15 Unbelievable Animals That Could Save Millions Of Lives, According To Scientists

Throughout the natural world, animals harbor remarkable abilities that could revolutionize medicine and technology.
Scientists are uncovering secrets within these creatures that promise to save millions of lives. From the deepest oceans to the densest jungles, these animals and their unique characteristics inspire and solve problems for modern science.
1. Horseshoe Crab
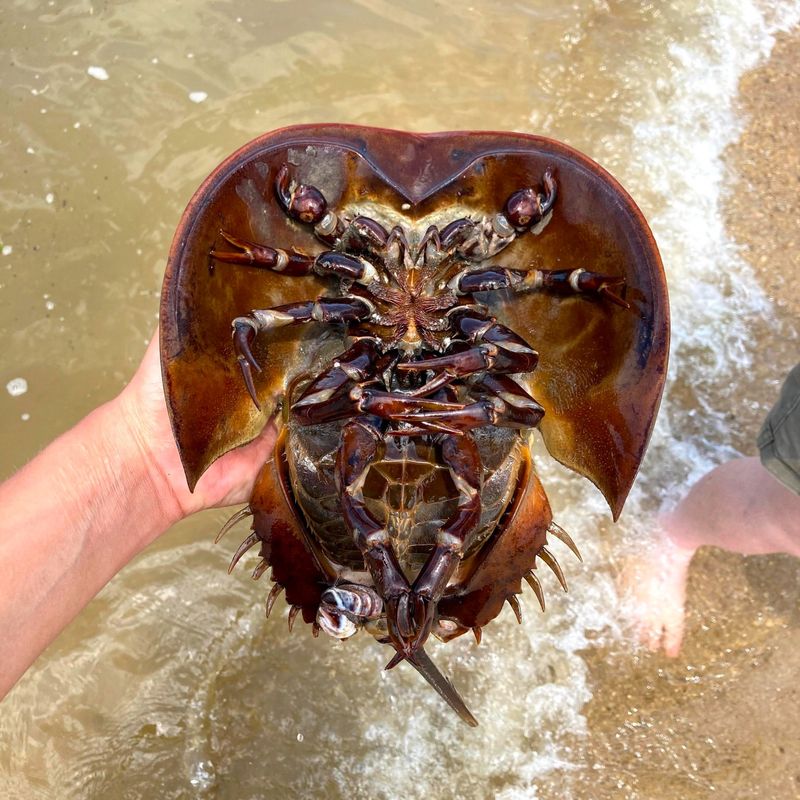

