10 Amazing Animals That Look Like Raccoons

These intriguing creatures, from various corners of the world, share astonishing similarities with the mischievous raccoon.
With their unique traits and appearances, they captivate nature enthusiasts and curious minds alike.
Explore how these animals parallel the raccoon in appearance and behavior, while also embracing their distinct identities.
1. Coatis
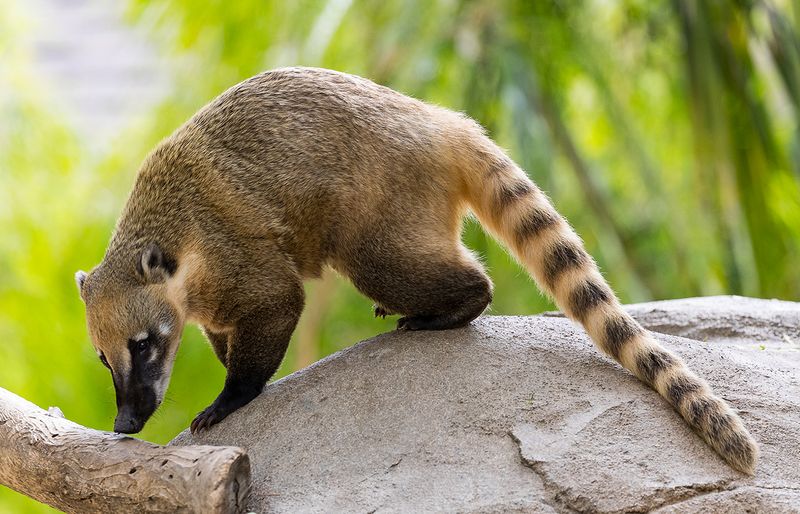

Coatis are members of the raccoon family, native to Central and South America. Their long, bushy tails with rings and dark facial masks resemble those of raccoons.
Inquisitive by nature, coatis forage for insects, fruits, and small animals. They often socialize in groups, making them fun to observe. Coatis also climb trees skillfully with their sharp claws.
Their playful antics and curious demeanor often make them the center of attention in their natural habitat.
2. Ring-Tailed Lemurs
Ring-tailed lemurs hail from Madagascar, boasting a black-and-white ringed tail similar to a raccoon’s. Their expressive eyes and facial markings create a resemblance to the masked bandit.
Spending much time in trees, they travel in groups called troops. These social creatures communicate with vocalizations, gestures, and scent markings.
Unlike raccoons, they bask in the sun with arms outstretched, appearing almost meditative. Despite differences in behavior, their appearance makes them a captivating sight.
3. Kinkajous
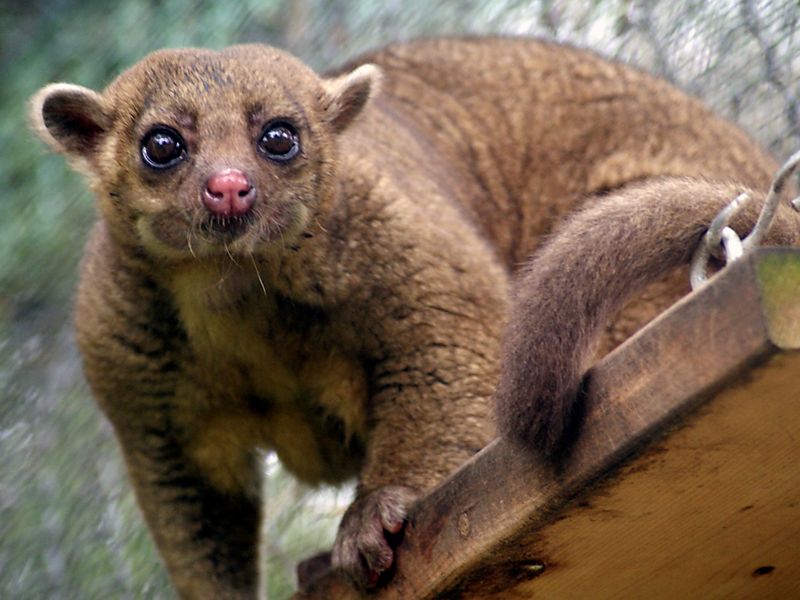

