bivalve mollusks found in both freshwater and marine environments, often burrowed in sand or mud. These filter feeders play a vital role in aquatic ecosystems by cleaning the water as they consume plankton and organic particles.
By filtering water, clams improve its quality and clarity, benefiting other aquatic life and supporting overall ecosystem health. Their presence in water bodies can indicate a thriving environment.
22. Midges

Midges are small, flying insects commonly found near water bodies, where they breed and develop. Despite their tiny size, midges play a significant role in ecosystems by serving as a food source for birds, bats, and fish.
These insects undergo a complete metamorphosis, with larvae living in water and adults emerging to breed and lay eggs. Their life cycle connects aquatic and terrestrial environments, transferring energy between these systems.
23. Barnacles
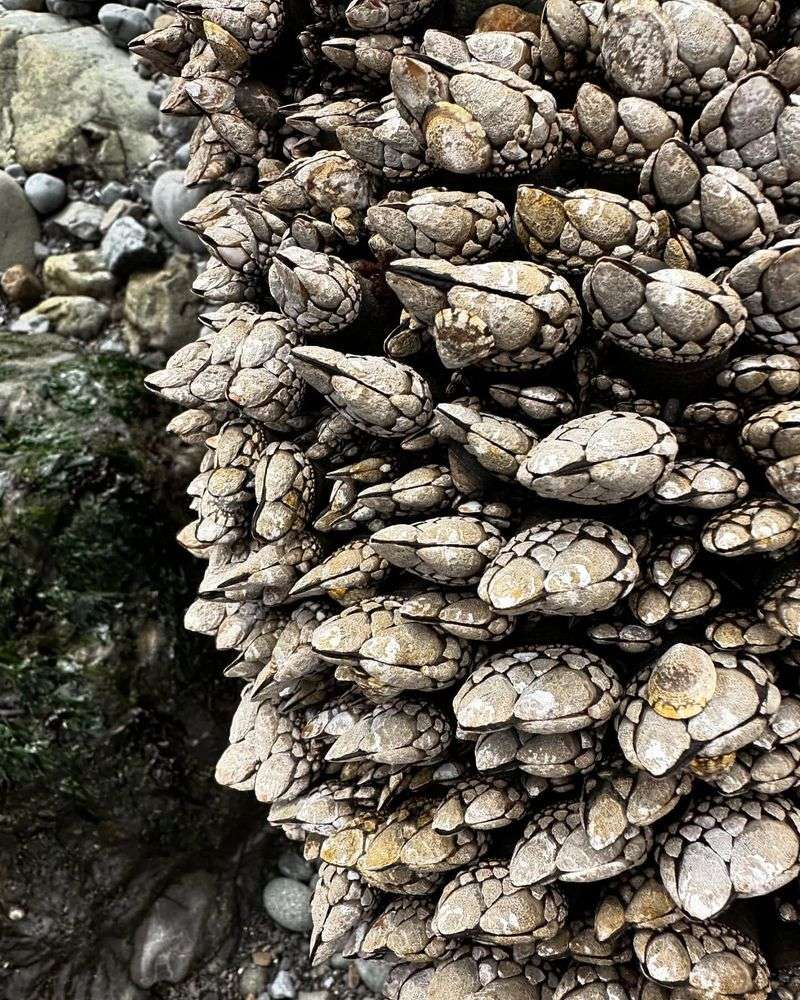

Barnacles are small crustaceans that attach themselves to hard surfaces, such as rocks, ship hulls, and even whales. Found in marine environments, barnacles are filter feeders, consuming plankton and organic particles from the water.
By filtering water, barnacles contribute to the cleanliness and health of their ecosystems. Their presence often indicates a thriving marine environment with abundant plankton.
24. Crickets
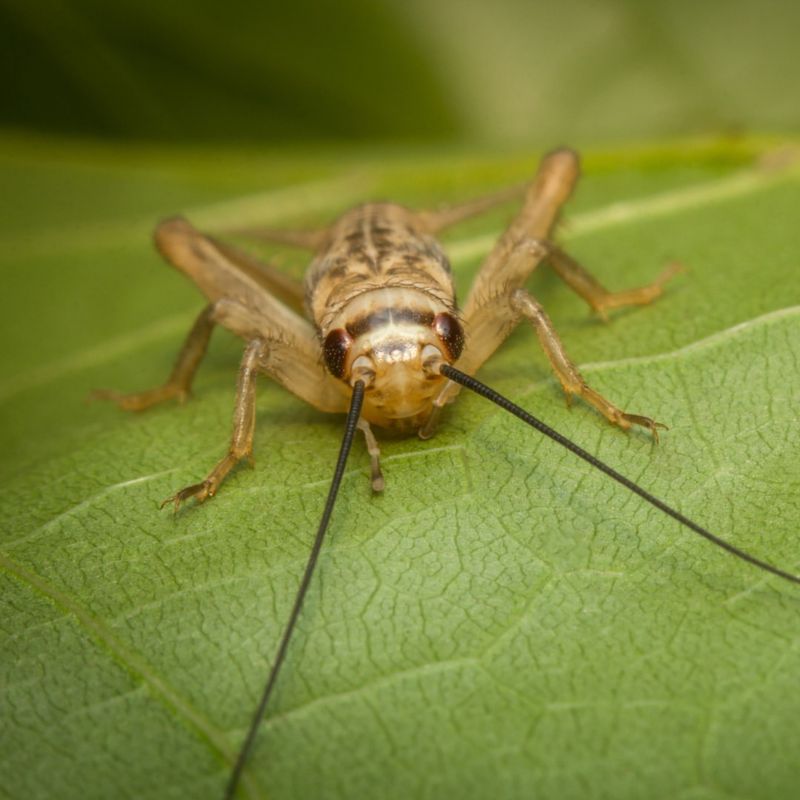

