13 Common Cat Eye Issues And How To Spot Them Early
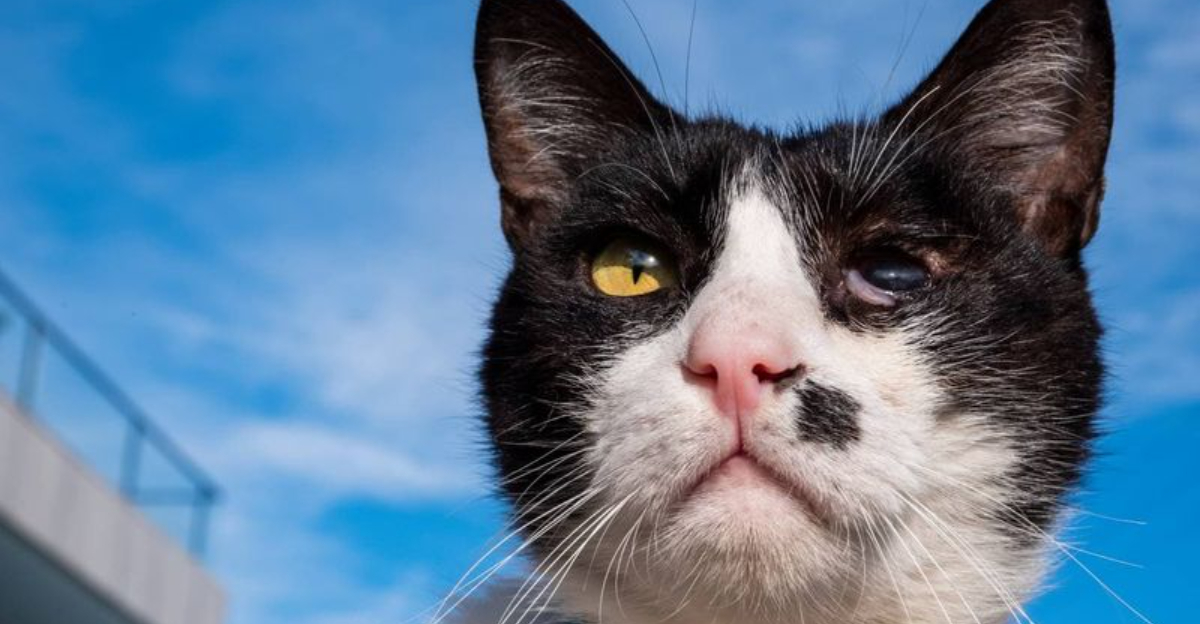

Cats, with their mysterious gaze and enchanting eyes, often face various eye ailments. These issues can range from mild irritations to serious conditions requiring medical attention.
Understanding these common eye problems is crucial for ensuring your feline friend’s health and happiness. Keep your cat’s eyes bright and healthy by being aware of these potential issues.
1. Eye Discharge
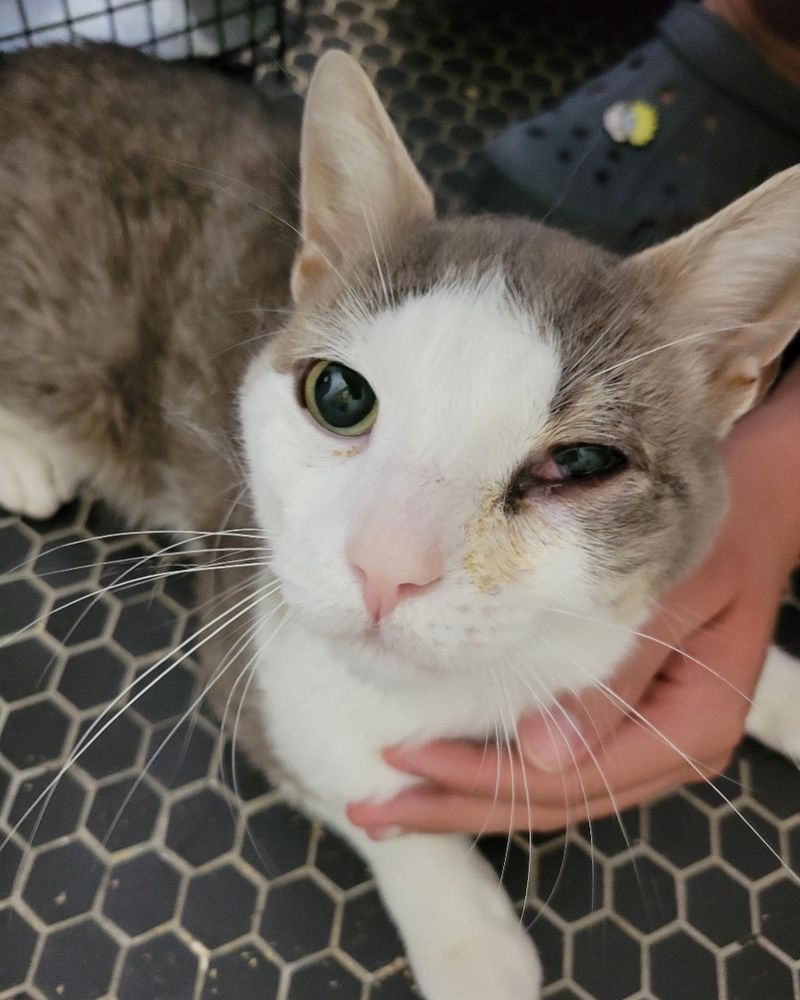
Eye discharge can occur due to a variety of reasons, including allergies, infections, or blocked tear ducts. It may appear as watery tears, pus, or mucus, and it can be clear, yellow, or green.
While some mild eye discharge may be normal, especially in the morning, persistent discharge could indicate an underlying health issue such as conjunctivitis, a respiratory infection, or an injury.
