Meet Ranitomeya Aetherea: The Newly Discovered ‘Heavenly’ Metallic Poison Dart Frog Of The Amazon
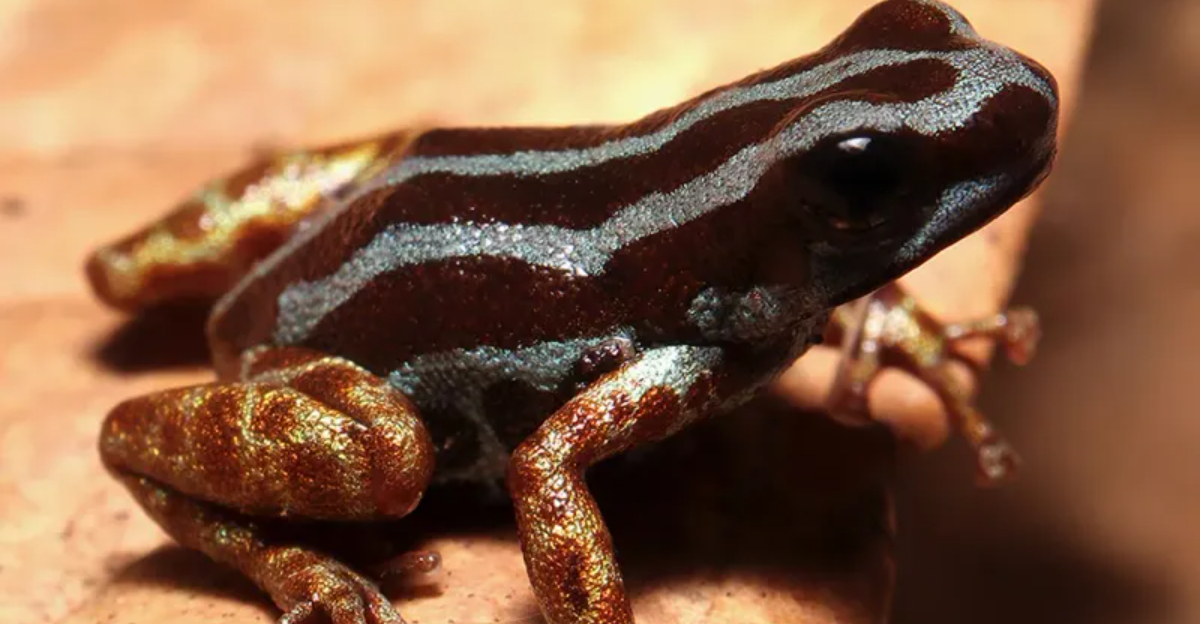

Deep in the heart of the Amazon rainforest, scientists have made an extraordinary discovery that has the biological world buzzing with excitement.
The Ranitomeya aetherea, nicknamed the ‘Heavenly’ poison dart frog, has emerged as nature’s newest marvel with its stunning metallic blue sheen that seems to capture the very essence of the sky.
This tiny amphibian, no larger than a thumbnail, isn’t just beautiful – it represents a whole new species that could hold secrets about evolution, adaptation, and possibly even medical breakthroughs.