Kinkajous, or ‘honey bears,’ are nocturnal mammals from Central and South America. They possess large, round eyes and a long tail used for maneuvering through trees.
Their facial features, particularly the dark eye markings, mimic a raccoon’s mask. These playful creatures feed on fruits, nectar, and insects.
At night, their curious nature leads them to explore their surroundings energetically. Despite their raccoon-like look, kinkajous are more closely related to olingos and coatis than raccoons.
4. Binturongs
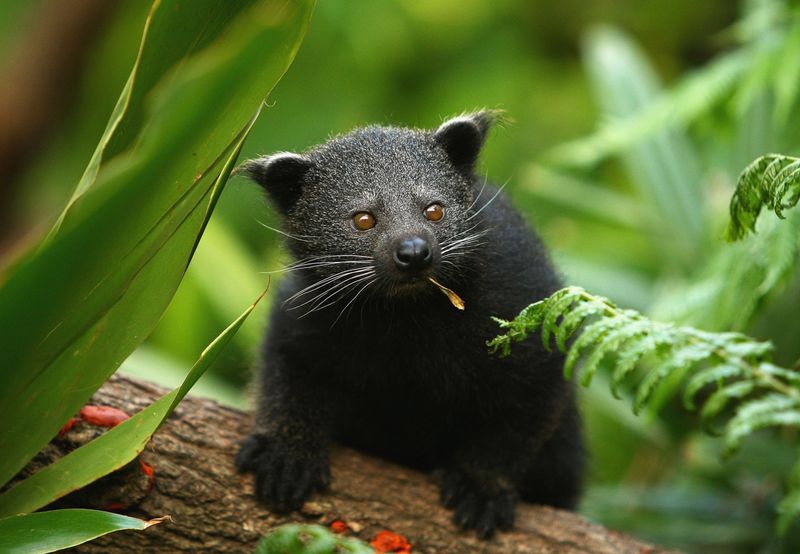