If your cat is having persistent eye discharge, it’s best to consult a veterinarian for proper treatment.
2. Corneal Dystrophy
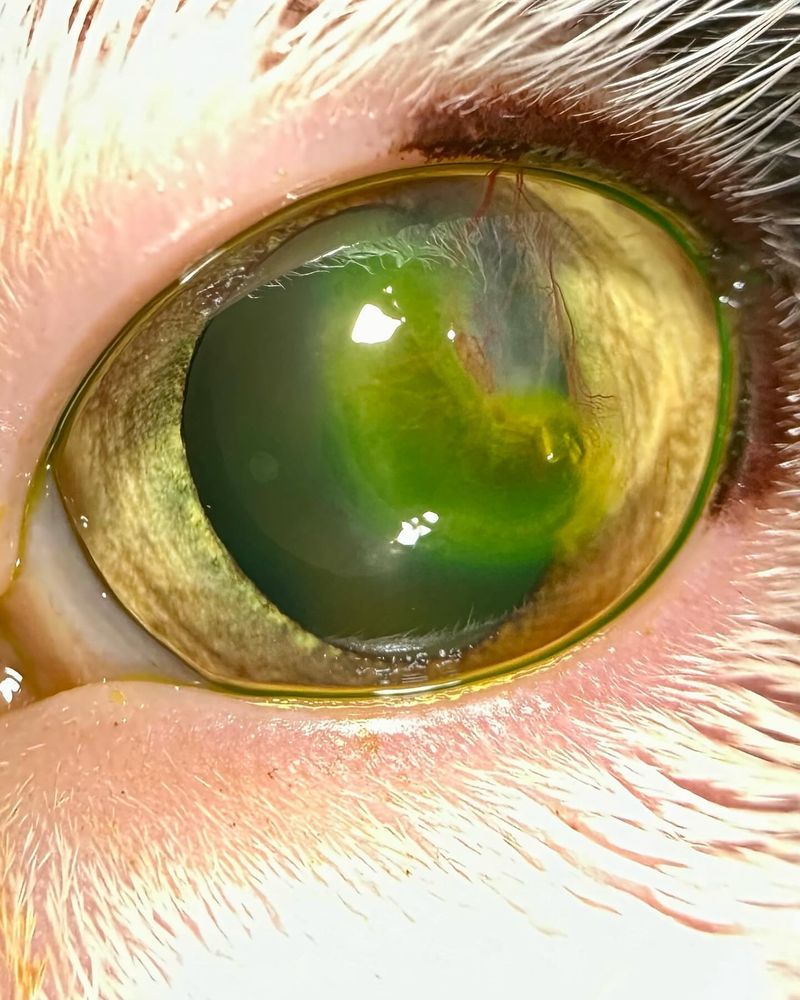
Corneal dystrophy is a hereditary condition that affects the cornea, causing it to become cloudy and leading to vision impairment. This condition is often found in certain breeds and can cause a gradual loss of sight.
Symptoms may include a cloudy or milky appearance in the eye, squinting, and sensitivity to light. While corneal dystrophy does not typically cause pain, it can affect the cat’s vision over time.
In some cases, treatment such as eye drops or surgery may be necessary to improve vision and prevent further damage. Early detection is important to manage the condition and protect your cat’s eyesight.
3. Conjunctivitis
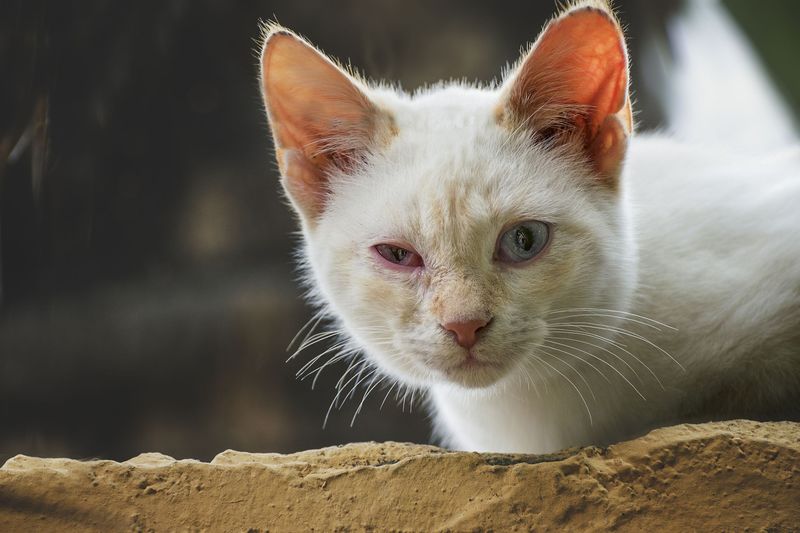