Fun fact: this species belongs to those animals that haven’t evolved in millions of years! The ancient horseshoe crab possesses a unique attribute that could be pivotal in medical advancements. Its blue blood contains a special compound used to detect bacterial contamination in medical equipment and vaccines.
This compound, called Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL), clots in the presence of bacterial toxins, ensuring sterility. Given the rise of drug-resistant bacteria, this discovery is more crucial than ever. Scientists are now exploring synthetic alternatives to replicate this life-saving feature.
As highlighted by the University of California, this could enhance our ability to fight infections without relying solely on antibiotics.
2. Tardigrade
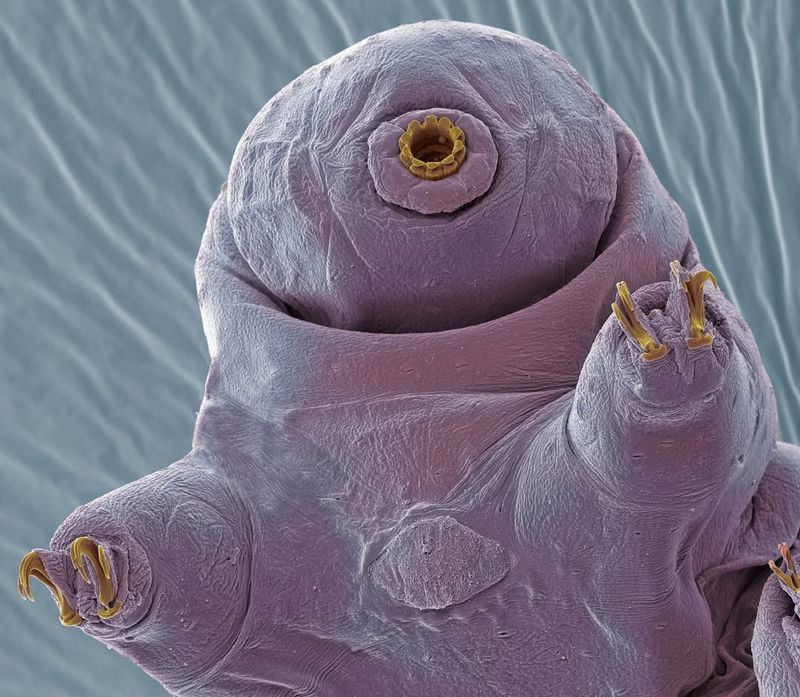
Tardigrades, often referred to as water bears, are microscopic marvels that inhabit the planet. Their resilience is unmatched, surviving extreme temperatures, pressures, and even outer space.
Researchers are studying tardigrades to understand their ability to withstand such harsh conditions, aiming to apply this knowledge to human organ preservation.
By mimicking tardigrade biology, according to eLife, scientists hope to extend the viability of organs for transplantation, significantly benefiting those in need of life-saving surgeries.
3. Electric Eel
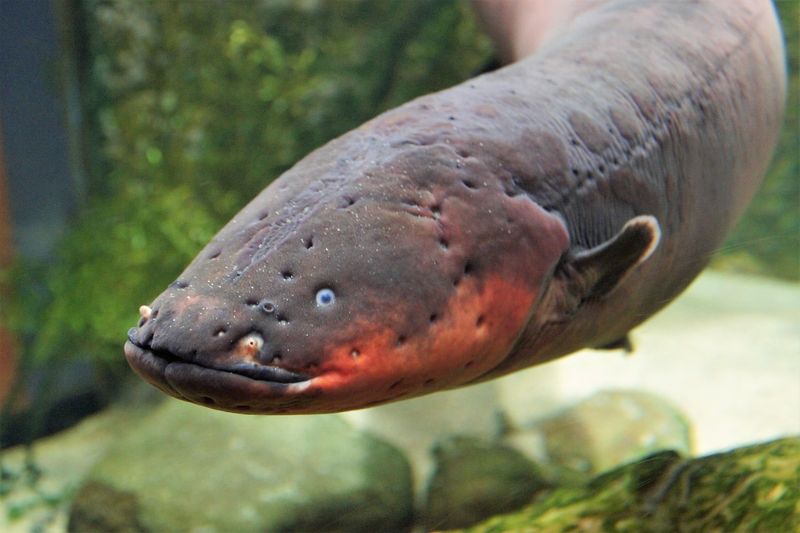

Electric eels, native to the Amazon, possess a shocking ability to generate electricity. This has inspired new ways to power medical devices, potentially transforming pacemakers and prosthetics. The eel’s unique electric organs function as biological batteries, offering insights into bioelectricity.
By harnessing this, scientists are designing devices that can be powered by the human body itself. Such innovations could lead to more sustainable and efficient medical technologies, reducing dependency on traditional power sources.
4. Cone Snail
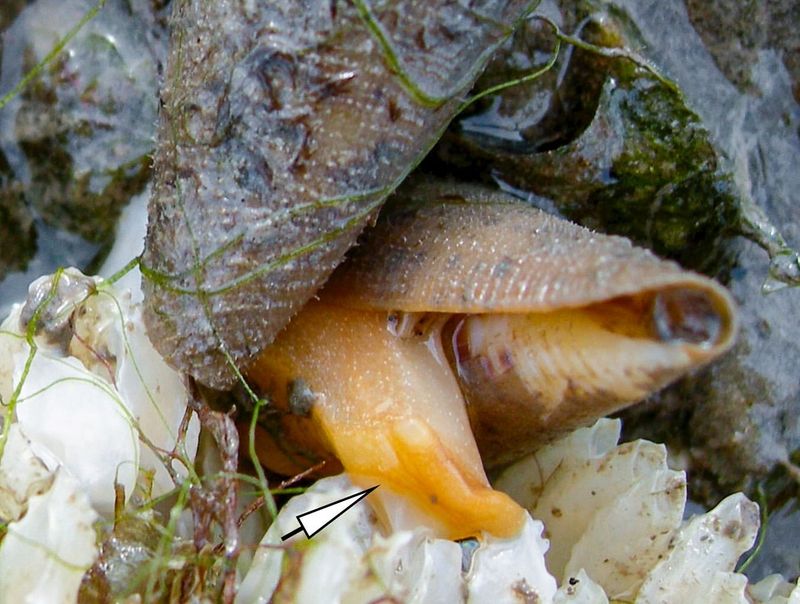