Binturongs, known as ‘bearcats,’ inhabit Southeast Asia, showcasing a stocky build and long tail. Their dark fur and facial markings give them a raccoon-like appearance.
These creatures are not related to raccoons but share habits like being arboreal and nocturnal. Binturongs emit a unique scent resembling buttered popcorn, making their presence known.
They rely on prehensile tails for balance while navigating treetops. Despite their intimidating appearance, they are generally gentle, feeding on fruits and small animals.
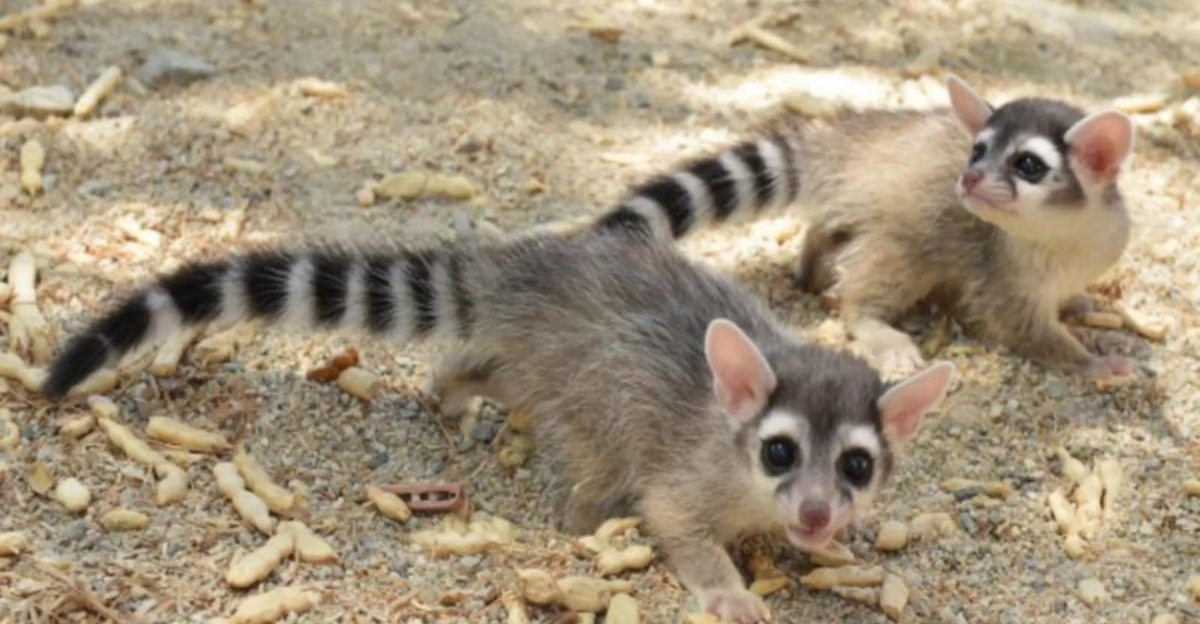
5. Cacomistles
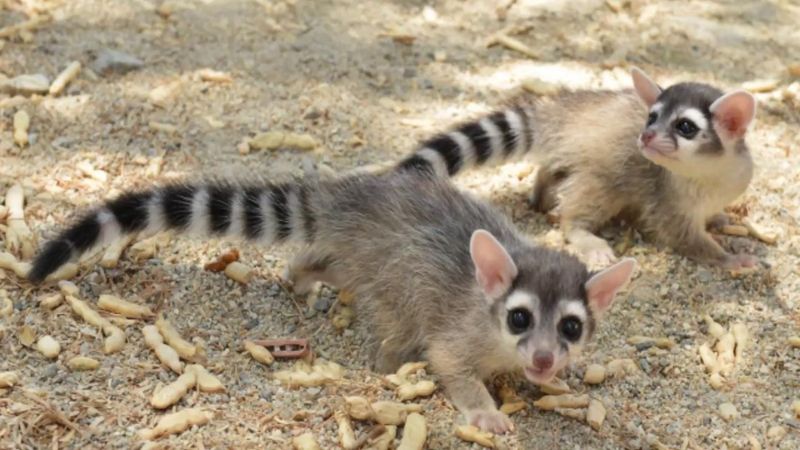

Cacomistles, or ‘ringtails,’ are small carnivores found in North America. Their sleek bodies, long ringed tails, and dark facial markings mirror raccoons.
Agile and adept climbers, they thrive in trees and rocky crevices. They feed on small animals, fruits, and insects. Cacomistles are solitary, nocturnal creatures, often heard before seen due to their vocalizations.
Observing them in their natural habitat reveals their playful yet elusive nature. While related to raccoons, cacomistles maintain unique traits, making them intriguing animals that balance familiarity with mystery.
6. Tayra
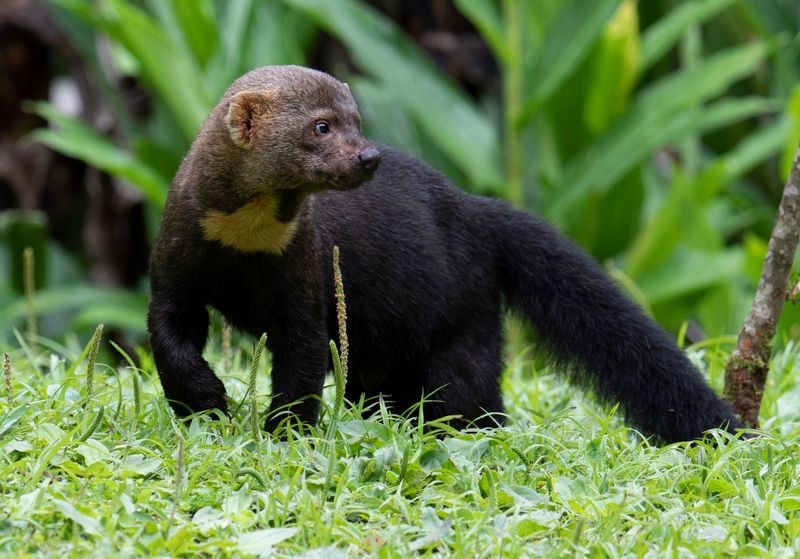