Conjunctivitis, or inflammation of the pink part of the eye, is one of the most common eye problems in cats. This condition is often caused by bacterial or viral infections, allergies, or irritants like dust or chemicals.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis in cats include redness, swelling, and discharge from the eyes.
It’s important to monitor your cat’s eyes closely, as untreated conjunctivitis can lead to more serious complications. Early treatment with eye drops or antibiotics can usually clear it up.
4. Corneal Ulcers
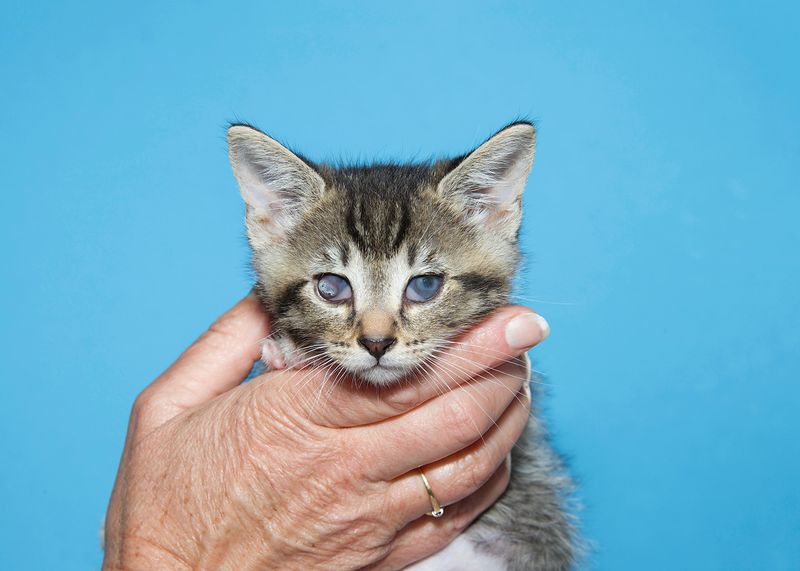