1. Stunning Electric-Blue Metallic Skin
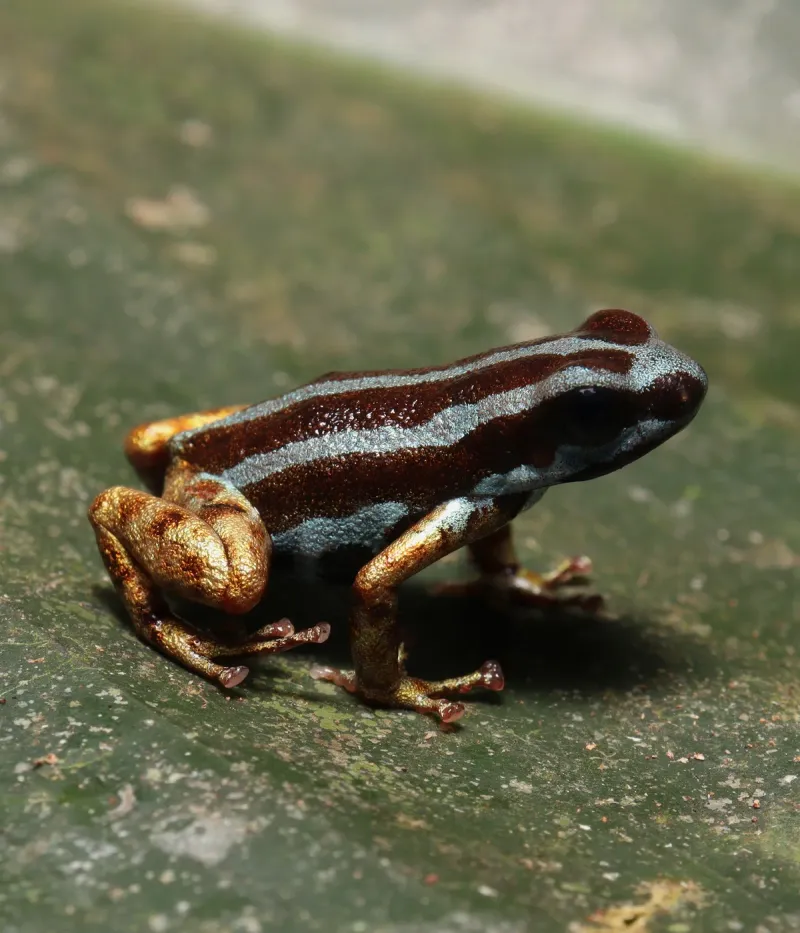

Glimmering like a piece of the sky fallen to earth, Ranitomeya aetherea boasts an electric-blue skin that shimmers with metallic brilliance under any light. The microscopic crystal structures in its skin reflect light in a way that creates this otherworldly metallic sheen.
Unlike other poison dart frogs with simple color patterns, the aetherea’s skin changes hue depending on the viewing angle – from deep sapphire to bright azure. This iridescence isn’t just for show; biologists believe it may help the tiny frog blend into dappled rainforest light or signal to potential mates.
2. Named After The Heavens
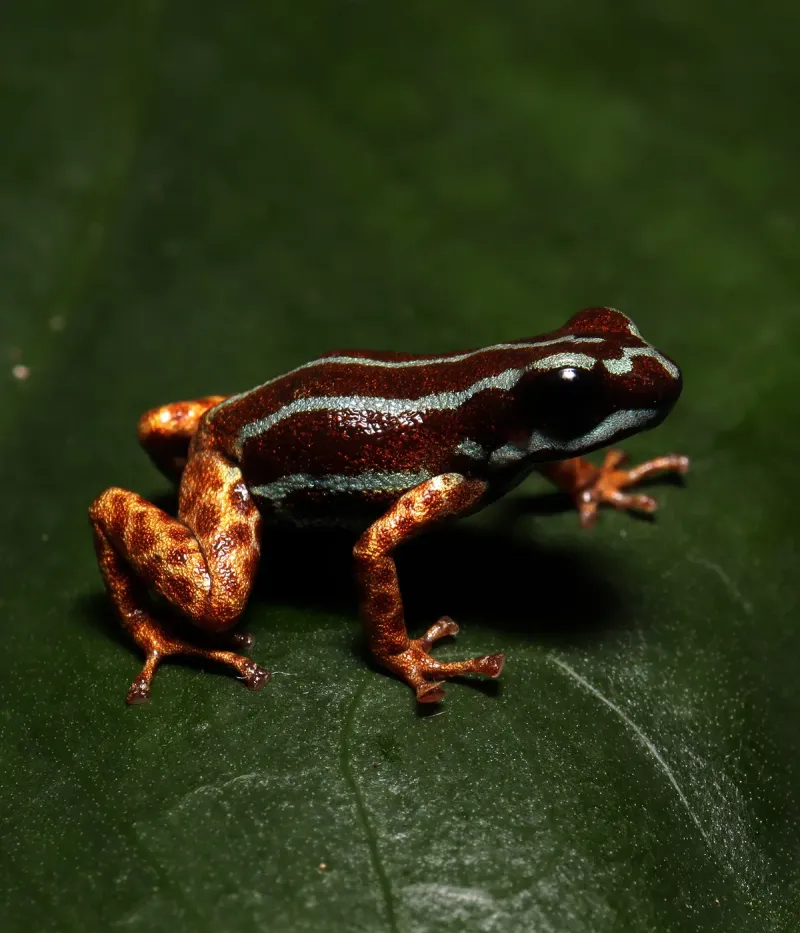

Scientists chose the name ‘aetherea’ from the Latin word ‘aethereus,’ meaning ‘of the heavens’ or ‘celestial.’ The name perfectly captures both the frog’s sky-blue coloration and the almost supernatural quality of its beauty.