Crickets are small, nocturnal insects known for their distinctive chirping sounds, produced by rubbing their wings together. Found in diverse habitats, crickets play a significant role in ecosystems by consuming plant material and serving as prey for numerous animals.
These omnivorous insects help control plant populations and contribute to nutrient cycling, supporting soil health and fertility. Their presence in ecosystems aids in the balance between plant and animal interactions.
25. Oysters
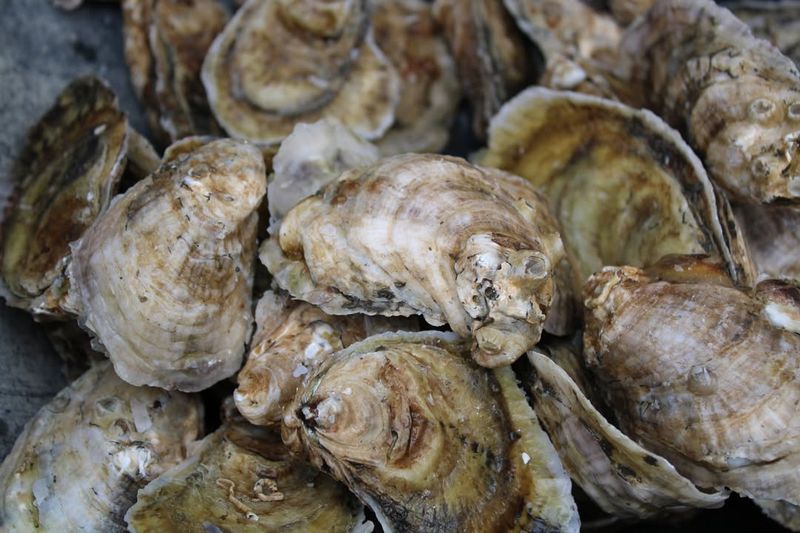

Oysters are bivalve mollusks found in marine environments, often forming dense colonies on rocky substrates. As filter feeders, oysters consume plankton and suspended particles, playing a critical role in water purification.
Their filtering activity improves water quality and clarity, benefiting other aquatic life and supporting overall ecosystem health. Oysters are also important habitat providers, creating beds that support diverse marine species.
26. Springtails
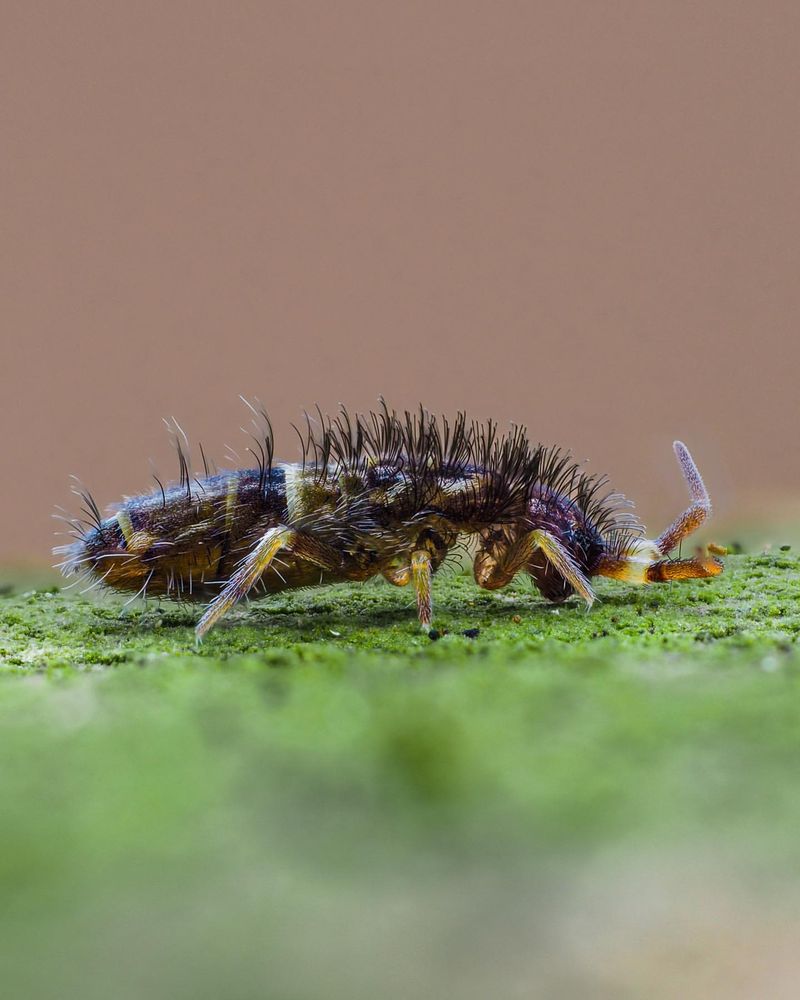

Springtails are tiny, soil-dwelling arthropods found in moist environments such as leaf litter and decaying wood. These creatures are known for their ability to jump great distances relative to their size, thanks to a specialized appendage called a furcula.
Springtails are decomposers, feeding on fungi, bacteria, and decaying organic matter. Their activities contribute to soil health and fertility, supporting plant growth and nutrient cycling.