Native to Central and South America, the tayra belongs to the weasel family. With a long body, bushy tail, and dark facial markings, it bears a raccoon-like look.
Agile and curious, tayras explore forests in search of small mammals, birds, and fruits. Observing them reveals their playful interactions and problem-solving skills.
Despite their resemblance to raccoons, tayras exhibit unique behaviors. Social and often seen in pairs or small groups, they add vibrancy to their ecosystem.
7. Potos
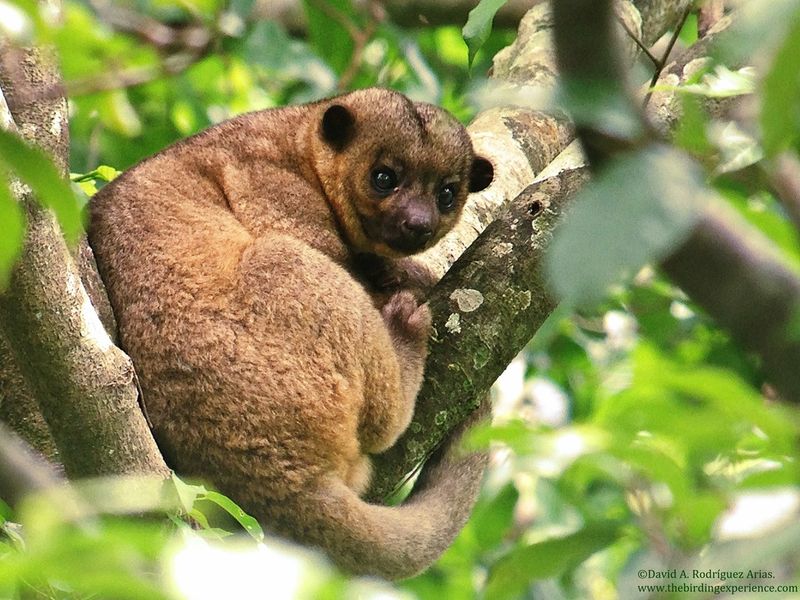

Potos, also known as ‘South American raccoons,’ are closely related to raccoons, sharing facial markings and habits. Their bushy tails and thick fur enhance their raccoon-like appearance.
Nocturnal and arboreal, potos are skilled climbers in their South American habitats. They feed on fruits, nectar, and small animals.
Their quiet, gentle presence often goes unnoticed in the dense forest. Despite similarities, potos maintain distinct behaviors and ecological roles.
8. Mongoose
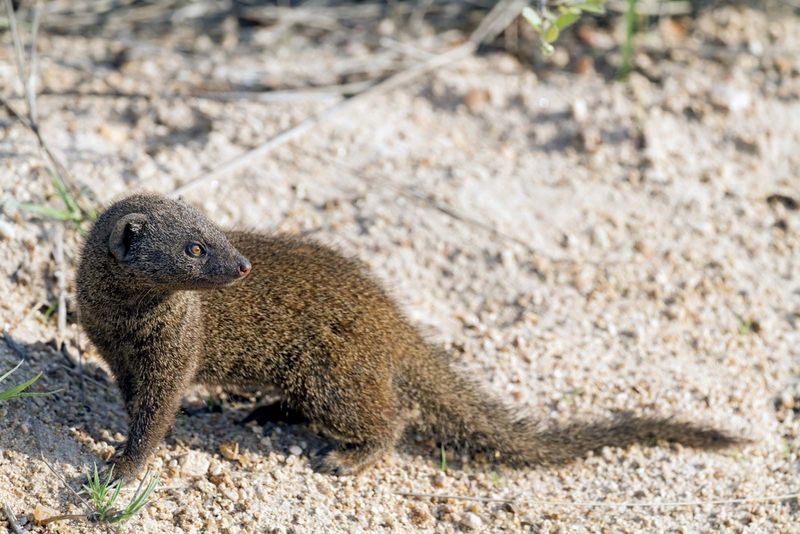