Corneal ulcers are open sores on the surface of the eye that can cause pain and vision problems. Cats can develop these ulcers from trauma, foreign objects, or infections.
If you notice your cat squinting, having excessive tears, or rubbing its eyes, it might be dealing with a corneal ulcer.
This condition can be diagnosed by a vet, who will prescribe ointments or sometimes surgical treatment to heal the ulcer and prevent further damage to the eye.
5. Cataracts
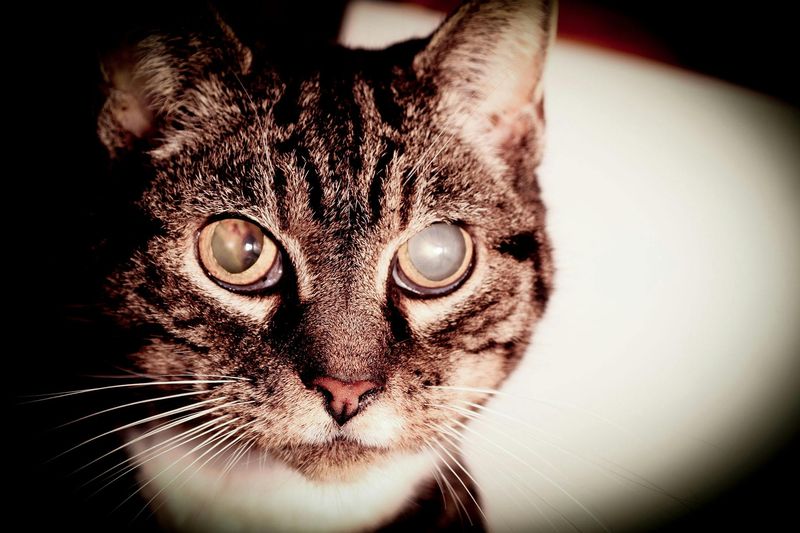

Cataracts are cloudy spots that form on the lens of the eye, obstructing vision. While cataracts are commonly associated with aging, they can also be caused by trauma, diabetes, or genetics.
If your cat seems to have difficulty navigating its environment, especially in dim light, cataracts may be the culprit. Though cataracts are difficult to treat in cats, surgical removal of the cataract is sometimes an option to restore vision.
6. Glaucoma

