10 Things Animals Do Better Than Humans That We Shouldn’t Be Jealous About

Ever watched a bird soar effortlessly through the sky or a cat land perfectly from a high jump and felt a twinge of envy? The animal kingdom is packed with incredible abilities that put our human talents to shame.
While we’ve mastered technology and built civilizations, our animal neighbors have evolved some truly remarkable skills through millions of years of adaptation. But before you start wishing you could breathe underwater or smell food from miles away, let’s explore some animal superpowers that might not be as enviable as they first appear.
1. Eating Absolutely Anything
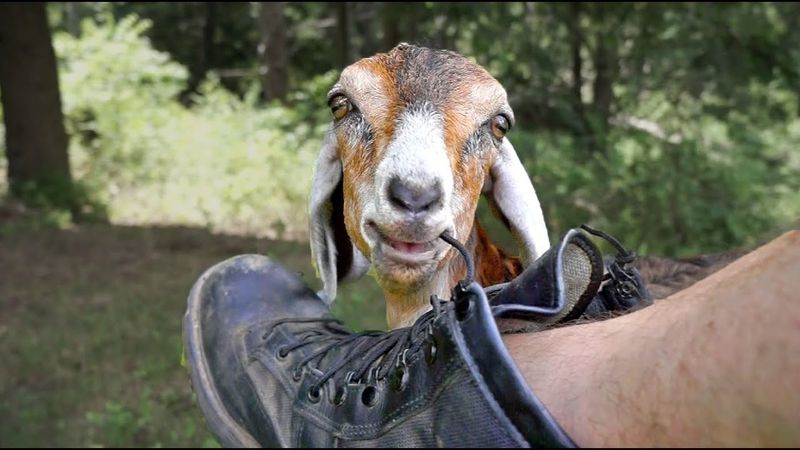

Goats can consume tin cans, paper, and even cardboard without getting sick. Their four-chambered stomach contains special bacteria that break down almost anything they munch on, including items that would send us straight to the emergency room.
While this might seem like a cool party trick, imagine the social implications of chomping through your friend’s furniture or your date’s cardboard coffee cup sleeve! Plus, goats don’t actually enjoy these inedible items – they’re just sampling everything in their environment to find food.
2. Sleeping With Half A Brain
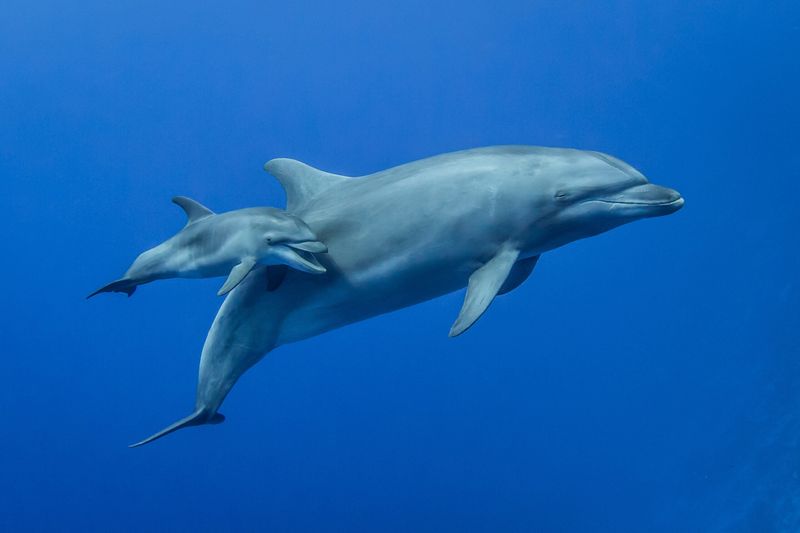

