5 Key Differences That Set Male And Female Sharks Apart

Sharks are fascinating creatures of the ocean, but did you know that male and female sharks are quite distinct from each other?
From physical traits to behavioral patterns, each gender plays an essential role in the marine ecosystem. While they might look similar at first glance, several key differences set them apart.
Let’s explore what makes male and female sharks unique in their own right.
1. Size Variations
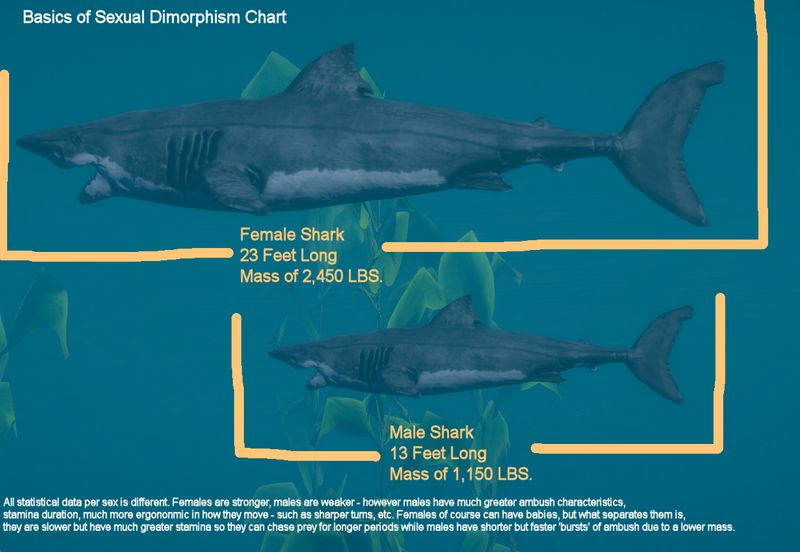
Female sharks are generally larger than their male counterparts. This size difference is evident across many species.
The reason behind their larger size is linked to reproduction. Larger females can carry more pups, providing a better chance for their offspring’s survival. This size advantage helps them avoid predators and hunt larger prey.
On the other hand, smaller male sharks are more agile, allowing them to navigate efficiently through the water.
In a world where survival is paramount, these size variations play a crucial role in defining their distinct lifestyles.
2. Clasper Presence
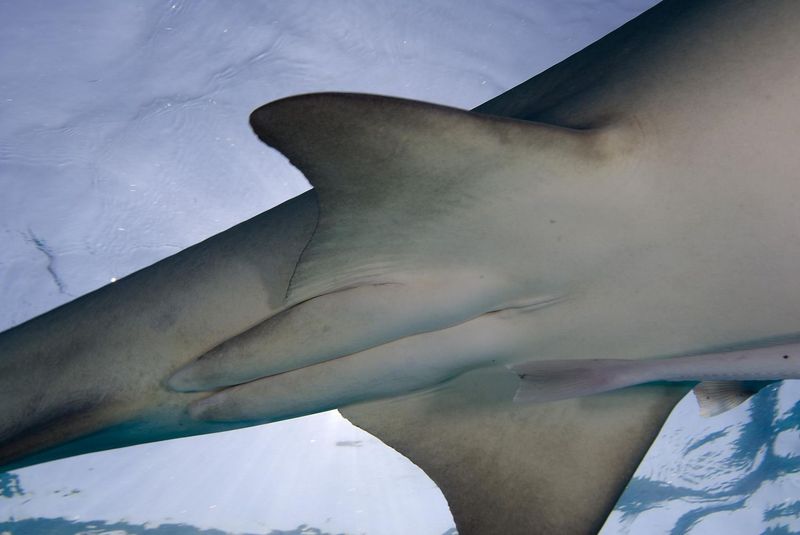

Male sharks possess claspers, which are reproductive organs not found in females. These are located near their pelvic fins. Claspers are used during mating to transfer sperm into the female shark.
This unique feature is crucial for reproduction, ensuring the survival of their species.
Female sharks, lacking claspers, have an entirely different reproductive system, suited for carrying and nurturing their young.
Understanding the presence or absence of claspers can help in identifying the gender of a shark. It’s a fascinating aspect of shark anatomy that many find intriguing.
3. Behavioral Differences

Male and female sharks exhibit distinct behaviors, especially during mating season.
Males are often more aggressive, actively seeking out females to mate with. This aggression is a natural part of their courtship.
Conversely, female sharks are more nurturing. Once they’ve mated, they focus on ensuring the safety of their young, often at the expense of their own safety.
This behavioral difference is vital for the continuation of their species. It’s intriguing to observe how these behaviors have evolved to adapt to the challenges of their environment.
4. Coloration Distinctions

Coloration can vary between male and female sharks, though it isn’t always pronounced. In some species, females exhibit darker tones, which might help in camouflage while protecting their young.
Males, on the other hand, may display brighter markings to stand out during mating displays.
These subtle differences in coloration are a testament to nature’s way of equipping each gender with unique survival tools.
Observing these color patterns can provide insights into their behavior and role within their habitat.
5. Reproductive Roles

Reproductive roles in sharks highlight a fascinating dynamic. Female sharks often have the more labor-intensive role, carrying the pups until birth. This process can last several months, depending on the species.
Males, however, are responsible for initiating mating, using their claspers for sperm transfer. The female’s role doesn’t end with birth; she’s tasked with protecting her young from predators.
These reproductive roles showcase a beautiful balance of responsibilities, ensuring the survival of future generations. It’s a remarkable display of nature’s intricate design in the animal kingdom.