The venomous cone snail is more than just a marine predator; it holds the key to revolutionary pain management. Its venom contains compounds that can block pain signals, offering alternatives to traditional painkillers.
Researchers from all over the world are isolating these compounds to develop new, non-addictive analgesics. This could be a breakthrough in addressing the opioid crisis, providing relief without addiction.
As scientists decode the snail’s complex venom, the potential for medical applications continues to grow, holding promise for chronic pain sufferers.
5. Gecko
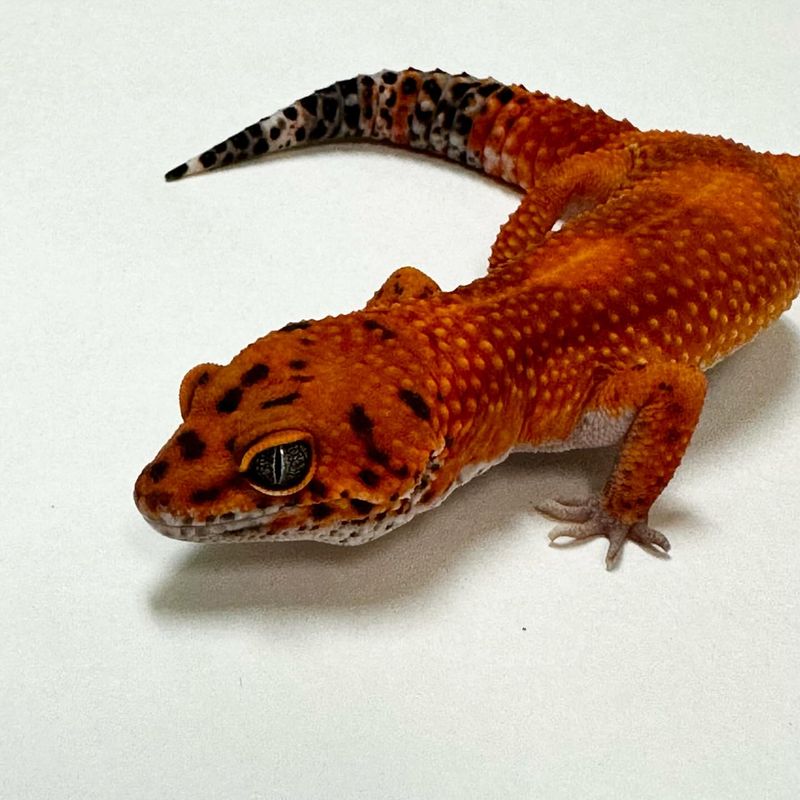

Geckos, renowned for their ability to scale walls and ceilings, have inspired groundbreaking adhesive technologies. Their feet have unique structures that allow them to adhere to surfaces without using liquids or glue.
This natural mechanism has been replicated to create advanced adhesives that are reusable and leave no residue.
Such innovations have applications in medical bandages and surgical tapes. By studying gecko biomechanics, researchers are developing products that could revolutionize wound care and surgical procedures.
6. Shark
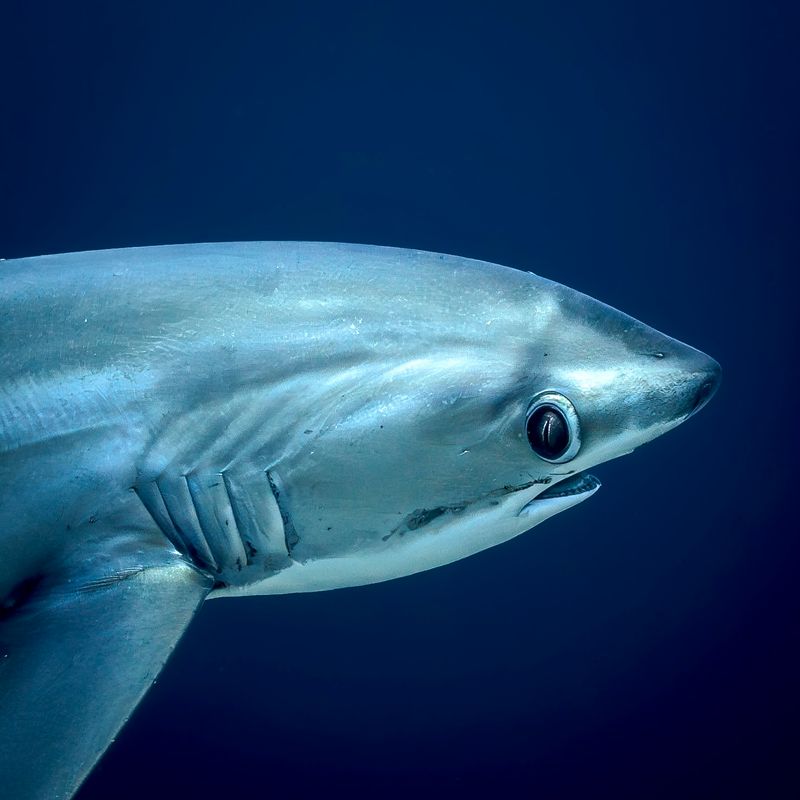