Dolphins and some birds master the art of unihemispheric sleep – resting one half of their brain while keeping the other half alert. This evolutionary adaptation helps them stay aware of predators and continue swimming or flying without drowning or falling.
Sounds amazing until you consider the consequences for humans. Imagine never experiencing deep, restorative sleep again! You’d be partially conscious all the time, missing out on those blissful hours of complete mental shutdown that help process emotions and memories.
3. Regenerating Body Parts
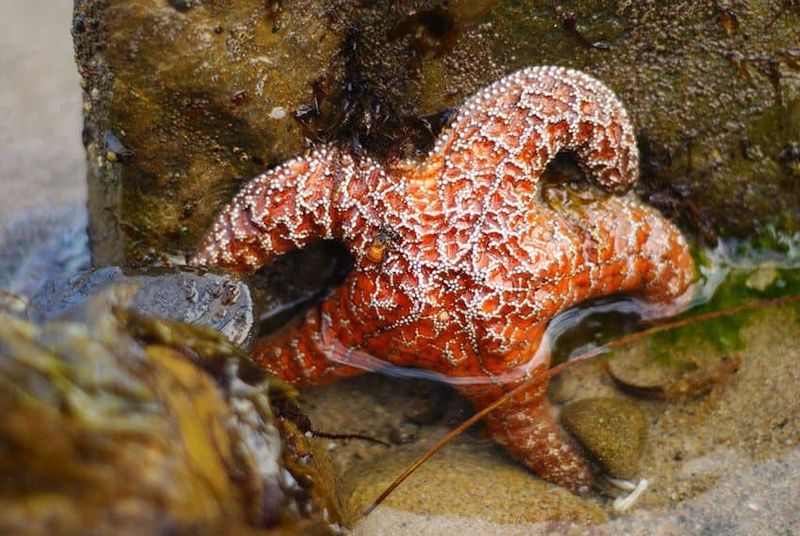

Starfish can regrow entire limbs after injury, while axolotls regenerate complex structures including spinal cord, heart, and even portions of their brain. This remarkable healing ability stems from specialized cells that can transform into whatever tissue type is needed.
Before you get too envious, consider the energy cost. Regeneration requires massive resources, forcing these creatures to divert energy from other functions. For humans, this would mean feeling constantly exhausted and hungry while growing back a finger – and possibly looking like a weird, incomplete version of yourself for months!
4. Smelling Food From Miles Away
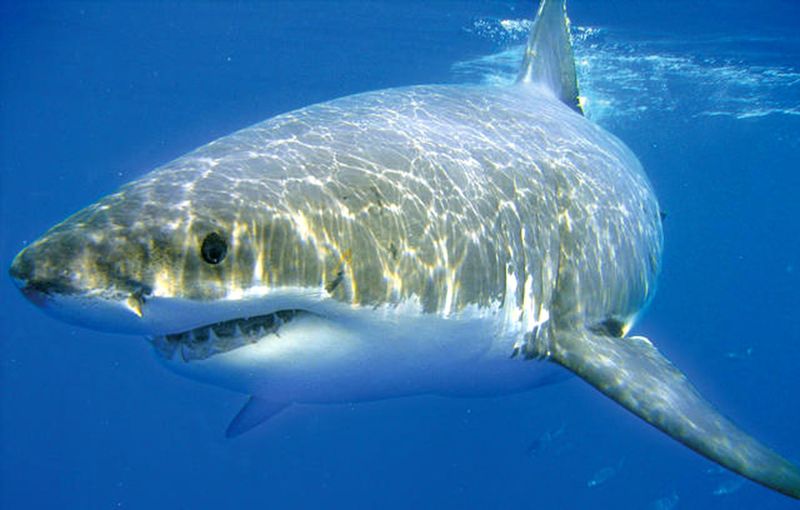