When the research team first spotted the frog during a night expedition, their headlamps caught its gleaming skin, making it appear like a fallen star on the forest floor. One researcher remarked it looked ‘like a piece of the night sky come to life.’ The heavenly connection extends to local legends too – indigenous guides immediately associated the frog with ancient stories of star-beings.
3. Miniature Marvel – Smaller Than A Quarter
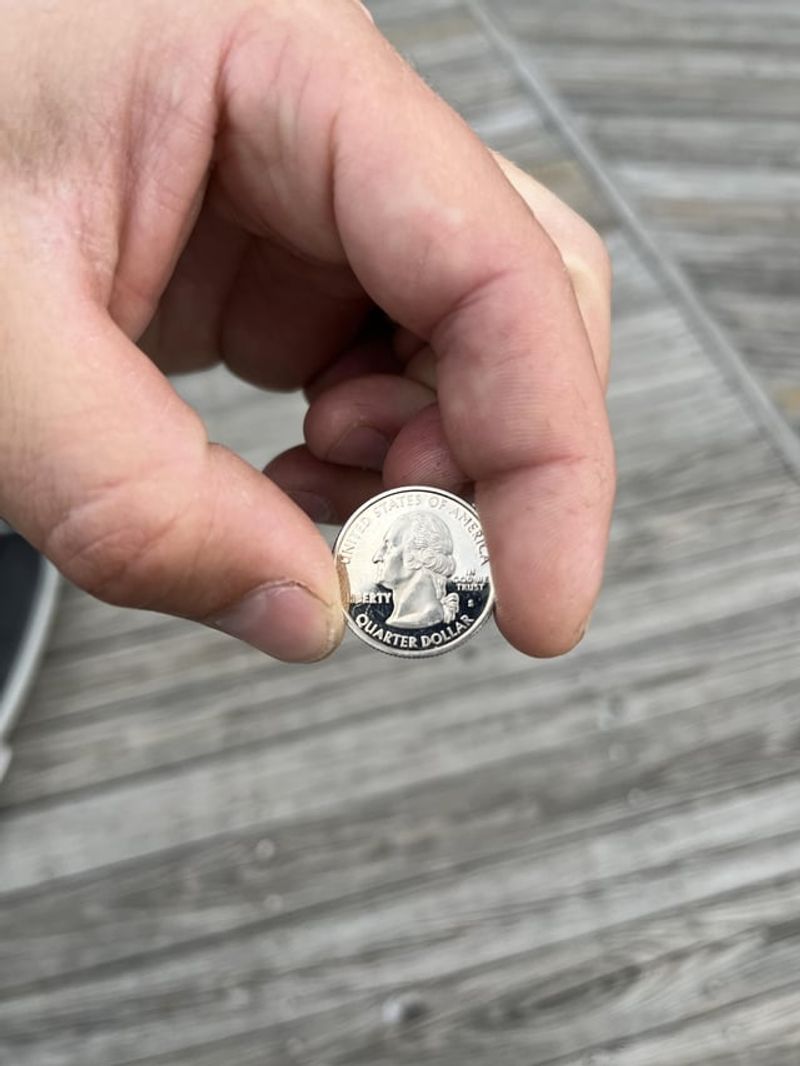

Despite its showstopping appearance, Ranitomeya aetherea is remarkably tiny – adults typically measure just 1.5 centimeters in length, smaller than a U.S. quarter! Their diminutive size helps them hide in the leaf litter of the rainforest floor or perch on small branches.