Sharks, with their sleek and efficient design, have inspired technological advances beyond the ocean. Their skin is covered in tiny, tooth-like structures called denticles that reduce drag and resist bacteria.
Scientists are applying shark skin patterns to surfaces to create antibacterial coatings for medical devices and hospital equipment. This bioinspired approach aims to reduce infection rates and improve patient outcomes, demonstrating the potential of nature-inspired technology to address modern challenges.
7. Platypus
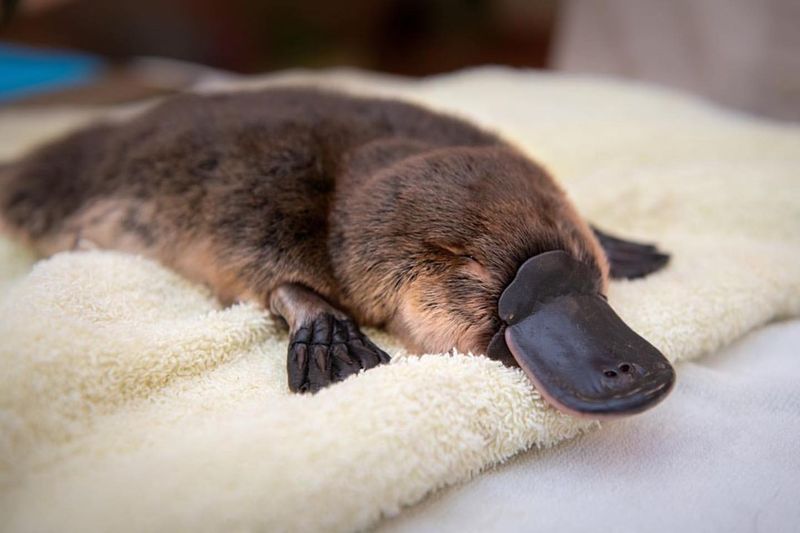

The enigmatic platypus, with its bizarre array of features, offers unexpected medical insights. Its milk contains unique antibacterial properties that could lead to new antibiotics. In the face of rising antibiotic resistance, researchers are eager to harness the platypus’s milk to combat superbugs.
This innovative research could pave the way for novel treatments. By understanding the platypus’s evolutionary traits, scientists hope to unlock solutions to one of modern medicine’s most pressing issues.
8. Jellyfish
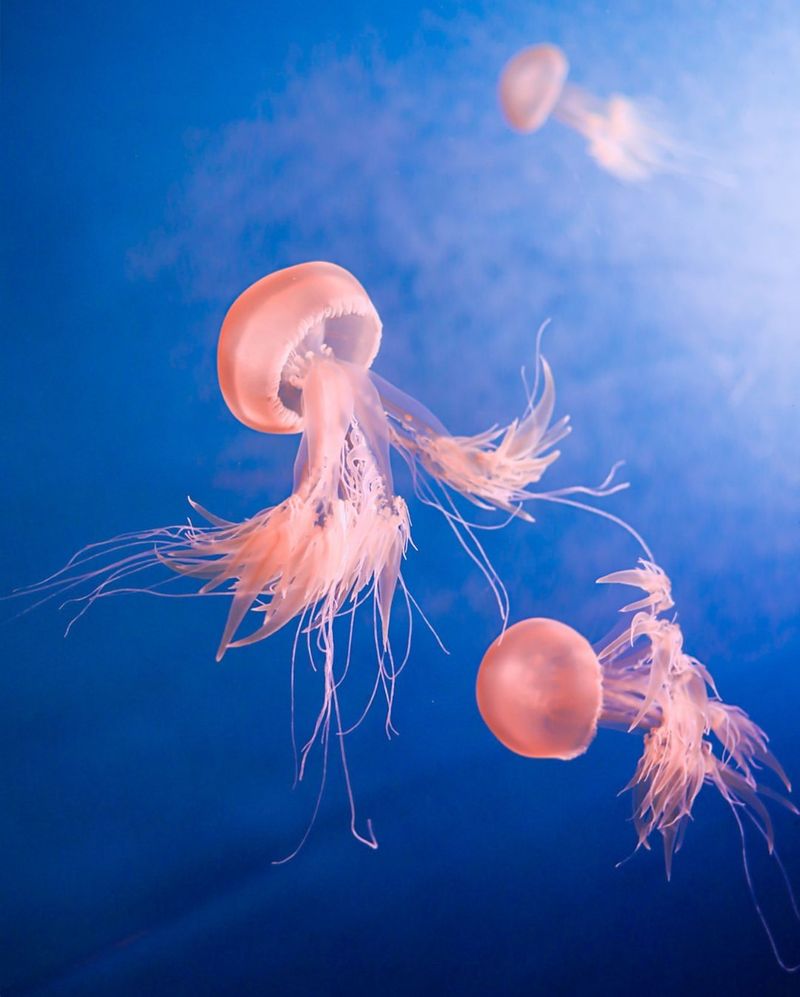