Sharks detect blood in water from up to three miles away thanks to an extraordinary sense of smell. Their nostrils contain specialized cells that pick up just one drop of blood in an Olympic-sized swimming pool.
Living with such sensitivity would be overwhelming in our world. Imagine walking through a city and being bombarded by every food scent, garbage odor, and personal hygiene issue within miles! You’d never escape the smell of your neighbor’s tuna casserole or the public restroom down the street.
That heightened awareness would make focusing on anything else nearly impossible.
5. Living Without Oxygen
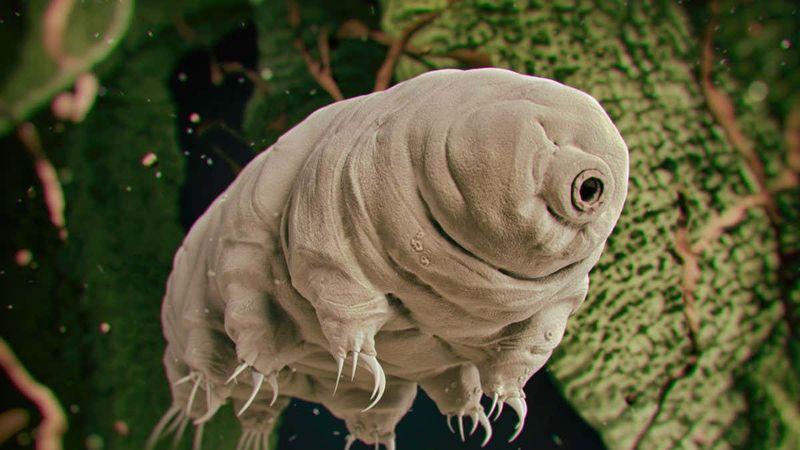
Certain microorganisms thrive in oxygen-free environments that would kill humans instantly. Tardigrades (water bears) can survive in the vacuum of space by entering a dehydrated state called cryptobiosis, essentially pausing their biological functions.
While breathing seems like a chore sometimes, not needing oxygen would fundamentally change what makes us human. Our big, energy-hungry brains require constant oxygen – it’s the trade-off for our intelligence.
Plus, entering suspended animation like tardigrades would mean missing out on life’s experiences while in that state!
6. Seeing Ultraviolet Light
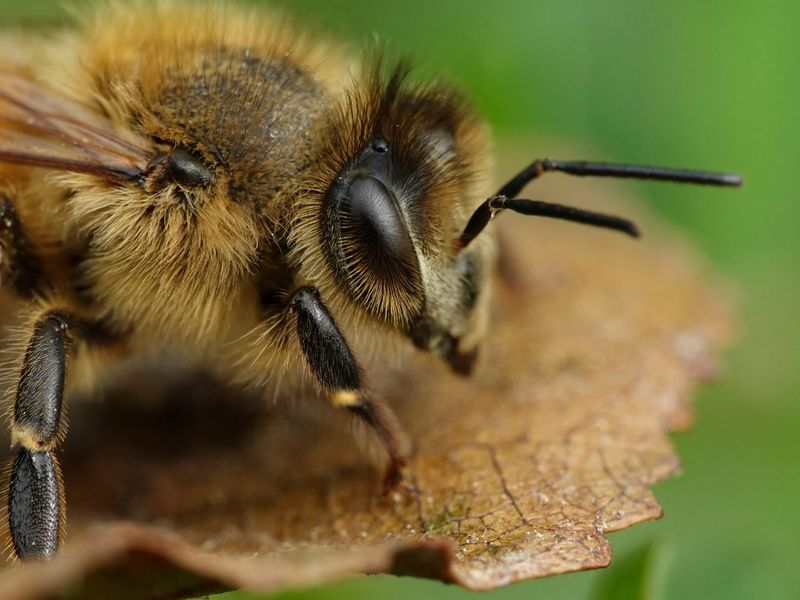