Female frogs tend to be slightly larger than males, though the difference is barely noticeable to human observers. What’s astonishing is how such a small creature contains so many complex biological systems – from the specialized glands that produce toxins to the vocal apparatus that creates their unique calls.
4. Potent Poison Packs A Punch
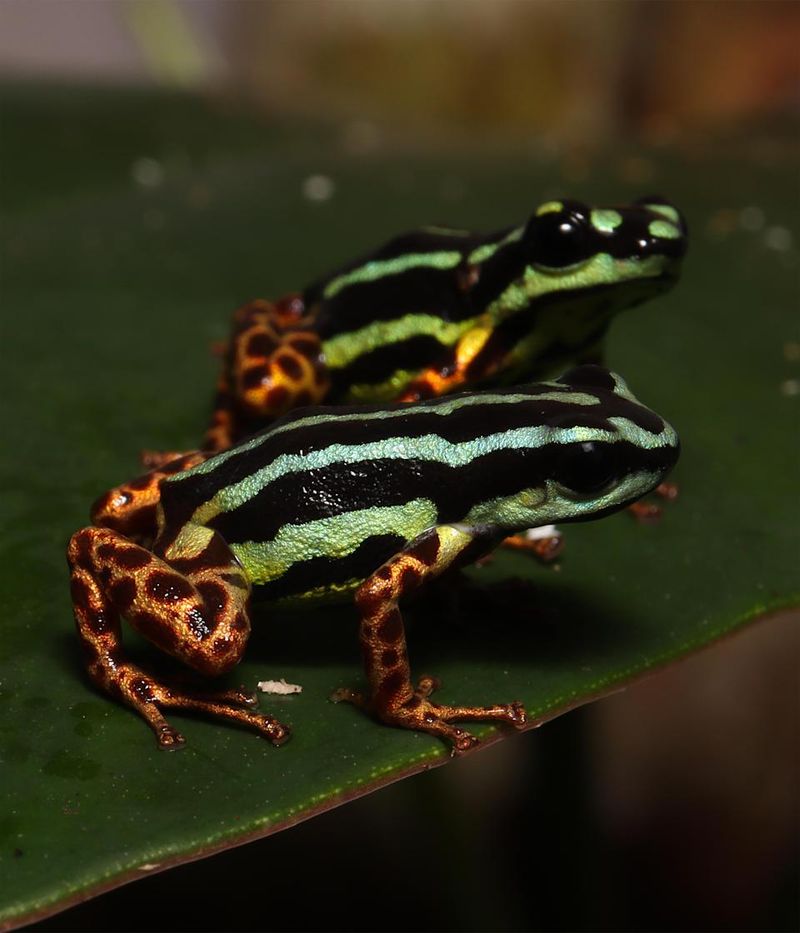

Don’t let its beauty fool you! Ranitomeya aetherea produces a unique cocktail of toxins that researchers are calling ‘aethereatoxin.’ This potent chemical defense makes the frog unpalatable to predators and potentially dangerous to humans if handled without proper protection.