Jellyfish, with their mesmerizing glow, have more to offer than aesthetic beauty. Their bioluminescence has paved the way for advances in medical imaging and research. The proteins responsible for their glow are used as markers in biological research, allowing scientists to track processes within cells.
This capability enhances our understanding of diseases and the development of treatments, showcasing the jellyfish’s potential in medical diagnostics.
9. Naked Mole Rat
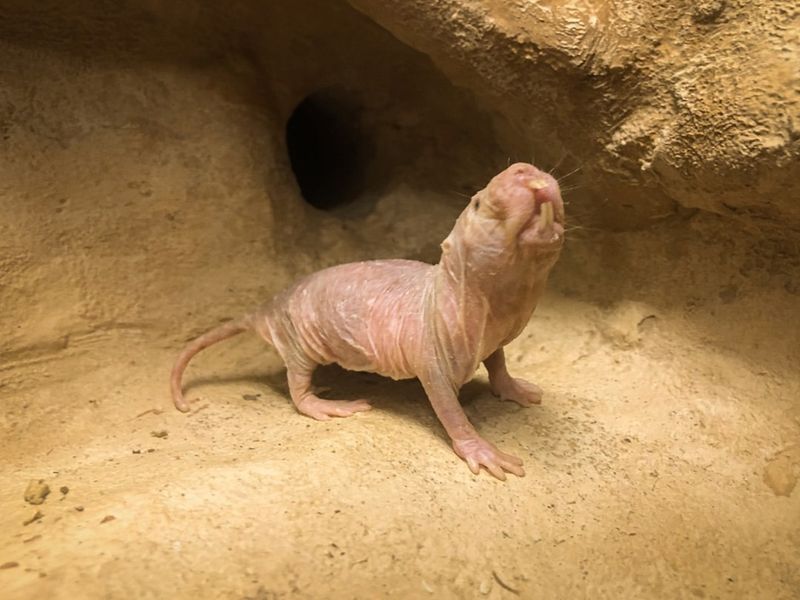

The peculiar naked mole rat thrives in harsh environments, offering insights into cancer resistance and longevity.
Unlike other mammals, it rarely gets cancer and lives significantly longer. Scientists study its cellular mechanisms to uncover potential cancer therapies and anti-aging treatments.
By understanding how the naked mole rat’s cells resist damage, researchers hope to translate these findings into human health benefits, potentially extending lifespan and reducing cancer incidences.
10. Axolotl
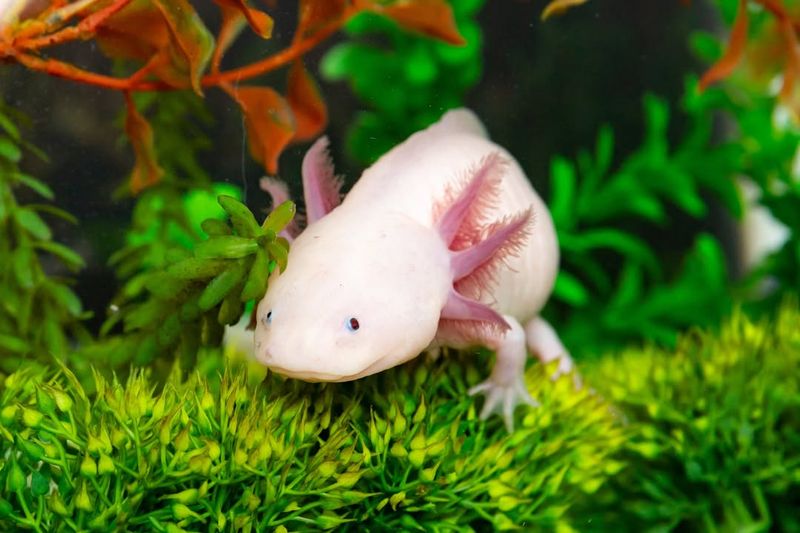