Bees and butterflies perceive ultraviolet patterns on flowers invisible to human eyes. These hidden markings act as landing strips, guiding pollinators to nectar sources with remarkable precision.
Having UV vision might seem cool until you realize how it would transform our world. Screens would appear completely different – possibly unbearable to look at. Your perfectly clean bathroom might reveal horrifying stains invisible to normal eyes.
And don’t even think about sunscreen – you’d see everyone walking around with bizarre, patchy faces where they missed spots in their application!
7. Surviving Extreme Temperatures
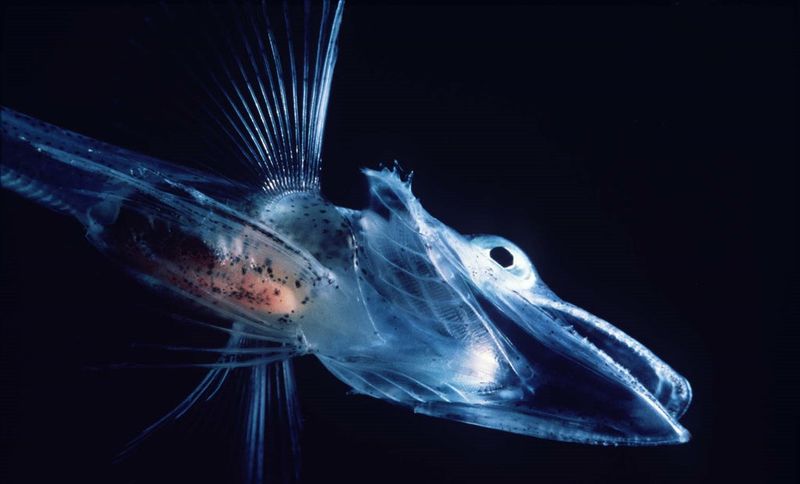
Arctic fish produce natural antifreeze proteins that prevent ice crystals from forming in their bloodstream. On the opposite extreme, certain desert insects withstand temperatures that would cook human proteins into a solid mass.
The biological cost of these adaptations is enormous. Cold-adapted creatures move sluggishly, with metabolisms slowed to a crawl. Heat-tolerant animals must devote tremendous resources to temperature regulation.
For humans, such adaptations would mean either functioning in slow motion or burning through calories at an unsustainable rate just to maintain basic functions!
8. Navigating Without Maps
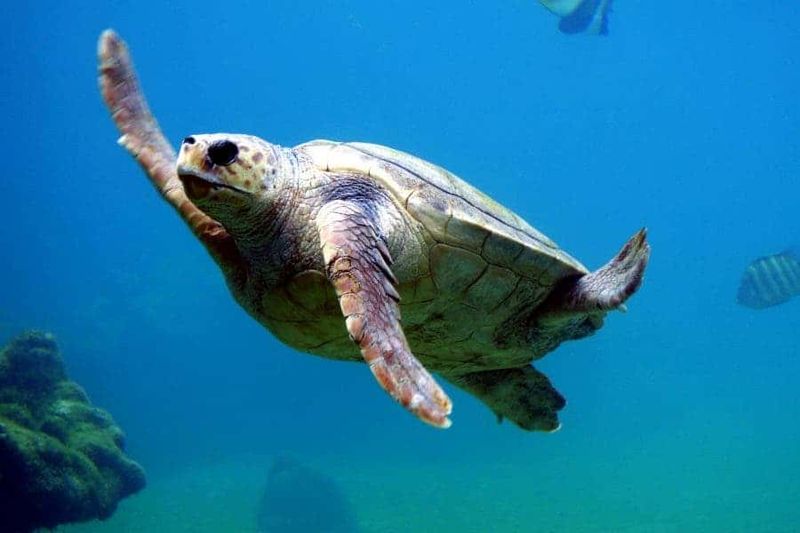

Sea turtles navigate thousands of miles across featureless oceans to return to their birthplace. They detect Earth’s magnetic field through specialized cells containing tiny crystals of magnetite that function like built-in compasses.
Having an internal GPS might save on phone battery, but it would come with serious drawbacks. Magnetic sensitivity makes animals vulnerable to electromagnetic pollution from power lines and electronics.
Imagine getting splitting headaches every time you pass under power lines or use your microwave! Plus, our reliance on technology has allowed us to navigate anywhere on Earth, not just along fixed migratory routes.
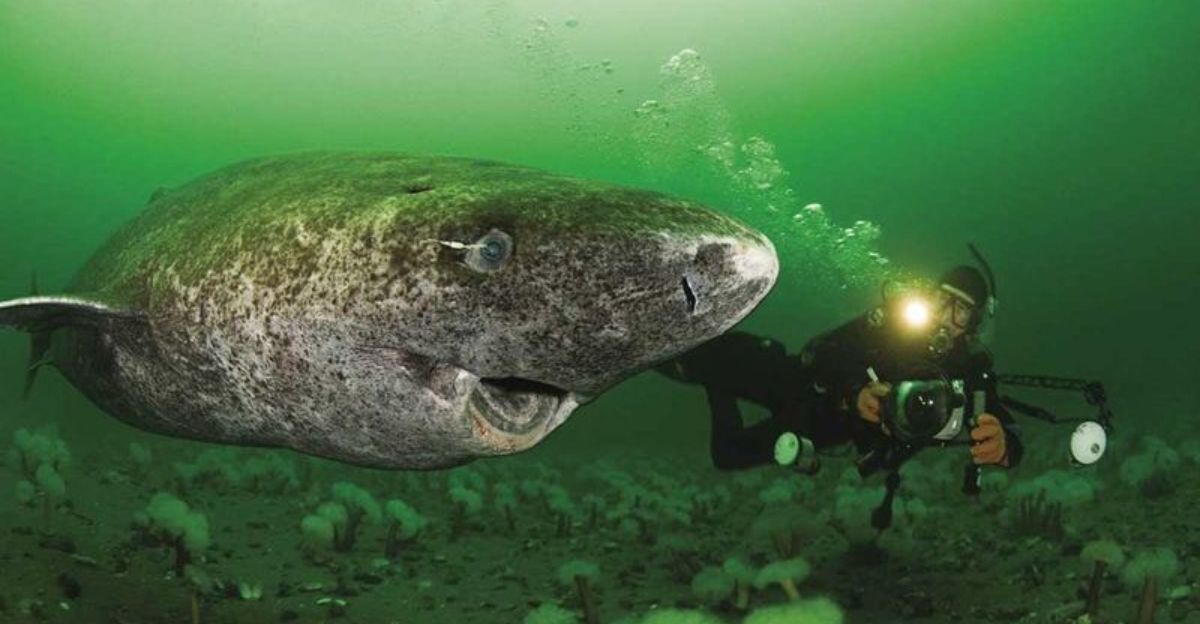
9. Living For Centuries
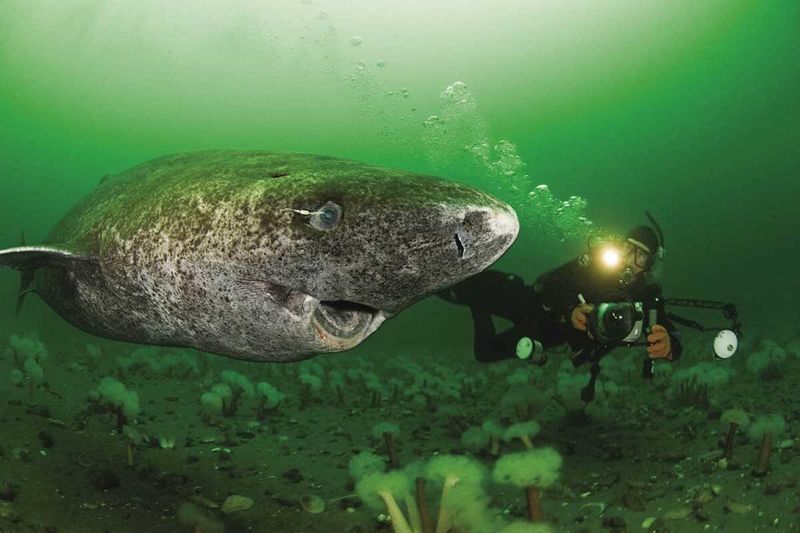