Fascinatingly, these frogs don’t manufacture their toxins from scratch. They sequester and modify chemicals found in their diet of tiny insects, especially ants and small beetles. Lab analysis shows their poison contains compounds never before documented in nature, sparking interest from pharmaceutical researchers looking for novel pain medications.
5. Musical Maestros Of The Microworld
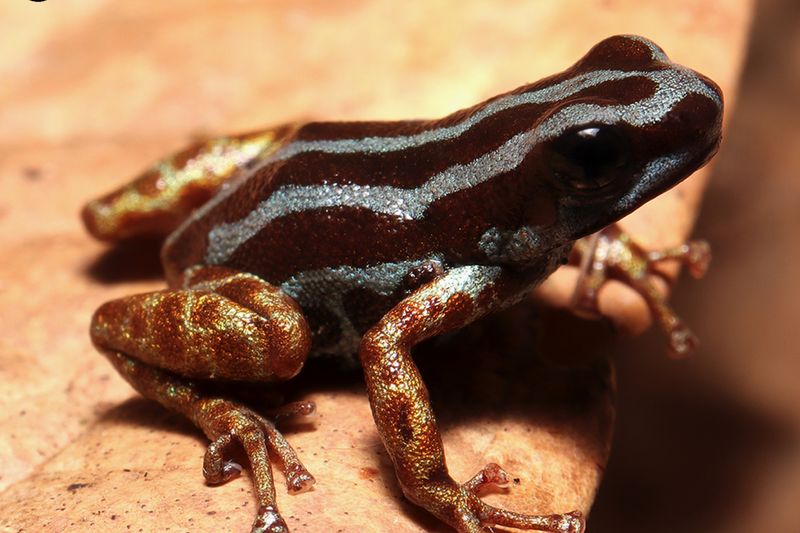

Morning visitors to the Amazon might hear the aetherea before seeing it. These tiny frogs produce surprisingly loud, bell-like calls that ring through the forest understory. Male frogs perch on leaves about 1-2 feet off the ground and sing complex patterns to attract females.
Each individual has its own signature call – a musical fingerprint as unique as a human voice. Recordings reveal that their calls contain ultrasonic components humans can’t hear without special equipment. Researchers have documented at least seven distinct call types used for different social situations, from mating requests to territorial warnings.
6. Devoted Dads Of The Frog World
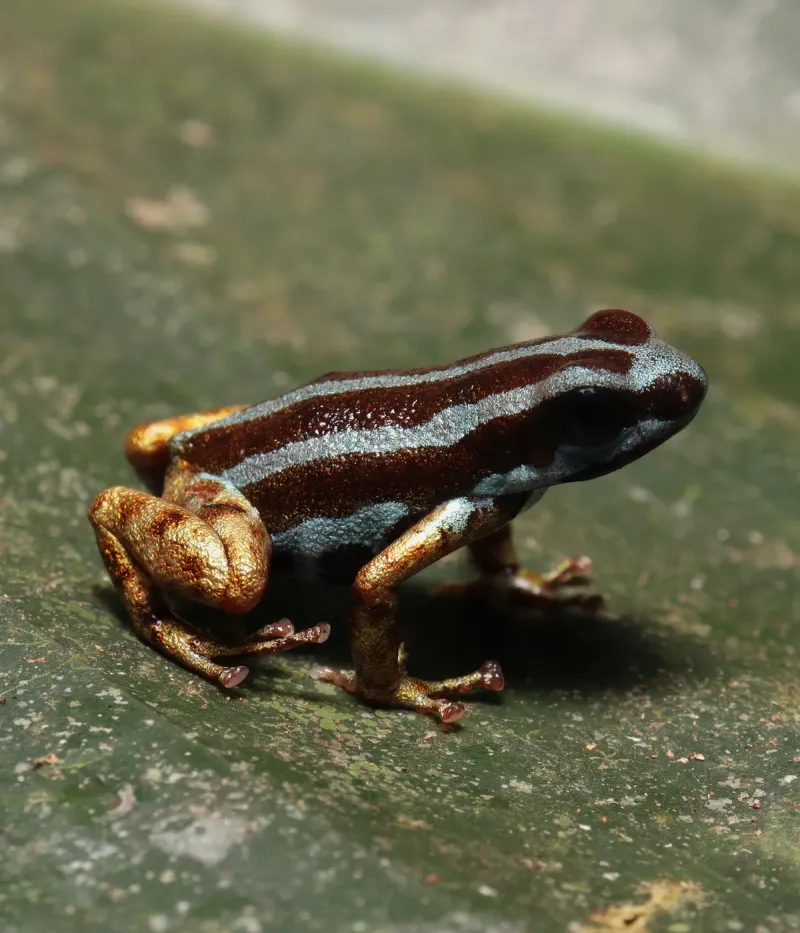

Male Ranitomeya aetherea take parenting to extraordinary levels! After females lay their eggs in hidden leaf pockets, dad takes over completely. He’ll guard the eggs against predators, keep them moist by urinating on them (yes, really!), and even transport hatched tadpoles on his back to safe water pools.