Axolotls, the Mexican salamanders, are extraordinary for their ability to regenerate limbs, spinal cords, and even parts of their hearts.
This has profound implications for regenerative medicine. By studying axolotls, scientists aim to unlock the secrets of tissue regeneration, potentially leading to breakthroughs in human healing and recovery.
The axolotl’s regenerative abilities could one day enable humans to recover from injuries that are currently irreversible, transforming medical treatments.
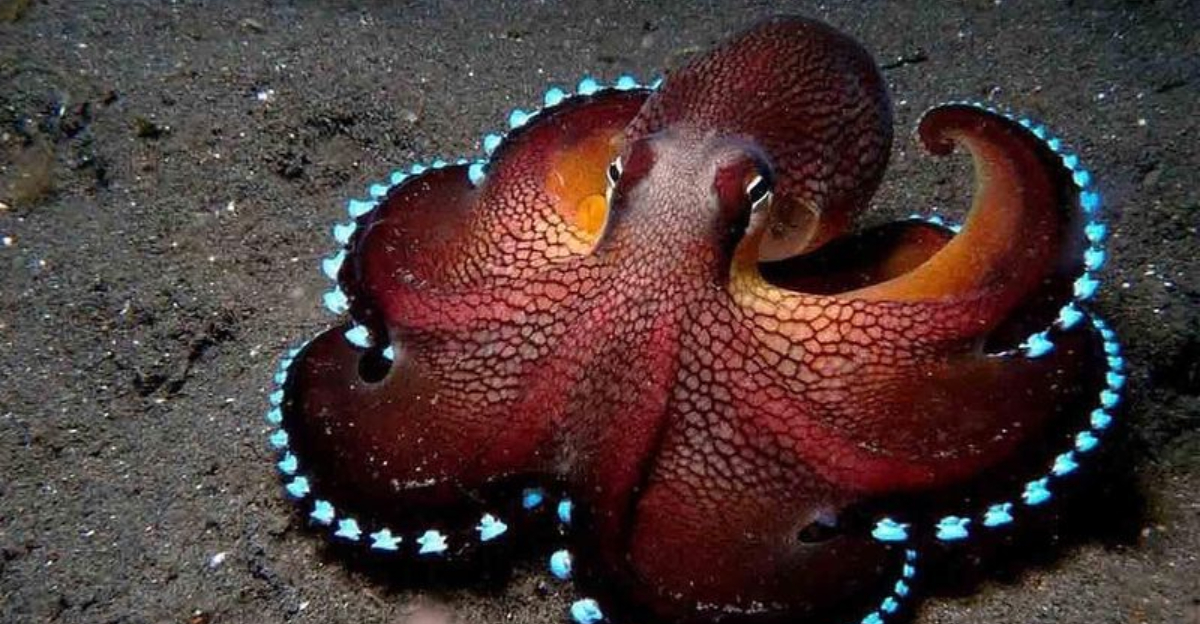
11. Octopus
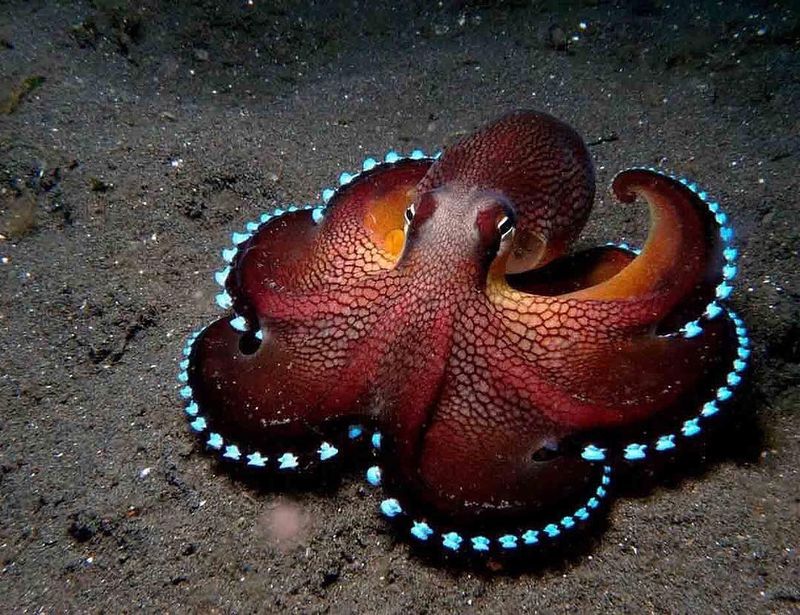