Glaucoma occurs when there is increased pressure in the eye, which can cause pain and potentially permanent vision loss. This condition is often accompanied by redness, a dilated pupil, or a cloudy appearance to the eye.
Glaucoma can develop rapidly and requires prompt treatment to prevent damage to the optic nerve. Medications, eye drops, and sometimes surgery can help manage the condition and reduce intraocular pressure.
7. Uveitis
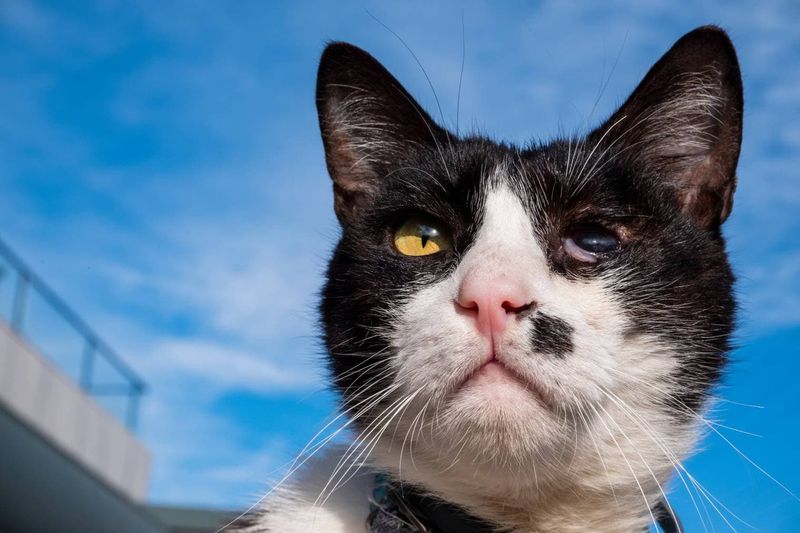

Uveitis is the inflammation of the middle layer of the eye, often caused by infections, trauma, or underlying diseases like feline leukemia or feline immunodeficiency virus. Symptoms can include redness, squinting, and sensitivity to light.
Left untreated, uveitis can lead to vision impairment or even blindness. If your cat is showing signs of eye discomfort or abnormal discharge, a visit to the vet is necessary for treatment with anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics.
8. Tear Duct Obstruction

A tear duct obstruction occurs when the ducts responsible for draining tears from the eyes become blocked. This leads to excessive tearing, and in some cases, discharge that can accumulate around the eyes.
You may notice your cat’s eyes are constantly wet, and there may be a visible buildup of mucus. The condition is often treated by flushing the tear ducts or, in more severe cases, surgery to remove the obstruction.
9. Entropion

Entropion is a condition where the eyelids roll inward, causing the eyelashes to rub against the surface of the eye. This leads to irritation, pain, and potential damage to the cornea.
Entropion is most commonly seen in younger cats and can be caused by genetics or injury. If you notice that your cat is squinting or frequently pawing at its eyes, it may be a sign of entropion.
Surgical correction is the most common treatment to prevent long-term damage and discomfort.
10. Cherry Eye

Cherry Eye occurs when the third eyelid (the nictitating membrane) prolapses, causing a pink, swollen mass to appear in the corner of the cat’s eye. This condition is more common in certain breeds and can be caused by weakness in the connective tissue.
While not painful, cherry eye can lead to irritation, and if left untreated, it may cause further damage to the eye. Surgery is typically required to reposition the third eyelid back to its normal position.
11. Dry Eye (Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca)

Dry eye, or keratoconjunctivitis sicca, occurs when there is insufficient tear production, leading to dryness and discomfort in the eyes. Cats with dry eye may squint, paw at their eyes, or have a thick, mucous-like discharge.
This condition can lead to inflammation, corneal ulcers, and infections if left untreated. Medications that stimulate tear production or artificial tears can help manage dry eye and prevent further damage.
12. Eyelid Tumors

Eyelid tumors can appear as lumps or growths on the eyelid, which may be benign or malignant. While most eyelid tumors in cats are non-cancerous, they can still cause irritation, rubbing, and discomfort for your cat.
If you notice abnormal lumps or bumps on your cat’s eyelids, it’s important to have them evaluated by a veterinarian. Surgical removal of the tumor is often necessary, followed by a biopsy to determine whether it’s benign or malignant.
13. Feline Herpesvirus Infection

Feline Herpesvirus is a viral infection that can cause upper respiratory issues and ocular problems in cats. It can lead to conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers, and inflammation of the eyes. Cats infected with feline herpesvirus may have persistent eye discharge, squinting, or excessive tearing.
Although there’s no cure for the virus, symptoms can be managed with antiviral medications, topical eye drops, and supportive care to prevent flare-ups.