Each tadpole gets its own private nursery – typically a tiny water-filled bromeliad cup high in the trees. Dad visits each tadpole regularly, dropping off unfertilized eggs that serve as food. This level of paternal care is extremely rare in amphibians and has evolved independently in this remarkable genus.
7. Extremely Limited Range – Found In Just One Valley
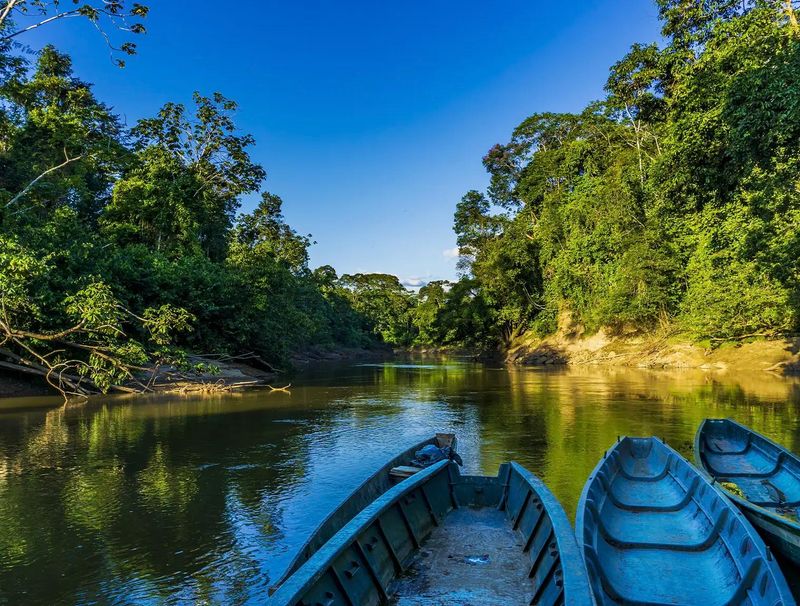

Currently, Ranitomeya aetherea has only been documented in a single remote valley in the Peruvian Amazon, spanning less than 5 square kilometers. This extremely limited range makes it one of the most geographically restricted vertebrates on Earth.
The valley features a unique microclimate – slightly cooler and moister than surrounding areas – creating the perfect conditions for these specialized frogs. Their restricted habitat immediately raised conservation concerns among the discovery team. Scientists are working with Peruvian authorities to establish protection for this valley before its location becomes widely known to collectors.