The intelligent octopus is known for its problem-solving skills and ability to adapt.
Its ability to change skin color and texture has implications for developing advanced materials. Researchers are investigating octopus skin to create adaptive camouflage and materials that can change appearance or texture on demand.
These innovations could have applications in military and consumer tech, revolutionizing how materials interact with their environment.
12. Sea Urchin
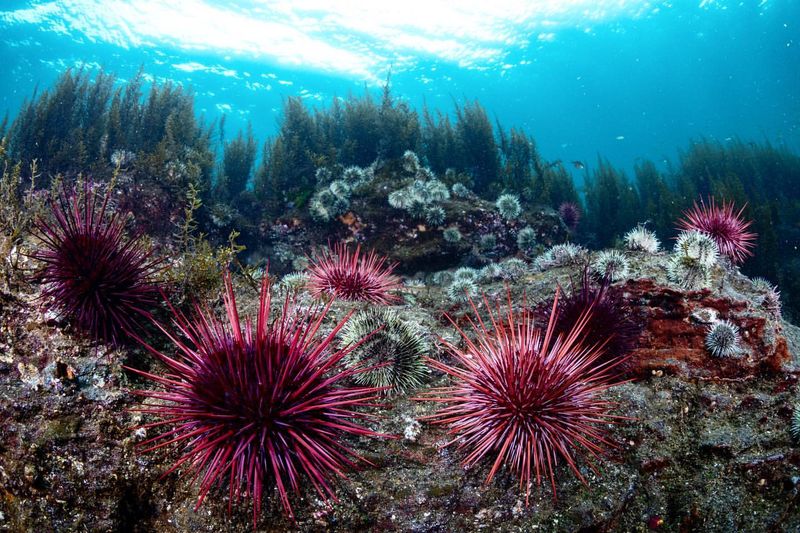

Sea urchins are intriguing marine creatures with regenerative capabilities. Their ability to regrow damaged spines offers insights into bone regeneration and healing. Scientists are studying these mechanisms to develop treatments for bone injuries and osteoporosis.
This research could lead to more effective therapies for bone-related conditions, improving recovery outcomes for patients.
13. Bat
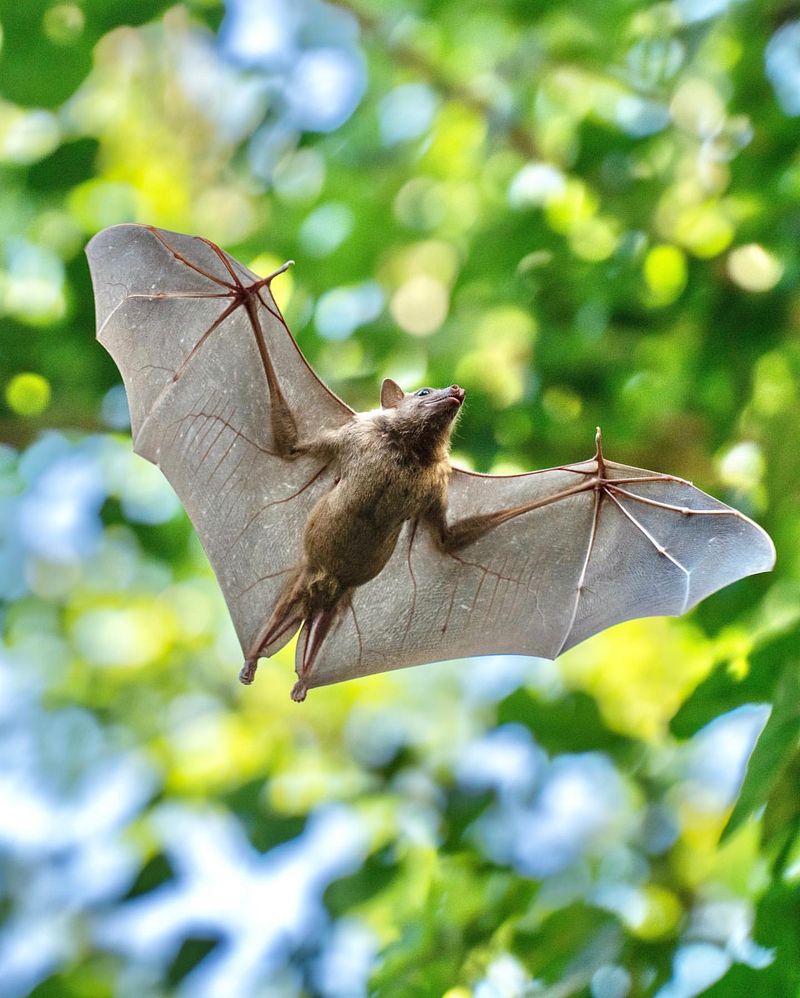