Mangrove mongooses are small mammals found in Africa and Asia, exhibiting raccoon-like features. Their bushy tails and body shape resemble raccoons. Social animals, they thrive in groups, displaying a playful and interactive nature.
Their rounded faces and dark markings enhance their resemblance to raccoons. Often found near water, they forage for insects, crabs, and small vertebrates. Observing their dynamic interactions with the environment offers valuable insights.
Despite not being closely related, their raccoon-like appearance captivates observers, highlighting the diversity of nature’s adaptations.
9. Spotted Genet
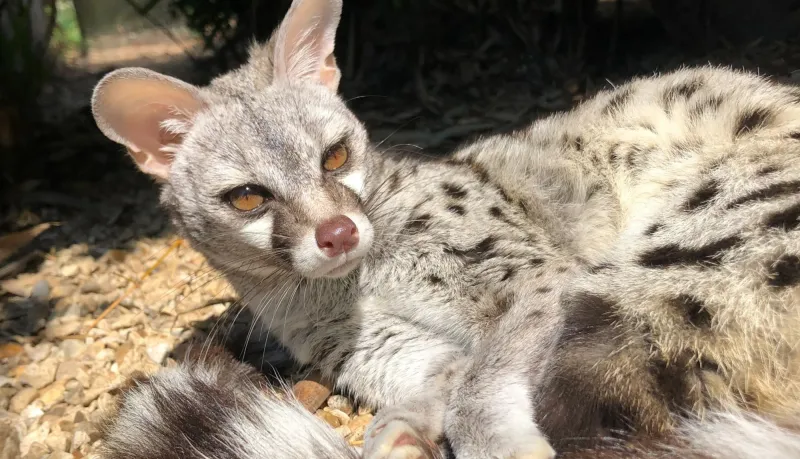

Spotted genets, native to Africa, exhibit a striking resemblance to raccoons, especially in their tails. Their long, spotted bodies and dark facial markings create a raccoon-like look.
Agile and solitary, they are often seen leaping gracefully between tree branches. Feeding primarily on small animals, birds, and insects, genets play a crucial role in controlling pest populations.
Despite their raccoon-like appearance, they are more closely related to cats and civets. Observing them offers a unique perspective on the intricacies of the African ecosystem and its diverse inhabitants.
10. Numbats
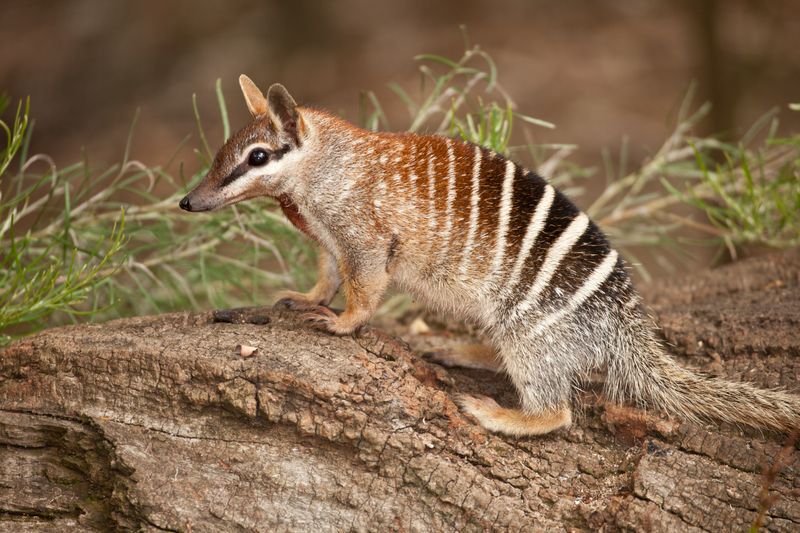

Numbats, native to Australia, share some raccoon-like features despite their distinct ecological role. Their slim bodies and bushy tails are reminiscent of raccoons. Primarily insectivorous, numbats consume termites, showcasing a different diet from raccoons.
They exhibit a nocturnal lifestyle, foraging actively during dusk and dawn. Observing numbats in the wild highlights their adaptability and unique behaviors.
While not closely related to raccoons, their appearance and habits draw intriguing parallels. Encountering a numbat offers a glimpse into a world where raccoon-like traits meet Australian uniqueness.