8. Evolutionary Mystery – Distant Relatives
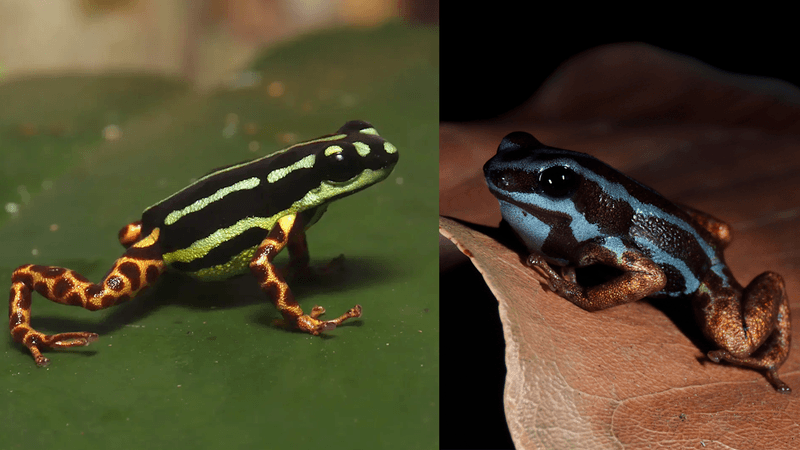

DNA analysis of Ranitomeya aetherea has left evolutionary biologists scratching their heads. While clearly belonging to the Ranitomeya genus, this species shows genetic markers suggesting it diverged from its closest relatives over 15 million years ago!
This represents an evolutionary puzzle, as other members of this genus appear much more closely related to each other. Some scientists propose that aetherea may be the sole survivor of an ancient lineage that once contained many now-extinct species. Others suggest it evolved in isolation for millions of years, preserving traits lost in other lineages.
9. Diet Of Exotic Microfauna
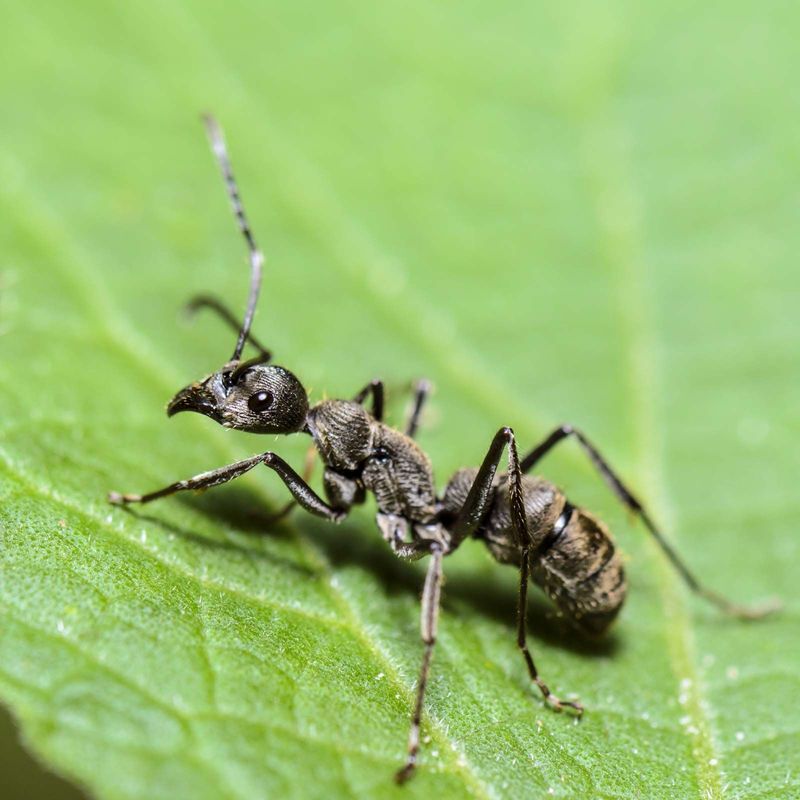

Ranitomeya aetherea has specialized dietary preferences that contribute to its unique biology. Field observations show these frogs primarily hunting for a specific type of miniature orchid ant found nowhere else in the world.