Bats are remarkable for their echolocation abilities, enabling them to navigate and hunt in complete darkness.
This sophisticated sense has inspired advances in sonar and ultrasound technology. By mimicking bat echolocation, scientists are developing improved imaging techniques for medical diagnostics.
These new methods could enhance the accuracy of non-invasive procedures, improving patient care and outcomes through better imaging solutions.
14. Frog
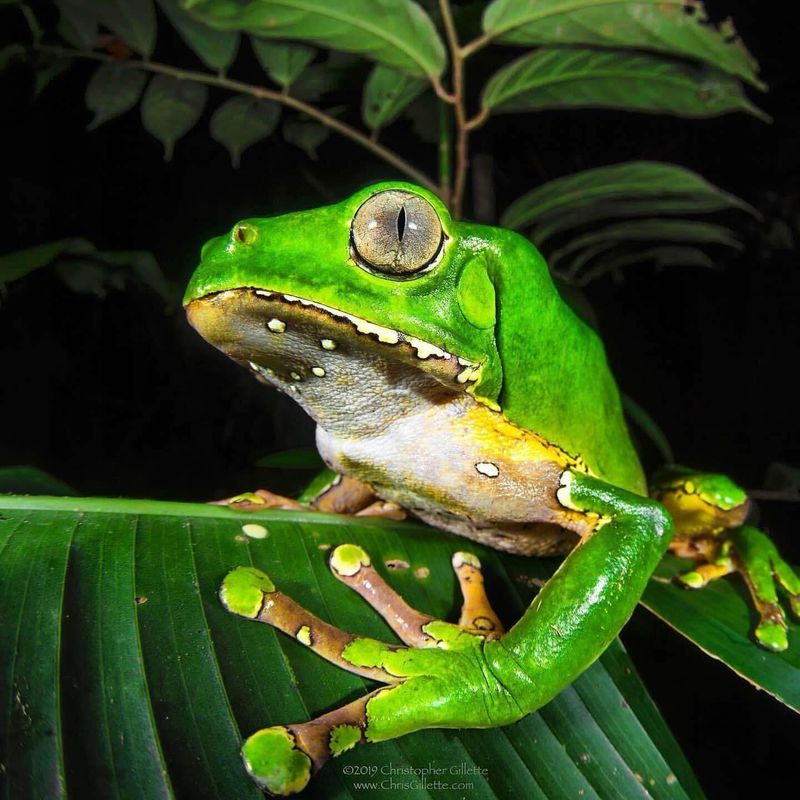

Poison dart frogs, with their vivid colors, produce potent toxins that have potential medical applications. These toxins are being studied for their ability to target nerve signals.
Researchers are exploring their use in developing new painkillers and treatments for neurological disorders. Understanding frog toxins helps scientists create precise therapies that target specific nerve pathways, offering novel approaches to pain management and neurological health.
15. Bees
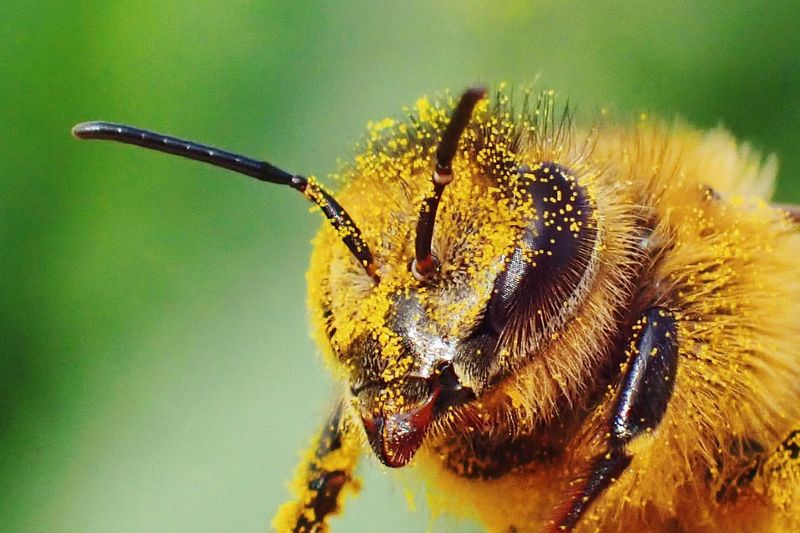

Bees are not just pollinators; their venom contains a compound called melittin, which has shown promise in cancer research. Melittin can penetrate cancer cell membranes, potentially leading to new treatments.
Scientists are investigating ways to harness melittin’s properties to target cancer cells without harming healthy ones. This research holds the potential to develop more effective cancer therapies, transforming how we approach cancer treatment and improving patient outcomes.