Greenland sharks can live over 400 years, growing at a glacial pace of less than 1 cm per year. Their incredible longevity comes from an extremely slow metabolism adapted to frigid Arctic waters.
This extended lifespan comes with significant downsides. These sharks reach sexual maturity around 150 years old – imagine waiting a century and a half before dating! Their slow metabolism also means they move like underwater sloths, barely able to catch prey that isn’t already dying or dead.
A human with such adaptations would experience everything in painful slow motion while watching countless generations of friends pass away.
10. Changing Gender At Will
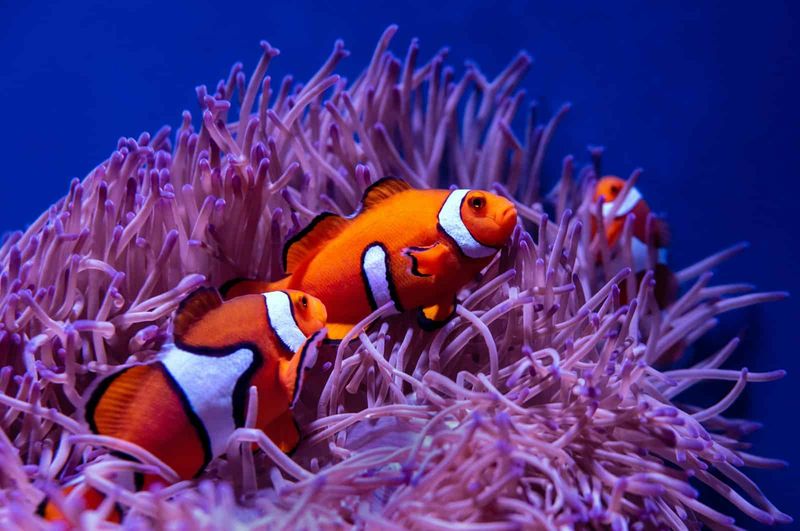

Many fish species can change their sex when environmental conditions make it advantageous. Clownfish begin life as males, with the dominant individual in a group transforming into a female when needed.
This biological flexibility serves reproduction in specific ecological niches but would create chaos in human society. Imagine your entire physiology, hormones, and identity potentially shifting based on social hierarchy or environmental triggers beyond your control!
Our complex social structures and self-identity would be constantly disrupted by such transformations, making long-term relationships and personal development extraordinarily challenging.