These ants contain alkaloid compounds that the frogs modify and concentrate in their skin glands. Remarkably, captive specimens refuse most common feeder insects, making them challenging to maintain in laboratory settings. Their specialized diet may explain why they’re confined to such a small geographic area – they can only live where their preferred prey exists.
10. Accidental Discovery During Filming

The world might never have known about Ranitomeya aetherea if not for a lucky accident during a documentary film shoot. Wildlife photographer Elena Ramirez wasn’t even looking for frogs when her camera equipment malfunctioned during a rainstorm, forcing an unplanned detour through an unexplored valley.
While waiting for the weather to clear, she spotted an unusual blue glint among the leaves. What she initially thought was a discarded candy wrapper turned out to be the first documented specimen. The discovery highlights how much remains unknown in the Amazon – even areas considered ‘explored’ likely harbor countless undiscovered species.
11. Conservation Status – Critically Endangered
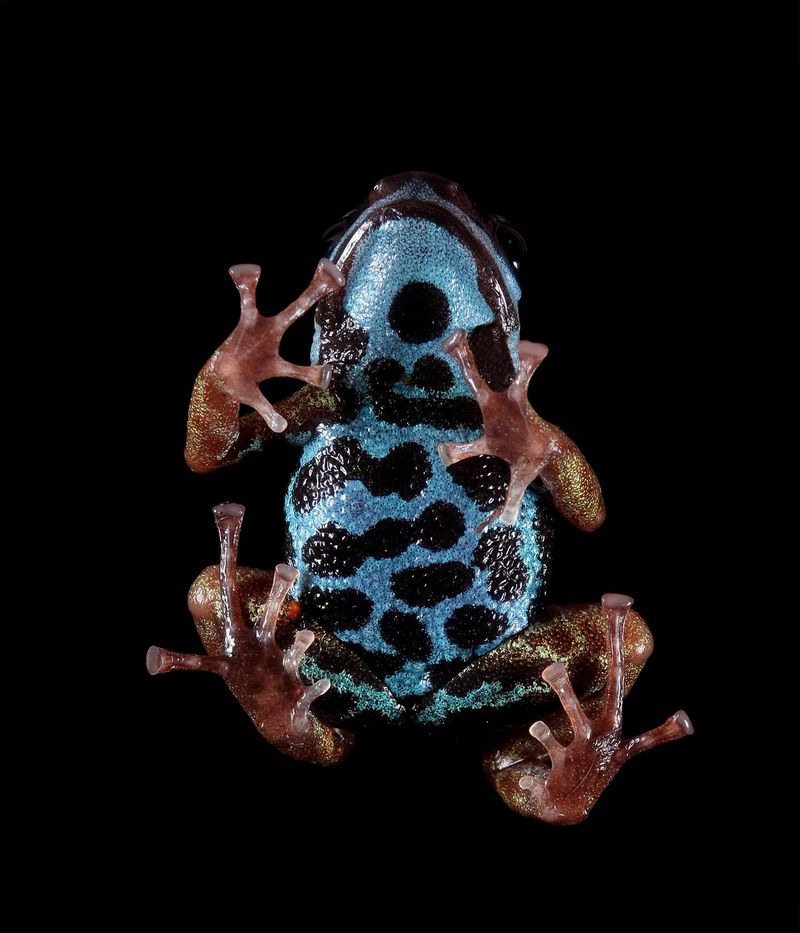

The moment Ranitomeya aetherea was discovered, it earned a place on the IUCN Red List as Critically Endangered. With fewer than an estimated 1,000 individuals in the wild and an extremely limited range, these frogs face multiple threats.
Climate change poses a particular danger, as their specialized habitat requirements make them vulnerable to even small temperature shifts. Illegal collection for the exotic pet trade has already begun despite legal protections. Conservation efforts include habitat protection, captive breeding programs, and educational outreach to local communities who serve as the first line of defense against poachers.